In the fast-paced world of business, maintaining accurate financial records is crucial for building trust and ensuring smooth operations. Mistakes happen—whether it’s underbilling, incorrect pricing, or returns—and that’s where debit notes come into play. These documents are more than just tools for correcting errors; they help businesses maintain transparency, comply with tax regulations, and foster fair transactions.
For businesses of all sizes, understanding how debit notes work is not just a matter of efficiency—it’s about staying compliant and organized in an ever-evolving financial landscape. This guide will take you through everything you need to know about debit notes, step by step.
Understanding Debit Notes
Debit notes play a vital role in financial transactions by addressing discrepancies, adjusting payments, and maintaining accuracy in records. Let’s explore their definition, purpose, and the scenarios in which they are typically issued.
What Is a Debit Note?
A debit note is a formal document issued by a buyer or seller to adjust errors or discrepancies in an invoice. It is used to notify the other party about an increase in the amount payable due to reasons like underbilling, incorrect quantities, or defective goods returned after invoicing.
In accounting, a debit note serves as a correction tool that ensures transactions are accurately recorded. Essentially, it works as an “I owe you” note, helping businesses maintain transparency and clarity in their financial dealings. Debit notes are crucial in reconciling accounts and ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
Why Is a Debit Note Created?
Debit notes are issued for various reasons, most commonly to rectify errors in original invoices. Some typical scenarios include:
- Underbilling: If an invoice reflects a lower amount than what was due, a debit note is issued to recover the difference.
- Return of Goods: When goods are returned due to defects or damages, a debit note can adjust the value of the transaction accordingly.
- Price Adjustments: If the agreed-upon price of goods or services changes after an invoice is issued, a debit note is used to update the payable amount.
- Additional Charges: Businesses may use debit notes to account for extra fees, like shipping costs or taxes, missed in the original invoice.
By documenting these adjustments formally, businesses can avoid disputes, streamline bookkeeping, and ensure compliance with tax laws like GST.
Who Issues a Debit Note and When Is It Issued?
A debit note can be issued by both buyers and sellers, depending on the situation:
- By Sellers: A seller issues a debit note when they need to increase the amount payable by the buyer. For instance, if an error led to underbilling or if additional charges like freight were excluded from the original invoice.
- By Buyers: A buyer may issue a debit note to inform the seller of goods being returned or to dispute incorrect pricing or quality issues.
When is a Debit Note Issued?
Debit notes are typically issued after the invoice but before the final payment is settled. For example:
- If goods are returned after inspection upon delivery.
- If the seller notices an error in the invoice after sending it.
- If there are late adjustments to pricing, tax, or charges.
By clearly outlining the reason and timing for issuing debit notes, businesses can manage transactions more effectively and maintain positive relationships with their stakeholders.
Benefits and Importance of Debit Notes
Benefits of Debit Note / Advantages of Debit Note
Debit notes offer a range of advantages that make them indispensable for businesses. Here are some key benefits:
- Ensures Accurate Records: By correcting errors in invoices, debit notes help maintain precise financial records, which is essential for effective bookkeeping and compliance.
- Facilitates Transparency: Debit notes provide clear documentation of adjustments, ensuring both parties—buyer and seller—are on the same page regarding financial obligations.
- Simplifies Reconciliation: These documents make it easier to reconcile accounts receivable and payable, reducing the likelihood of disputes.
- Supports Compliance with GST and Tax Laws: Debit notes are critical for businesses operating under GST or similar tax systems, as they help maintain compliance by accurately reflecting adjustments in tax liabilities.
- Builds Trust in Transactions: Issuing debit notes demonstrates professionalism and accountability, fostering trust between businesses and their clients or vendors.
Role of Debit Notes in Ensuring Fair Transactions
Debit notes play a pivotal role in ensuring fairness in business transactions. By formally documenting adjustments, they prevent financial misunderstandings and disputes. For instance:
- In case of errors: If a buyer is undercharged, a debit note ensures the seller receives the correct payment.
- When goods are returned: It ensures the buyer’s account is credited accurately for the returned items.
- For price corrections: Any post-invoice price changes are transparently communicated through a debit note.
By using debit notes, businesses can align their financial transactions with ethical practices, promoting long-term business relationships and trust. These documents also act as safeguards in audits and legal proceedings by providing a detailed trail of transaction adjustments.
How do Debit Notes work?
How Does a Debit Note Work?
The process of issuing and using a debit note involves a series of steps that ensure transparency and accuracy in financial transactions. Here’s how it works:
Identifying the Need for Adjustment:
A debit note is created when an error or discrepancy is identified in an invoice or transaction.
Common triggers include underbilling, additional charges, or returned goods.
Preparation of the Debit Note:
The issuer prepares a debit note containing all relevant details, such as the reason for the adjustment, invoice reference, and the revised payable amount.
Communicating to the Recipient:
The debit note is sent to the buyer or seller, depending on who needs to be informed about the adjustment.
This communication serves as a formal notification of the change in financial terms.
Acceptance by the Counterparty:
The recipient reviews the debit note and acknowledges the adjustments.
If there are disputes, both parties work to resolve them before proceeding.
Updating Financial Records:
Once accepted, both parties update their respective accounting records.
The seller reflects the increased receivable, and the buyer adjusts their payable accordingly.
Tax Implications:
If applicable, the debit note is used to update the tax liabilities in compliance with GST or other tax regulations.
Process of Issuing a Debit Note
Scenario 1: Issued by a Buyer
Green Valley Traders placed an order for 3,000 ceramic plates from Sunrise Ceramics on credit, priced at Rs.25 per plate. Upon delivery, Sunrise Ceramics provides an invoice for the full order. However, during the inspection, Green Valley Traders finds that 200 plates are chipped and 100 are completely broken.
To resolve this, Green Valley Traders prepares a debit note for the 300 damaged plates and returns them to Sunrise Ceramics. The debit note specifies that Sunrise Ceramics should deduct Rs.7,500 (300 plates × Rs.25) from the total amount payable by Green Valley Traders.
Scenario 2: Issued by a Seller
Sunrise Ceramics delivers 3,000 ceramic plates to Green Valley Traders on credit, priced at Rs.25 per plate. The invoice issued to Green Valley Traders at the time of delivery incorrectly states the unit price as Rs.23, leading to an underbilling of Rs.6,000.
To correct this oversight, Sunrise Ceramics issues a debit note to Green Valley Traders, notifying them of the error. The debit note formally adjusts the payable amount by Rs.6,000, ensuring the transaction reflects the accurate price.
Steps to Create a Debit Note
Creating a debit note involves the following steps:
- Details of the Issuer and Recipient: Include the name, address, contact details, and Tax Identification Numbers (TIN) of both parties.
- Reference to Original Invoice: Mention the invoice number and date associated with the debit note to establish context.
- Details of Goods or Services: Specify the description, quantity, and unit price of the goods or services involved.
- Adjustment Amount: Clearly state the amount being adjusted and include the rate of tax, if applicable.
- Reason for Issuance: Provide a concise explanation of why the debit note is being issued.
- Signature and Date: Sign the document and mention the date of issuance for authenticity.
By following these steps, businesses can create a debit note that is professional, clear, and compliant with financial regulations.
Format and Examples
Key Elements of a Debit Note
A well-structured debit note includes specific details to ensure clarity and compliance. Below are the essential components that should be included:
- Details of the Issuer and Recipient: Name, address, contact details, and Tax Identification Number (TIN) of both parties.
- Unique Debit Note Number: A sequential number to distinguish the debit note for tracking and record-keeping purposes.
- Date of Issue: The date on which the debit note is issued.
- Invoice Reference: Reference to the original invoice, including its number and date, to establish a connection between the documents.
- Description of Goods or Services: Details such as quantity, unit price, and total value of goods or services being adjusted.
- Adjustment Amount: The total amount to be adjusted, including tax rates and applicable taxes.
- Reason for Issuance: A clear explanation for issuing the debit note, such as damaged goods or pricing discrepancies.
- Signature: The signature or authorized seal of the issuer to validate the debit note.
How a Debit Note Looks: Template and Example
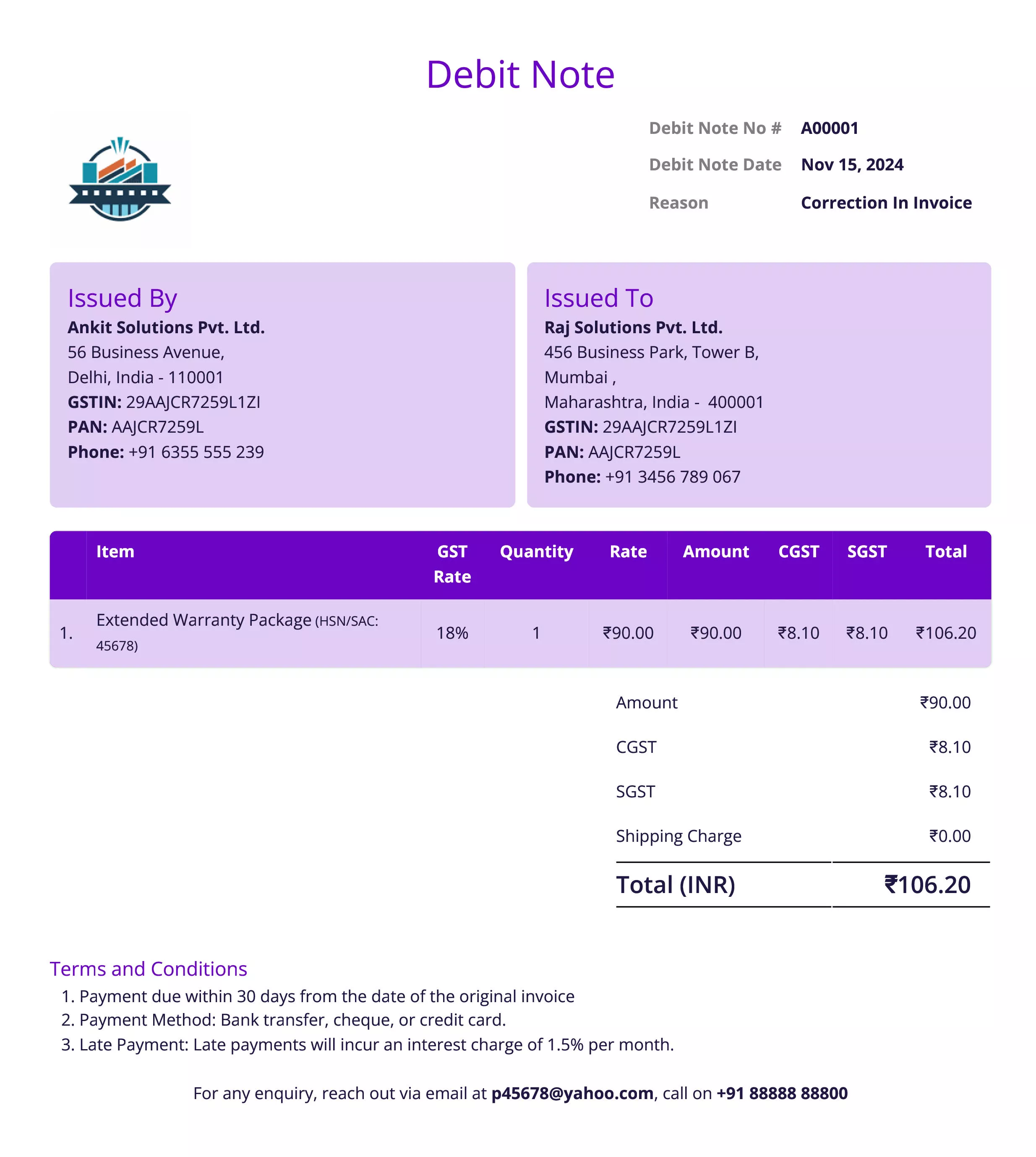
Debit Notes in Accounting
What Is a Debit Note in Accounting?
In accounting, a debit note acts as a formal “correction notice” for errors in invoices or transaction records. For sellers, issuing a debit note increases their accounts receivable, while for buyers, receiving a debit note reduces their accounts payable.
Debit notes are essential tools for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring that transactions are properly reflected in the books. They play a crucial role in correcting discrepancies and supporting transparent accounting practices.
Whether you own a shop, run a business, or manage finances, understanding how debit notes work can simplify account management. They help keep records organized and compliant with regulations. So, the next time an error occurs, a debit note can serve as your go-to solution.
Debit Note Book or Ledger
A Debit Note Book or ledger is a dedicated record maintained to document all issued debit notes systematically. This ensures efficient tracking and balancing of financial adjustments. Typically, two copies of each debit note are prepared:
- Supplier’s Copy: One copy is handed over to the supplier, serving as an official notification of the adjustment.
- Business Copy: The second copy is retained in the debit note book as a record for the issuer’s reference.
When the supplier issues a credit note in response to the debit note, the corresponding entry in the debit note book is marked off, making it easier to reconcile accounts. This system creates a seamless process for tracking outstanding adjustments and maintaining accurate financial records.
Additionally, the supplier can use the debit note as a reference point when preparing their credit note, ensuring both parties are aligned on the transaction adjustments. By maintaining a well-organized debit note book, businesses can ensure transparency and accuracy in their financial dealings.
The ledger typically contains:
- The date of issuance.
- Debit note number.
- Reference to the original invoice.
- Amount adjusted (including tax, if applicable).
- The reason for issuing the debit note.
By maintaining a dedicated record, businesses can streamline their financial operations and minimize the risk of errors or disputes in the future.
Debit Notes and GST Compliance
Importance of Debit Notes Under the GST Law
Debit notes play a crucial role under GST regulations, ensuring compliance and accuracy in tax filings. According to Section 34(3) of the CGST Act, 2017, a supplier of goods or services issues a debit note in situations such as:
- When a tax invoice has already been issued for the supply of goods or services.
- When the tax amount charged on the invoice is less than the actual taxable value of the supply.
- When the quantity of goods or services supplied exceeds the originally agreed amount in the invoice.
A debit note becomes part of the GSTR-1 return for the month in which the supply occurred and is auto-populated in the recipient’s Form GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B. After verification, the recipient can include the details in their GSTR-3B return. This process ensures a smooth reconciliation of tax liabilities.
Impact of Amendments on Debit Notes
Previously, when reporting debit or credit notes, quoting the original invoice number was mandatory. However, recent amendments introduced the delinking of debit notes from their associated invoices. This has led to:
- Flexible Reporting: For determining the supply type (intra-state or inter-state), the place of supply can now be specified separately in the debit note.
- Tax-Specific Debit Notes: If a debit note adjusts only the tax rate difference, the taxable value can be set to zero, with just the tax amount recorded.
- Revised ITC Timeline: Earlier, the time limit for availing Input Tax Credit (ITC) was linked to the invoice date. Post-amendment, ITC eligibility is calculated from the debit note’s issue date.
Example:
If an invoice was issued in March 2022 and a debit note was issued for it in October 2022, the last date for claiming ITC would be the due date of Form GSTR-3B for October 2023, as the debit note was issued during the 2022–2023 financial year.
Amendments to Debit Notes
The GST portal allows for amendments to debit or credit notes under two scenarios:
- For Registered Recipients:
- Changes to debit notes issued to registered entities must be reported under Table 9C – Amended Debit/Credit Notes (Registered) in Form GSTR-1.
- For Unregistered Recipients:
- Amendments for notes issued to unregistered entities are reported in Table 9C – Amended Debit/Credit Notes (Unregistered) in Form GSTR-1.
These updates ensure that businesses can correct errors in a structured and compliant manner.
Time Limit to Issue a Debit Note
GST laws specify a deadline for issuing debit notes. A debit note must be issued no later than:
- September 30th of the financial year following the year of supply; or
- The date of filing the GSTR-9 (Annual Return) for the corresponding financial year, whichever is earlier.
Importance of Timely Issuance:
Failure to issue a debit note within the stipulated time can lead to increased tax liability, interest penalties, and non-compliance issues. For example, if goods were supplied in June 2023, the debit note must be issued by either September 30, 2024, or the filing date of GSTR-9 for FY 2023–2024.
By adhering to these deadlines, businesses can avoid unnecessary financial burdens and ensure proper alignment with GST rules.
Debit Note vs Credit Note
Definition and Purpose
- A Debit Note is issued when there is an upward revision in the value of a previously issued invoice. It serves to increase the amount payable by the recipient.
- A Credit Note, on the other hand, is issued to reflect a downward adjustment, such as when a customer is overcharged or goods are returned, reducing the recipient’s liability.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Debit Note | Credit Note |
| Purpose | Used to increase the invoice value or rectify underbilling. | Used to decrease the invoice value or adjust overbilling. |
| Impact on Seller’s Books | Increases accounts receivable. | Reduces accounts receivable. |
| Impact on Buyer’s Books | Reduces accounts payable. | Reduces accounts receivable or adds to refund claims. |
| Issued By | Generally by the seller to the buyer (or vice versa). | Generally by the seller to the buyer. |
| Reason for Issuance | Incorrect quantities, undercharged taxes, or added charges. | Overcharged amounts, incorrect pricing, or goods returned. |
| Tax Implications | Adjustments in tax liabilities may be required. | Adjustments in tax liabilities may be required. |
Example
- Debit Note: A seller realizes that an invoice for goods worth Rs.50,000 was undercharged by Rs.5,000. A debit note is issued to adjust the total payable to Rs.55,000.
- Credit Note: A customer returns goods worth Rs.3,000 due to defects. The seller issues a credit note to reduce the payable amount by Rs.3,000.
Usage in GST Compliance
Both debit and credit notes are essential under GST for reconciling tax liabilities and ensuring accurate reporting. Debit notes reflect additional tax liability, while credit notes adjust for reductions. Both must be recorded in GSTR-1 and cross-verified in the buyer’s GSTR-2A or GSTR-2B.
Tools and Best Practices for Managing Debit Notes
Top 5 Debit Note Generators
Efficient management of debit notes requires reliable tools to streamline creation, tracking, and compliance. Here are five top debit note generators:
1. Refrens
- Features: Simplifies debit note generation, links to invoices, automatically updates the respective ledgers, and ensures compliance with GST and other tax laws.
- Benefits: Free-to-use and ideal for freelancers, agencies, and businesses of all sizes, with an intuitive interface for hassle-free operations.
2. Zoho Books
- Features: Automated debit note creation, GST compliance, and seamless integration with other accounting modules.
- Benefits: Offers robust accounting tools for precise record-keeping and easy reconciliation with invoices.
3. TallyPrime
- Features: Supports GST-compliant debit notes, tracks adjustments, and ensures comprehensive record-keeping.
- Benefits: A trusted solution for small and medium-sized businesses with advanced accounting needs.
4. QuickBooks
- Features: Customizable debit note templates, real-time tracking, and detailed financial reporting.
- Benefits: Simplifies debit note management with an easy-to-navigate interface.
5. Vyapar
- Features: Mobile-friendly application for creating and tracking GST-compliant debit notes on the go.
- Benefits: Perfect for small businesses seeking an accessible and straightforward solution.
With these tools, businesses can manage debit notes efficiently, minimize errors, and ensure compliance with financial regulations.
Best Practices for Managing Debit Notes
- Start with Reliable Software: Use trusted platforms like Refrens to automate debit note creation and integrate with your accounting system for seamless management.
- Verify Details Thoroughly: Double-check all information, including invoice references, amounts, and tax calculations, to ensure accuracy.
- Maintain a Centralized Ledger: Keep a well-organized record of all issued and received debit notes to simplify reconciliation and audits.
- Communicate Adjustments Clearly: Share debit notes promptly with the other party, ensuring both sides agree on the adjustments.
- Stay Compliant with GST: Report all debit notes in the appropriate GST returns (e.g., GSTR-1, GSTR-3B) within the specified deadlines.
- Reconcile Periodically: Regularly reconcile debit notes with invoices and credit notes to maintain accurate financial records.
- Educate Your Team: Train your staff on the significance of debit notes and the correct process to manage them efficiently.
By leveraging the right tools and following these best practices, businesses can manage debit notes effectively, ensuring transparency, compliance, and financial accuracy.
Common Challenges in Using Debit Notes
While debit notes are essential for managing financial adjustments, businesses often face the following challenges:
- Errors in Documentation: Inaccurate details such as incorrect amounts, invoice references, or tax calculations can lead to disputes between parties.
- Delayed Issuance: Failing to issue debit notes promptly can disrupt reconciliation and compliance, particularly under GST regulations where time limits apply.
- Lack of Tracking: Without proper tracking systems, businesses may lose track of issued debit notes, causing mismatches in accounts payable and receivable.
- GST Compliance Issues: Misreporting or failure to include debit notes in GST returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B) can result in penalties or complications during audits.
- Inefficient Communication: Delays or miscommunication in sharing debit notes with counterparties can lead to confusion and strained business relationships.
How to Overcome These Challenges:
– Use automated tools like Refrens to generate and track debit notes accurately.
– Train staff on proper procedures and GST compliance requirements.
– Regularly reconcile debit notes with invoices and credit notes to ensure alignment of records.
FAQs About Debit Notes
Q1. Is a Debit Note the Same as an Invoice?
No, a debit note is different from an invoice. While an invoice initiates the transaction, a debit note is issued to make adjustments to the original transaction, such as increasing the amount payable.
Q2. Who Issues a Debit Note?
Debit notes can be issued by either the buyer or the seller, depending on the scenario. Sellers typically issue debit notes to adjust underbilling, while buyers issue them for returns or disputes over pricing.
Q3. How Do Debit Notes Affect the Supplier’s Tax Liability?
Debit notes increase the taxable value of a supply. Under GST, the supplier must include the additional taxable value in their GSTR-1 return, which is reflected in the recipient’s GSTR-2A or GSTR-2B for reconciliation.
Q4. Can a Debit Note Be Issued After a Credit Note?
Yes, a debit note can be issued after a credit note if further adjustments are required in the original transaction. Both must be reported in GST returns accordingly.
Q5. What Is the Time Limit for Issuing a Debit Note?
A debit note must be issued by the earlier of:
- September 30th of the financial year following the year of supply.
- The date of filing the GSTR-9 (Annual Return) for that financial year.
Q6. Can a Debit Note Be Issued for Tax-Only Adjustments?
Yes, debit notes can be issued solely for adjusting tax amounts, with the taxable value set to zero.


















