E-invoicing is revolutionizing business processes in Malaysia, replacing traditional paper-based systems with efficient digital invoicing. Set to become mandatory by 2025, this initiative is led by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) and the Malaysian Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC). E-invoicing aims to improve tax compliance, reduce errors, and enhance payment cycles.
This blog will explore how businesses can adapt to e-invoicing, its benefits, and the challenges they may encounter during implementation.
Understanding e-invoicing
(A) What is e-invoicing?
E-invoicing is the process of issuing invoices electronically, replacing paper-based systems with automated digital workflows. These e-invoices are created, sent, received, and stored in a digital format, and they comply with government regulations for taxation and business transparency.
In Malaysia, e-invoicing will soon be mandatory for businesses of varying sizes, with full implementation expected by 2025. The system is designed to reduce errors, improve payment cycles, and ensure enterprises adhere to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) requirements.
LHDN focuses on improving tax transparency and compliance, while MDEC promotes e-invoicing as part of Malaysia’s digital transformation. These government-led efforts aim to streamline business processes, boost efficiency, and modernize the financial landscape.
(B)Types of e-Invoices in Malaysia
- Invoices:
Records the sale of goods or services between a supplier and buyer. Self-billing is allowed for international transactions, with validation through the MyInvois Portal. - Credit Notes:
Issued to reduce a previously issued invoice due to errors or discounts. No direct refunds are involved, and it’s submitted to IRBM for correction. - Debit Notes:
Used to increase the value of an issued invoice for additional costs. It adjusts the transaction amount after the initial invoice. - Refund E-Invoices:
Issued to document payment refunds to buyers. Acknowledges the return of goods or services and the corresponding refund amount.
(C)E-invoicing Implementation Timeline in Malaysia
Malaysia is rolling out e-invoicing in phases to give businesses time to adapt. The timeline for mandatory e-invoicing is as follows:
- August 2024: Mandatory for businesses with annual turnover exceeding MYR 100 million.
- January 2025: Mandatory for businesses with annual turnover exceeding MYR 25 million.
- July 2025: Mandatory for all other businesses.
During the first phase (August 2024 – January 2025), businesses can submit consolidated e-invoices monthly, giving them time to transition to the full real-time invoicing process.
(D)Legal Requirements in Malaysia
- Tax Compliance: E-invoicing is regulated by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) under the Sales and Services Tax (SST) framework, ensuring accurate tax reporting, particularly for large enterprises.
- Mandatory Fields: For compliance, an e-invoice must include:
- Supplier and buyer details (name, address, and TIN).
- Invoice number, date, and description of goods/services.
- Pre- and post-tax amounts, tax rate, and total tax.
- Integration with Tax Systems: Malaysia is developing systems for direct e-invoice submission to LHDN for real-time tax reporting to enhance transparency and reduce fraud.
- Phased Mandates: Large taxpayers and government suppliers may be the first required to adopt e-invoicing, with a gradual roll-out expected for all businesses.
- Digital Signatures: E-invoices must be digitally signed to verify their authenticity and prevent tampering, ensuring legal validity.
- Retention: Businesses must securely store e-invoices for up to 7 years, as required by law, for potential audits by LHDN.
This streamlined process ensures Malaysian businesses stay compliant while benefiting from the efficiency and security of e-invoicing.
Key Benefits of e-invoicing
1. Faster Payment Cycles
E-invoicing accelerates payment by eliminating manual tasks and postal delays. Invoices are sent instantly, reducing the gap between issuing and receiving payments, and improving cash flow and overall financial efficiency.
2. Fewer Errors, Lower Costs
By automating data entry, e-invoicing minimizes errors common in manual processes. It also cuts costs on paper, printing, and postage while offering easy digital storage for better invoice management and cost savings.
3. Enhanced Tax Compliance
E-invoicing simplifies tax reporting with real-time transaction records, helping businesses comply with Malaysia’s tax regulations. Seamless integration with tax systems ensures accurate filing and reduces the risk of penalties.
Key Features of Malaysia’s e-Invoicing System
- Unique Identifier Number (UIN) and QR Code: After validation by LHDN, each e-invoice is assigned a UIN and QR code, which play a key role in tracking and verifying invoices for tax compliance.
- Digital Signature: To ensure invoice security and authenticity, e-invoices must be digitally signed, protecting against tampering and providing legal assurance.
- Seamless Integration with Accounting Software: E-invoicing platforms integrate effortlessly with top accounting solution, automating tax calculations, payment tracking, and syncing financial data, simplifying business processes.
How e-invoicing Works in Malaysia
(A)E-Invoicing Model in Malaysia
In Malaysia, businesses can choose from various transmission methods to report e-invoices, known as e-invoicing models.
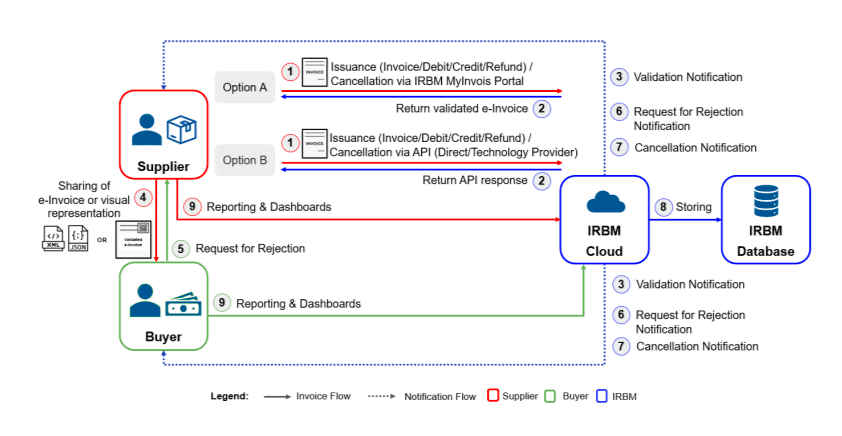
Below is an overview of the available options.
1. MyInvois Portal
The MyInvois Portal lets users generate e-invoices manually, individually, or in bulk by uploading a spreadsheet in a specific format. This method is particularly suitable for Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) or companies with lower transaction volumes, as it requires manual data entry.
Launched by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) on June 28, 2024, the portal provides both testing and production environments. Businesses can access it at mytax.hasil.gov.my.
For step-by-step guidance on how to log in and generate e-invoices, refer to the MyInvois User Guide Video and e-invoice generation guide.
2. Application Programming Interface (API)
Larger businesses can integrate their ERP, billing, or accounting systems with the MyInvois system via an API. This integration allows for the automatic generation, transmission, receipt, and correction of e-invoices directly from their systems, which is ideal for handling high transaction volumes in real time.
To simplify this complex integration process, the Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) has introduced the e-invoice Malaysia Software Development Kit (SDK).
(B)E-Invoicing Process in Malaysia
Malaysia’s e-invoicing system managed through the MyInvois Portal developed by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN), is designed to streamline invoicing and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
While the steps may vary based on the type of transaction (B2B or B2C) and the e-invoicing model used (API or MyInvois Portal), the overall process remains consistent.
Here is a structured, step-by-step breakdown of how the e-invoicing process works in Malaysia for both B2B and B2C transactions.
1) E-Invoicing Process for B2B Transactions
B2B e-invoices, or Business-to-Business electronic invoices, have revolutionized the conventional invoicing process by converting the exchange of invoices between companies into a fully digital format. This shift enhances efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
- Creating and Sending the e-Invoice: The supplier generates an e-invoice using either the MyInvois Portal or a business system integrated with the MyInvois System via API. The e-invoice is then submitted to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM) for validation.
- Real-Time Validation: The IRBM validates the submitted e-invoice in real-time. Once the invoice is verified, a Unique Identifier Number (UIN) is issued to the supplier.
- Notification of Validation: Both the supplier and the buyer are notified by the IRBM once the e-invoice is successfully validated and assigned the UIN.
- Sharing the Validated e-Invoice: The supplier shares the validated e-invoice with the buyer. The validated e-invoice will include a QR code that can be used for easy access and verification by the buyer.
- Rejection or Cancellation Option: The buyer has a 72-hour window to request the rejection of the invoice if needed. Similarly, the supplier can cancel the invoice, but any rejection or cancellation must be justified within this period.
- Storage & Archiving: Invoices are securely stored digitally for easy retrieval during tax audits, ensuring compliance with Malaysian regulations.
2) E-Invoicing Process for B2C Transactions
For B2C transactions, suppliers are generally required to issue e-invoices. However, not all buyers, especially individual consumers, need e-invoices. The process for generating e-invoices in B2C transactions depends on whether the buyer requests it:
- When the Buyer Requests an e-invoice: If the buyer requests an e-invoice, the supplier gathers the necessary details from the buyer and generates the e-invoice in real-time, similar to how it’s done in B2B transactions.
- When the Buyer Does Not Require an e-Invoice: For buyers who do not need individual e-invoices, the supplier is allowed to consolidate multiple transactions into a monthly summary, which is submitted as a single consolidated e-invoice to the IRBM.
This flexible process ensures that businesses comply with e-invoicing regulations while also catering to different buyer preferences, making the system adaptable to both B2B and B2C environments.
How to Choose the Right e-Invoicing Software
Selecting the right e-invoicing software is essential for a smooth transition to digital invoicing while ensuring compliance with Malaysia’s regulations. Consider these key factors:
- Compliance: Ensure the software meets all legal requirements in Malaysia, including the correct formats and mandatory data fields.
- Ease of Use: Opt for a user-friendly platform that your team can easily adopt with minimal training.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your business, whether you’re an SME or a larger enterprise.
- Security: Prioritize software with strong security features, like encryption, to protect sensitive financial information.
- Automation: Look for features such as recurring invoices, payment reminders, and tax integration to reduce manual tasks and stay compliant.
- Customer Support: Reliable support is vital for resolving technical issues and staying updated with regulatory changes.
- Integration with Accounting Systems: Ensure the software integrates smoothly with your existing accounting system, syncing data automatically for real-time invoice tracking, tax calculations, and payment processing. This minimizes errors, avoids duplicate entries, and ensures tax compliance.
Check out our detailed guide on Best Invoicing Software in Malaysia.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing e-invoicing comes with its own set of challenges, but with the right approach, these can be effectively managed. Here are some common hurdles and strategies to overcome them:
- Initial Setup and Integration: Integrating e-invoicing software with existing systems and training staff can be challenging. Opt for solutions that offer seamless integration and provide comprehensive training resources.
- Cost of Implementation: While initial costs may be significant, the long-term savings from automation, reduced errors, and increased efficiency will outweigh the investment.
- Compliance Issues: Adapting to evolving regulations can be tough. Regular software updates and dedicated customer support ensure businesses remain compliant with Malaysia’s tax laws.
Conclusion
e-invoicing is rapidly becoming essential for businesses in Malaysia, offering benefits like faster payments and improved tax compliance. By embracing this shift early, businesses can streamline their processes and ensure legal compliance.
With the right software and preparation, the transition can be smooth, helping companies stay ahead in Malaysia’s evolving digital landscape. As e-invoicing becomes mandatory by 2025, early adopters will be better positioned for success.
FAQs
Is e-invoicing mandatory for all businesses in Malaysia?
e-invoicing is being rolled out gradually, with large taxpayers and government suppliers expected to adopt it first, followed by other businesses.
How do I choose e-invoicing software that complies with local regulations?
Ensure the software meets Malaysia’s legal requirements, supports the correct formats, includes mandatory fields, and integrates with local tax systems like LHDN.
Does e-invoicing in Malaysia apply only to domestic transactions?
No, e-invoicing applies to both domestic and international transactions in Malaysia
What are the penalties for non-compliance with Malaysia’s e-invoicing regulations?
Penalties for non-compliance may include fines or legal consequences, depending on the nature and extent of the violation.
How does e-invoicing impact tax reporting in Malaysia?
E-invoicing streamlines tax reporting by ensuring real-time submission of invoice data to the authorities, reducing errors, and improving tax compliance.
