E-Way bill is a mandatory document required as per the mandate by the government under Section 68 of the Goods and Services Tax Act, along with Rule 138 of associated rules.
This blog simplifies the essentials of e-Way bills, from creation to compliance, offering a comprehensive resource for all your queries.
What is an e-Way Bill?
An e-Way bill is a necessary document for anyone transporting goods valued at over INR 50,000. All registered individuals or transporters are required to create this document on the GST Common Portal before initiating the transportation.
It was introduced to enforce GST compliance and combat tax evasion as it streamlines the movement of goods, saves time, and ensures transparency in logistics processes. Additionally, it enhances accountability by effectively tracking the transportation of goods, aligning with the principles of the GST Law.
Who Is Required To Create The e-Way Bill?
Registered individuals or transporters, whether they are the consignor (supplier) or consignee (recipient), can generate the e-Way bill for goods transportation.
Unregistered transporters can also sign up on the common portal to create e-Way bills for their clients’ goods. Additionally, any citizen, aside from the above-mentioned parties, can generate an e-Way bill for moving goods for personal use.
When Is An e-Way Bill Required?
An e-Way Bill is required when goods worth more than 50,000 are transported interstate or intrastate.
(Note: States were given the freedom to decide the limit for the intrastate movement of goods. Hence, the limit for generating e-Way bills varies with each state. For example, the limit to generate e-Way bills within Delhi is 1Lakh rupees.)
When is an e-Way Bill not required?
Similarly, when the value of goods to be transported is not more than 50,000; then an e-Way bill is not required.
Though movement of handicraft goods, and goods for job work are required to generate an e-Way bill, even if the value of goods in transit is less than 50,000rs.
Along with that, certain goods and transactions are exempted from generating e-Way Bills, as per the provisions under rule 138(14) of the Central Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017
The following are the exempted goods:
- Liquefied petroleum gas for household and non-domestic exempted category customers
- Kerosene oil distributed through the Public Distribution System (PDS)
- Postal baggage transported by the Department of Posts
- Natural or cultured pearls, precious or semi-precious stones, precious metals, and metals coated with precious metal
- Jewelry, goldsmiths’ and silversmiths’ items, and related articles
- Currency
- Used personal and household effects
- Unworked and worked coral
- Goods like alcoholic liquor for human consumption, natural gas, petroleum crude, high-speed diesel, petrol, or aviation turbine fuel.
- Goods not considered as supply under Schedule III of the Act, which includes activities that are neither supply of goods nor an employee’s service to an employer in their employment, and functions performed by MPs, MLAs, etc.
- Empty cargo containers.
- Goods except de-oiled cakes, specified in notification No. 2/2017–Central Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017, including items like curd, lassi, buttermilk, fresh milk, vegetables, fruits, unprocessed tea leaves, unroasted coffee beans, live animals and plants, meat, cereals, unbranded rice and wheat flour, salt, and items of educational importance like books, maps, and periodicals.
- Goods exempted under notification No. 7/2017–Central Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017 (supply by CSD to unit-run canteens and authorized customers) and notification No. 26/2017–Central Tax (Rate) dated 21st September 2017 (consists of heavy water and nuclear fuels).
There are also certain transactions where e-Way bills are not required. They are –
- If you’re moving goods using non-motorized transport like horse carts or manual carts.
- When goods are being moved from a port, airport, air cargo complex, or land customs station to an inland container depot (ICD) or a container freight station (CFS) for customs clearance.
- When goods are going from an ICD or CFS to a customs port, airport, or air cargo location under a customs bond
- If goods are moving between different customs ports/stations under a customs bond
- When goods are transported with customs supervision or a customs seal.
- For goods transported within a specific notified area.
- When goods are in transit to or from Nepal or Bhutan.
- If goods are transported to a weighbridge within 20 kilometers and then back to the original business location, you have a Delivery Challan (DC).
- When the government or local authorities transport goods by rail as the consignor.
- For goods going to or coming from the Ministry of Defence.
How to generate an e-way bill?
Before you start creating e-Way bills, you need the following significant documents –
- Taxable Invoice / Bill of Supply / Delivery Challan
- For road transport – Transporter ID, or Vehicle Number
- For ship/air/rail transport – Transporter ID, Transport document number, and date.

STEP 1. Now to create an e-Way bill, you first need to be registered in the common portal.
Keep your GSTIN and registered mobile number handy for the following process.
- Go to the e-Way bill portal, and under the Registration option, select e-Way Bill Registration.
- In the registration form, submit your GSTIN, displayed captcha, and click on Go.
- Some of your information, like your Applicant name, Trade name, Address, Mail ID, and Mobile Number, will be automatically filled in once you enter your GSTIN number and captcha. If these details are incorrect or have changed, you can click ‘Update from GST Common Portal’ to fetch the latest data from the GST Common Portal.
- Click on ‘Send OTP’ to receive OTP on your GST-registered mobile number. Enter this OTP and click ‘verify OTP’ to validate it.
- Now, create a Username and Password for operating your account on the e-Way Bill System
If you work as a transporter and are not yet registered on the GST portal, you can still complete your registration on the e-Way bill portal.
Simply click on the ‘Registration’ option, choose ‘Enrolment For Transporters,’ and complete the provided form.
STEP 2. Login and Generate New e-Way Bill
- Click on Login, enter your Username, Password, and displayed Captcha.
- Go to the e-Waybill option and select ‘Generate New’ from the drop-down menu.
- It will open up the EWB Entry Form, which consists of Part A and Part B. Majorly, Part A consists of the supply details, whereas Part B consists of transport details.
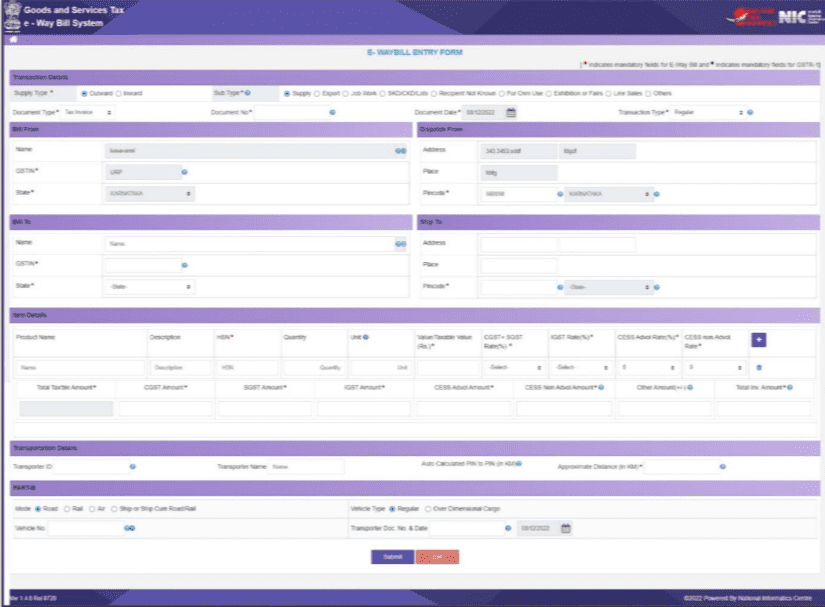
STEP 3. Select Supply Type and SubType
- In Part A the first step is to choose the ‘Supply Type.’: ‘Outward’ if you are supplying goods or ‘Inward’ if you are receiving them. Depending on your selection, the system will display relevant sub-types of transactions for you to choose from.
- Next choose the Sub-Type, and the relevant document in the ‘Document Type’ dropdown. Enter the document number and date as shown on your document. Ensure the Document No. is unique for all E-Way Bills, and the Document Date is correct.
STEP 4. Fill Billing Details
- Billing Details: For ‘Outward’ transactions, fill in the ‘Bill From’ section, including Name, GSTIN, and Address. If you have additional places of business, you can edit the address in the ‘Dispatch From’ section. For ‘Inward’ transactions, complete the ‘Bill From’ section with Name, GSTIN, State, and Address. These details can be auto-populated if you’ve entered the consignor details in the Supplier Master. If not, you can manually enter the details, including GSTIN as ‘URP’ for ‘Unregistered Person’ if applicable.
STEP 5. Fill Consignee Details
- Consignee Details: For ‘Outward’ transactions, provide the consignee’s Name, GSTIN, and Address in the ‘Bill To’ section. These details can be auto-populated if you’ve entered consignee details in the Client Masters. For ‘Inward’ transactions, the system will auto-populate the Name, GSTIN, and address of the recipient based on your user details. You can edit these details if necessary.
STEP 6. Fill Product Details
- Product Details: In the ‘Item Details’ section, enter the product details. If you’ve entered the product details in the Product Masters, you can auto-populate them by entering 2-3 characters of the product name. The system will display the related product name.
- Fill in the description, HSN, Unit, and Tax rate, which will be auto-filled from the master. Please note that you must include at least one HSN code belonging to goods, as E-Way Bills cannot be generated with only SAC codes (99) for Services.
STEP 7. Fill in Tax Details
- Tax Details: Enter the quantity and total taxable value for each product. Tax rates (%) will be auto-populated based on the HSN code. Select the applicable tax rate slab (%) from the dropdown. For the ‘CESS Non Advol Rate,’ enter the tax rate in Rupees instead of a percentage. You can add multiple products by clicking the + button.
STEP 8. Enter Transportation Details
- Transportation Details: In this section, enter the transporter’s name, transporter ID, and the approximate distance (in kilometers) the shipment will cover. The system will estimate the motorable distance between the supplier and recipient addresses based on PIN codes entered in ‘Bill From & Bill To.’ You can also manually enter the actual distance, which should not exceed 10% more than the auto-calculated distance. If the source and destination PIN codes are the same, you can enter a distance of up to 100 kilometers.
STEP 9. Entering Part B details
- Next comes the Part B of the form.
Please note that Part B of the E-Way Bill contains vehicle details. If, during the E-Way bill creation process, you don’t have all the necessary vehicle details, you can create a Part A slip with the information filled in Part A. Subsequently, the transporter can complete the Part B details based on the Part A slip before starting the journey.
STEP 10. Fill in Vehicle Details
- Vehicle Details: Select the mode of transportation (road, rail, air, or ship/road cum ship) and enter the vehicle number and transporter document number and date. If you are moving the goods directly without a transporter, you can enter the vehicle number without transporter details.
STEP 11. Submit form
- That’s it! After completing all the necessary details, submit your request. The system will validate your inputs and generate a unique 12-digit E-Way Bill number. Keep in mind that this E-Way Bill is not valid for the movement of goods until Part-B details are added to the form. Once Part-B details are included, the system will display the E-Way Bill’s validity based on the estimated distance, indicating when you can legally move the goods.
The system also offers a convenient feature that allows users to generate multiple E-Way Bills simultaneously, which can be quite useful when you have several bills to create at once.
How to generate e-Way Bills In Bulk?
The system also offers a convenient feature that allows users to generate E-Way Bills in bulk, which can be useful when you have several bills to create simultaneously.
Here’s how to do it:
STEP 1. Download the Required Tools
First, visit https://docs.ewaybillgst.gov.in/html/formatdownloadnew.html and download the “e-Way Bill JSON preparation” tool. This tool comes as an Excel file with multiple sheets.
STEP 2. Understanding the Excel File
The Excel file contains several sheets. The first one is a welcome sheet. The second sheet, labeled “e-Way Bill,” is where you’ll input your e-Way Bill details, just as you would on the standard e-Way Bill form. The third sheet provides Master Codes, which offer information for placeholder dropdowns. The fourth sheet includes a Sample e-Way Bill for reference, FAQs, and validation instructions.
STEP 3. Generating Bulk E-Way Bills
To generate bulk E-Way Bills, go to the e-Way Bill portal and select the sub-option ‘Generate Bulk’ under the ‘eWaybill’ option. When you click this option, you’ll see a screen where you can choose a file. Select the JSON file you want to upload (please note that the maximum allowed file size for upload is 5 MB).
STEP 4. Uploading the JSON File
Once you’ve chosen the JSON file from your system, upload it to the e-Way Bill portal. This file will be used to generate the bulk E-Way Bills.
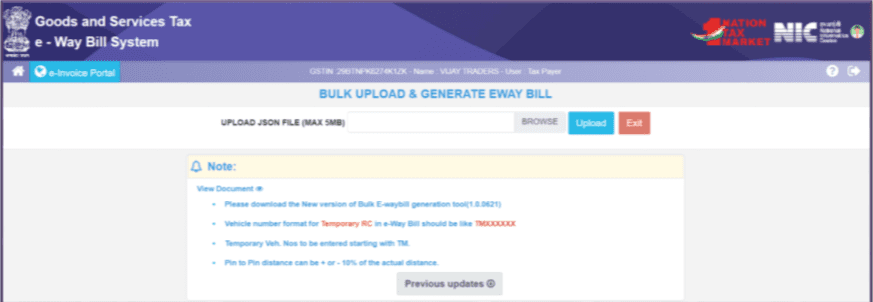
STEP 5. Processing and Results
After the JSON file is processed, the system will generate the E-Way Bills and display them, one for each request. If any issues arise during this process, the system will show the appropriate error messages for each request.
How to create a consolidated e-way bill?
When a transporter is carrying multiple consignments in a single vehicle, they can generate a Consolidated E-Way Bill. It replaces the need for separate documents for each consignment in the same vehicle.
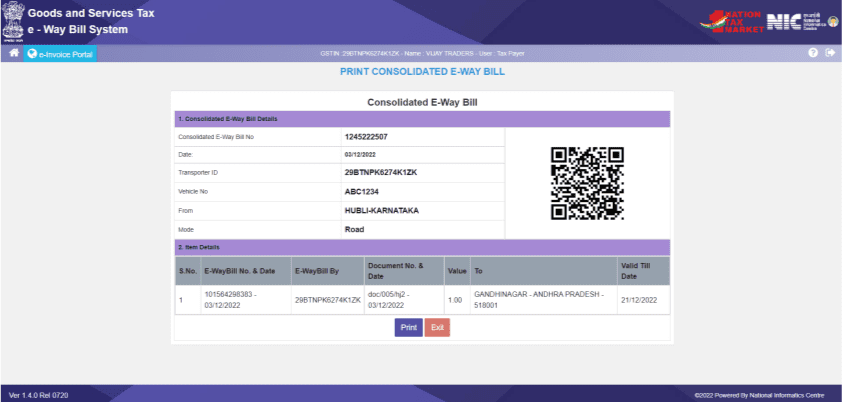
To generate a Consolidated E-Way Bill, the user must have the E-Way Bill numbers of all the consignments being transported in one vehicle, and follow the given steps:
- Select the ‘Generating New’ sub-option under ‘Consolidated EWB.’
- Choose the mode of transportation (Road/Rail/Air/Ship/Road cum Ship).
- Enter the ‘From State,’ where the vehicle starts from, and the ‘Vehicle Number.’
- Now, enter the E-Way Bill Numbers. The other fields in the form will auto-populate.
Note that the user should either be the generator or the transporter of the selected E-Way Bills to use them in a Consolidated E-Way Bill. Otherwise, updating the details will not be allowed.
- Click ‘Submit,’ and the system will display a Consolidated E-Way Bill with the consolidated E-Way Bill Number (EBN).
Note: You can also generate e-Way bills via other platforms and automate them too! Check out Top e-Way Bill Software for easy compliance!
How to print an e-way bill?
Once you generate the e-Way Bill, you’ll find the option below the bill.
But in case you missed printing the e-Way bill, then it can be done in the following ways –
Sure, here are the steps to print an e-Way Bill:
1. Go to the ‘e-Waybill’ option on the e-Way Bill portal, and select the ‘Print EWB’ sub-option.
Please note that only the person who generated the e-Way Bill and the transporter can print it.
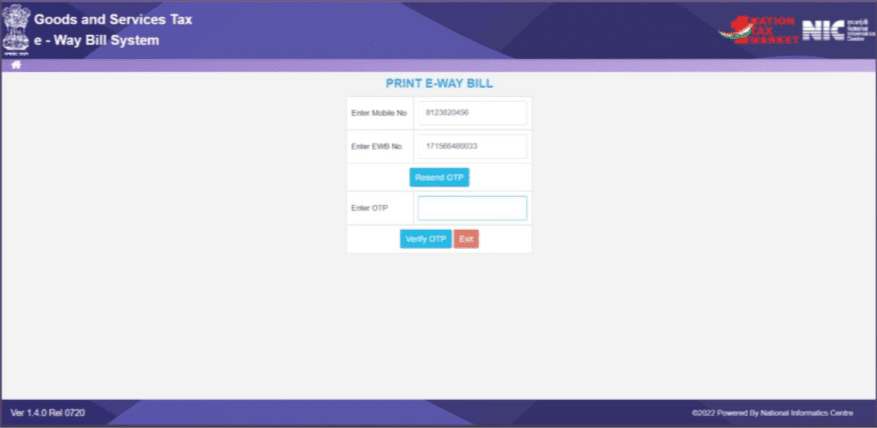
2. Enter the e-Way Bill number and find all the e-Way Bill details.
To find your e-Way Bill number, click on ‘Reports’ on the sidebar, select ‘Outward Supplies’ and fill in ‘EWB. Generated Date’, ‘To’ and ‘Subuser.’
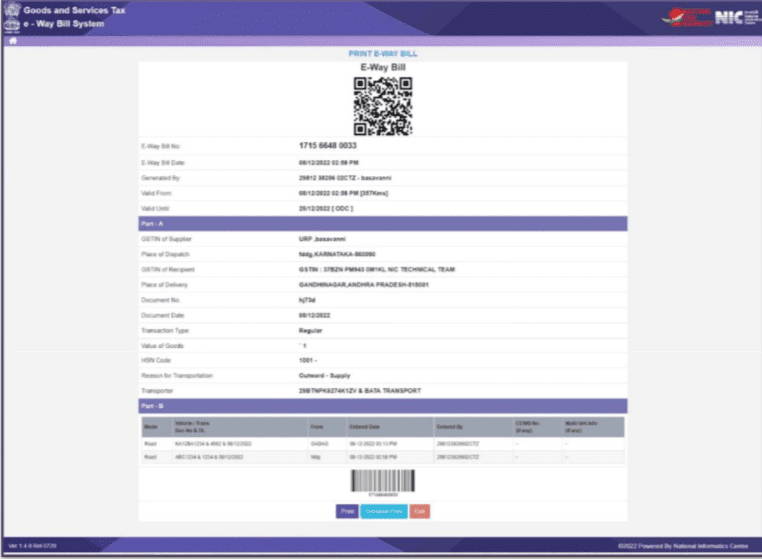
3. You’ll also see an option to print the e-Way Bill.
4. If you need a more detailed print, you can select the “Detailed Print” option.
How to cancel an e-way bill?
Taxpayers can cancel an E-way Bill for various reasons, such as when the goods are not being transported or if there was an incorrect entry made on the E-way Bill.
Note: E-way can be canceled within 24 hours of its generation by the person who generated it. It can also be canceled by the receiver or consignee within 72 hours of its generation. The E-Way can also be canceled if the goods are not transported or transported in a manner that doesn’t match the information provided in the e-Way bill.
However, an E-Way bill cannot be canceled if a proper officer has already verified the said e-Way bill.
To cancel an E-way Bill, follow the given steps:
- Go to the ‘e-Waybill’ option, and then select the ‘Cancel’ sub-option. This action will lead you to the cancellation screen.
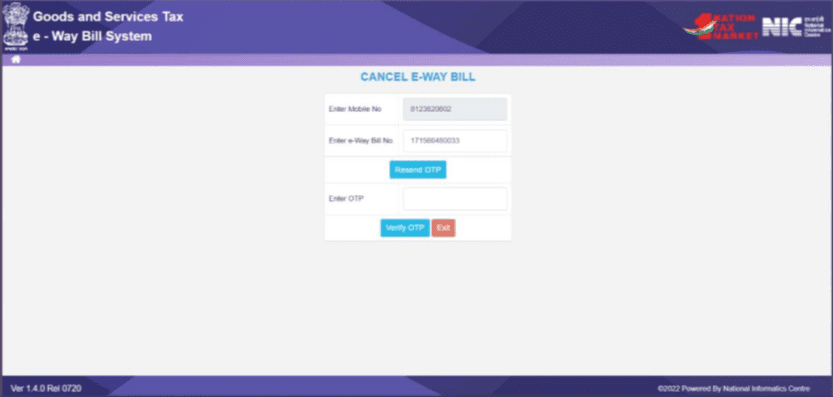
- Enter the 12-digit E-way Bill number in the designated field and click ‘Go.’ The specific E-way Bill associated with that number will be displayed.
- State the reason for cancellation, and cancel the e-Way bill.
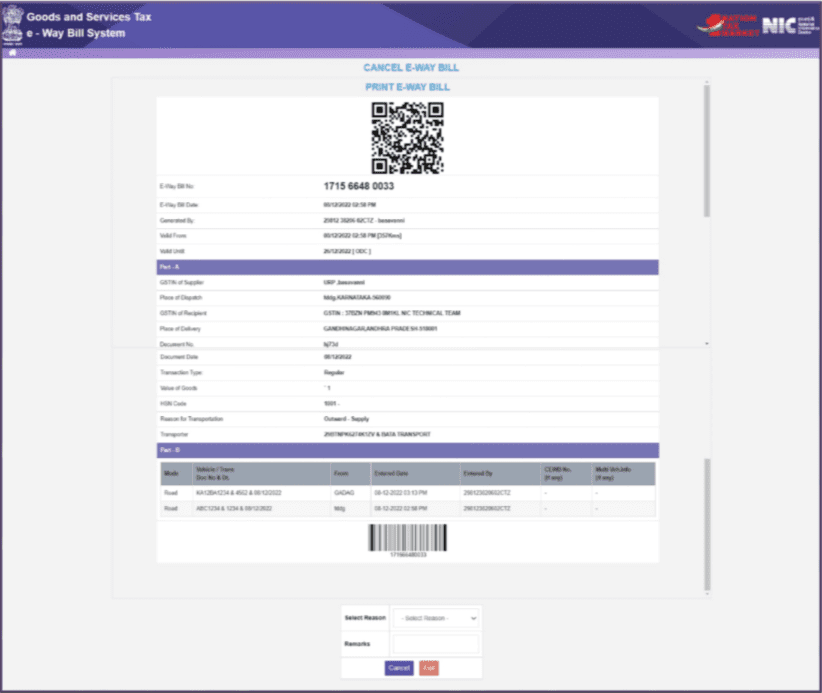
Remember: Once an E-way Bill is canceled, it becomes illegal to use the same E-way Bill for any transportation.
How to reject an e-way bill?
This option allows taxpayers to keep an eye on E-Way Bills generated by other taxpayers when they are the recipient or supplier. If the recipient does not receive the goods mentioned in the E-Way Bill, they can reject it using this feature.
- To begin, select ‘Reject’ from the sidebar.
- Next, choose the date when the E-Way Bill you want to reject was generated and click ‘Submit’.
- You can select the specific E-Way Bill you wish to reject by checking the checkbox next to it.
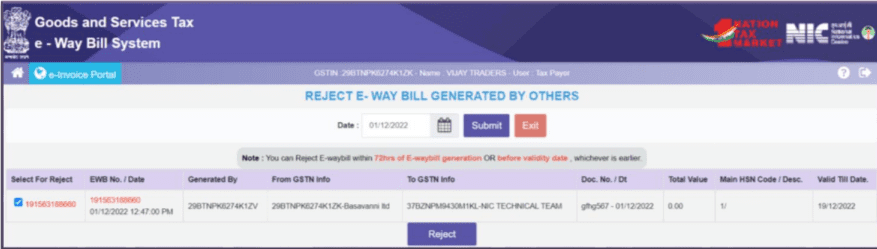
Note: When you are the other party (recipient or supplier), you have the responsibility to communicate your acceptance or rejection of the goods specified in the E-Way Bill. If you do not communicate your decision within 72 hours from the time the E-Way Bill was generated, it is considered that you have accepted the details.
Blocking and Unblocking Of E-Way Bill Generation
What is the Blocking of the e-Way Bill?
If a GST registered taxpayer has not filed Return 3B for two consecutive months on the GST Common portal, their GSTIN (as a Supplier) will be blocked from generating further E-Way Bills and a pop-up message will appear with ‘ERROR’ every time they attempt to generate the e-Way bill.
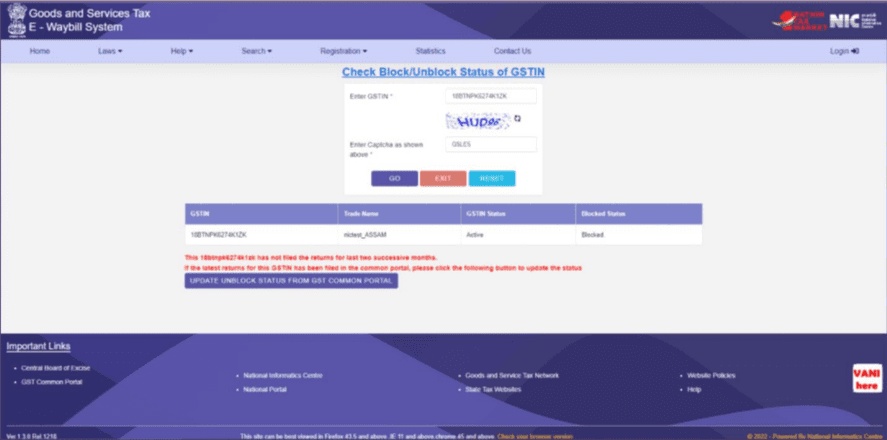
Although, you can unblock the same using the following steps:
How to Unblock the e-Way Bill Generation Option?
1. When the taxpayer files Return-3B on the GST Common Portal, the blocked GSTIN will automatically change its status to ‘Unblocked’ within a day in the E-Way Bill system, allowing the taxpayer to resume E-Way Bill generation.
· If the status does not update in the E-Way Bill system, the taxpayer can do it manually by visiting the E-Way Bill portal and selecting the option ‘Search > Update Block Status.’
· Here, enter your GSTIN, complete the CAPTCHA, and click ‘GO.’
· The system will retrieve the filing status from the GST Common Portal, and if the return has been filed, the status in the E-Way Bill system will be updated accordingly.
2. Alternatively, the unblocking process can be initiated by the jurisdictional officer online through the GST Portal. This action is typically taken after considering a manual representation received from the taxpayer.
E-Way Bill Validity – Calculation & Extension
How to calculate e-way bill validity?
The E-Way Bill’s validity period is based on the approximate distance entered during its generation. For every 100 kilometers, one day of validity is granted, and for any part of 100 kilometers, an additional day is added.
For example, if the distance is 440 kilometers, the validity period is 4+1 days.
However, for Over Dimensional Cargo (ODC), the validity is one day for every 20 kilometers and an additional day for any part thereof.
Validity Extension
The validity of the e-Way bill starts with the first entry in Part B.
In road transportation, it’s the vehicle entry, while in rail/air/ship transportation, it’s the first transport document number entry.
A transporter can also extend the validity of the e-Way bill if exceptional circumstances like natural calamities, law and order issues, trans-shipment delays, accidents, etc. prevent the consignment from reaching its destination before the validity expires.
However, only the current transporter has the option of extending the validity.
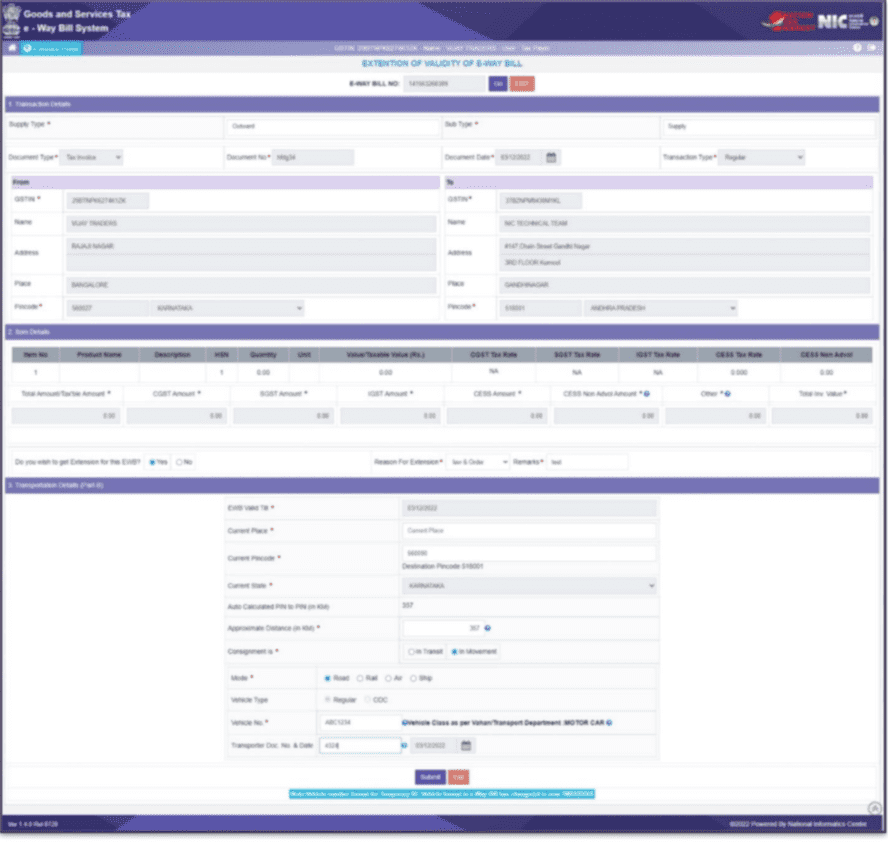
How to extend validity?
To extend your EWB validity, follow the given steps:
- Log into the portal, and under e-Waybill, select ‘Extend Validity’
- Enter the desired EWB number and click on ‘Go’

- Right below your item details, you’ll find the option with the message ‘Do you wish to get Extension for this EWB?’ Select Yes.
- Provide a reason from the dropdown menu and explain it in detail in the remarks field.
- Next, depending on the situation, select either “In Movement” or “In Transit.”
- For “In Movement,” you’ll be required to provide mode and vehicle details. For “In Transit,” specify the transit type (e.g., On Road, Warehouse) and address details of the transit place.
- Update Transportation Details-Part B, including the approximate remaining distance from the current location to the destination.
- Click “Submit,” and after system validation, the EWB’s validity will be extended.
Recommended Reads: Best CRM Software with Invoicing
Other E-Way Bill Related FAQs
Q. How does an e-way bill work?
E-way Bill is generated by either of the registered parties, (be it supplier or recipient) or the transporter; specifically stating the information of goods in transit. This reduces the amount of tax evasion and fraudulent activities by keeping the authorities informed of the business activities.
Q. How to generate e-way bills for unregistered buyers?
Follow these steps to generate an E-way bill as an unregistered buyer:
- Go to the E-way bill portal.
- Select “E-way Bill for Citizens” from the Registration tab.
- Choose “Generate New EWB.”
- Provide registration details, verify OTP, and click “Continue To Bill Generation.”
- Next, you will receive the “e-Way Bill Entry Form”.
- Fill in the details. Under the ‘ Bill To’ section, write ‘URP’ in GSTIN, and complete filing the form.
- Click “Submit” to get a 12-digit E-way bill number.
- Optionally, print the E-way bill.
Remember to carry a copy while transporting goods.
Q. Can we cancel an e-way bill?
E-way can be canceled within 24 hours of its generation by the person who generated it. The E-Way can also be canceled if the goods are not transported or if they are transported in a manner that doesn’t match the information provided in the e-way bill.
However, an E-Way bill cannot be canceled if a proper officer has already verified the said e-way bill.
Q. How to know the e-way bill password?
If you have forgotten your username or password, then select ‘Forgot Username’ or ‘Forgot Password’ to recover your username or reset your new password. Enter the details asked and authenticate via OTP, for a new username and password.
Q. How to check the E-way bill generated by others?
One can view and check the E-Way bill generated by others too. According to the rule, taxpayers or recipients have the ability to decline e-way bills that have been generated using their GSTIN by other parties. To facilitate this, the following options have been provided to them for viewing the list of e-way bills:
1. Dashboard: Upon logging into the system, the taxpayer or recipient can access details about e-way bills generated under their GSTIN on their dashboard.
2. SMS Notifications: They will receive a daily SMS summarizing the total e-way bill activities associated with their GSTIN.
3. Reject Option: By going to the “Reject” option and selecting a date, they can view the list of e-way bills generated using their GSTIN by other parties.
4. Reports: Another option is to navigate to the “Reports” section and check for ‘EWBs by other parties,’ which provides a list of e-way bills generated on their GSTIN by external parties.
Q. Is e-way bill mandatory for inter-state supply?
Yes, if the goods in transit value more than 50,000; then generating an e-way bill is necessary for interstate supply. However, in cases like the transfer of handicraft goods or movement of goods for job work, the e-way bill is to be generated even if the value of the goods is less than 50,000rs.
Certain exemptions are provided, which are discussed above.
Q. Is an e-way bill mandatory for intra-state?
Yes, if the goods in transit value more than 50,000; then generating an e-way bill is necessary for intra-state supply.
However, exceptions are provided under rule 138(14) of Central Goods and Service Tax, 2017, which are discussed above.
Q. Is e-way bill mandatory for local sales?
Yes, if the goods in transit value more than 50,000; then generating an e-way bill is necessary for intra-state supply or local sales.
However, exceptions are provided under rule 138(14) of Central Goods and Service Tax, 2017 which are discussed above.
Q. What to do if e-way bill validity expires?
When an e-way bill’s validity expires, it typically means that the goods should not be transported. However, in exceptional situations like natural calamity, trans-shipment delays, law and order issues, accidents of conveyance, etc. the transporter has the option to extend the validity period. This extension can be requested within 8 hours after the original expiry time by updating the reason for the extension and providing the necessary details in PART-B of FORM GST EWB-01.
The steps to increase e-way bill validity are discussed above.
Q. Who can extend the validity of an e-way bill?
If a transporter is in possession of a consignment at the time when the e-way bill’s validity period expires, they have the option to extend the validity period of the e-way bill.
Q. How to make changes in e-way bills?
Once an e-way bill is generated, it cannot be edited or modified, except for updating Part B. However, if incorrect information was included during generation, the e-way bill can be canceled and a new one can be generated. It’s important to note that cancellation must take place within 24 hours of the original generation time to rectify any errors.
Q. Is e way bill required for hand delivery?
No, e-way is required when the goods are transferred through motorized conveyance.
Q. What is a consolidated e-way bill?
A consolidated e-way bill is a single document that includes multiple e-way bills for various consignments all transported in a single vehicle (goods vehicle). This means that a transporter who is carrying multiple consignments for different senders and recipients in one vehicle can generate and carry just one consolidated e-way bill instead of needing multiple separate e-way bills for each of those consignments.
Steps to create a consolidated e-way bill are discussed above.
Q. How to change mobile number in the e-way bill portal
Mobile numbers cannot be changed directly in the e-way bill portal.
EWB System( www.ewaybillgst.gov.in ) is dependent on the GST Common portal (www.gst.gov.in) for taxpayers’ registration details like legal name/trade name, business address, mobile number, and e-mail ID. EWB System will not allow taxpayers to update these details directly in the EWB portal. If the taxpayer changes these details at the GST Common portal, it will be updated in the EWB system within a day automatically. Otherwise, the taxpayer can update the same instantaneously by selecting the option ‘Update My GSTIN’ in the e-Way bill system. The details will be fetched from the GST common portal (www.gst.gov.in) and updated in the e-Way bill system.
Q. How to fill Part A of the e-way bill?
An e-way bill consists of Part A and Part B. Part SA consists of information about the sender, receiver, and goods, whereas Part B contains details of the transportation vehicle.
To fill Part A of the e-way bill,
- Log into your e-way bill portal
- Select the ‘e-Way’ Bill from the dashboard and click on ‘Generate New’
- Next, fill in the following details
- Transaction Details: Fill in transaction details like Supply Type, Sub Type, Document Type, Document No., Document Date and Transaction Type.
- Bill From and Bill To Details: Provide information about the supplier and recipient, and the dispatch details. Some details may be auto-filled based on the transaction type.
- Item Details: Provide comprehensive details about the items being transported.
- Transporter Details: Provide information about the transporter, mode of transportation, and the vehicle used.
Once you click on ‘Submit’ without adding information about Part B, you can create the Part A slip. The transporter can add the Part B details to activate the e-way bill before starting the journey.
Q. How to extend e-way bill validity after the expiry date?
A transporter can extend the validity of the e-way bill 8 hours before and 8 hours after the e-way bill expiration.
- Log into the portal, and under e-Waybill, select ‘Extend Validity’
- Enter the desired EWB number and click on ‘Go’
- Right below your item details, you’ll find the option with the message ‘Do you wish to get an Extension for this EWB?’ Select Yes.
- Provide a reason from the dropdown menu and explain it in detail in the remarks field.
- Next, depending on the situation, select either “In Movement” or “In Transit.”
- For “In Movement,” you’ll be required to provide mode and vehicle details. For “In Transit,” specify the transit type (e.g., On Road, Warehouse) and address details of the transit place.
- Update Transportation Details-Part B, including the approximate remaining distance from the current location to the destination.
- Click “Submit,” and after system validation, the EWB’s validity will be extended.
Read more: Top E-Invoicing Software in India: Detailed Analysis
Q. Is an e-way bill required for services?
No, an e-way bill is not required for services if they don’t involve the transit of goods.
Q. How to fill up the e-way bill for job work?
To fill up an e-way bill for job work, log into e-Way Bill Portal > e-Way Bill > Generate New.
Select ‘Job Work’ under ‘Sub Type’ and proceed to enter further details like you would for any other e-way bill generation, as guided above.
Q. How to update part B of the e-way bill?
To generate/update Part B of an e-way bill, follow these steps:
Step 1: Visit the E-Way Bill Portal and log into your account.
Step 2: Go to the dashboard and select the “Update Part B/Vehicle” option from the “e-Way Bill” drop-down list.
Step 3: Choose the appropriate option for “Show EWB by” and enter the EWB number or EWB Generated Date under “Generated by me (date)” Then, click on “Go.”
Step 4: Select the specific e-Way Bill you want to update, which will take you to the “Vehicle Updation” page.
Step 5: Fill in the following details:
- Vehicle Number
- Place of Change
- State of Change
- Reason (Choose the appropriate reason from the drop-down list)
Step 6: Finally, click on the “Submit” option.
After submitting the form, you can see the changes you made in Part B of the E-Way Bill on the E-Way Bill page.
Recommended Reads: E-invoicing In GST: A Complete Guide
Q. How to view the e-way bill generated by me?
To view e-way bills generated by you, go to the e-way bill dashboard and select ‘Reports’. From the drop-down, select ‘My EWB Reports’ to view e-way bills generated by you.
Q. Is an e-way bill required in Delhi?
Yes, an e-way bill is required for the transport of goods within Delhi valued above 1L rupees.
Q. How should I generate an e-Waybill for carrying goods by train?
e-waybills may be generated for all modes of travel such as Road, Train, Air, and Ship. In the case of a train, you may enter the railway receipt number and date instead of the vehicle number.
Recommended Reads:
15 Best Invoicing Software In 2024
Top 10 Inventory Invoice Software
Top 7 Invoice Generator Software
Top 10 Billing Software For Chartered Accountants
Top Invoicing Software For Consultants
Billing Software For Export Business
Top Locksmith Invoice software
Top 10 Accounting Software
Top Desktop Based Accounting Software
Top Accounting and Inventory Management Software for Businesses: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Invoice and Packing List Software: A Complete Guide