Key Takeaways
Definition and Importance: An export invoice is a critical document for international trade, serving as proof of the transaction and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Legal Compliance: Export invoices must meet specific legal criteria, including timely issuance, accurate details, and adherence to GST or customs regulations.
Essential Components: A comprehensive export invoice includes exporter and buyer details, product descriptions, trade terms (INCOTERMS), payment terms, and shipping details.
Types of Export Invoices: Common types include proforma invoices, commercial invoices, consular invoices, and packing list invoices, each serving a specific purpose.
Currency and Payments: Clearly state the transaction currency, include exchange rates if applicable, and address potential fluctuations through clauses or hedging strategies.
Practical Steps for Creation: Use standardized templates or invoicing software to ensure accuracy, professionalism, and compliance with international trade standards.
Special Scenarios: Export invoices are essential for all types of exports, including goods, services, re-exports, and temporary exports like exhibition samples.
An export invoice is a key document that bridges the gap between buyers and sellers in global trade. It not only lists the details of goods or services being exported but also acts as proof of the transaction for customs, taxation, and payment purposes.
Exporters rely on it to meet regulatory requirements and ensure seamless international shipments. Without a properly drafted export invoice, businesses risk delays, penalties, and payment disputes. This comprehensive guide explores every aspect of export invoices, including their significance, legal requirements, and how to create one effortlessly.
Understanding Export Invoices
What is an Export Invoice?
An export invoice is a legal document issued by a seller to a buyer during international trade. It acts as proof of sale and details the goods or services being exported. This document includes critical information such as the description of the goods, quantity, unit price, total value, payment terms, delivery conditions, and shipping details.
Export invoices are not just a means of billing; they play a vital role in customs clearance, allowing authorities to determine the value of the goods for tax and duty purposes. Additionally, they provide transparency in transactions, ensuring both parties are aware of the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
This document is integral to maintaining compliance with export laws in both the seller’s and buyer’s countries. Errors or omissions can lead to delays, fines, or shipment rejections, making accuracy crucial. By issuing a comprehensive export invoice, businesses safeguard their interests and build trust with international clients.
What is the Need for an Export Invoice?
Export invoices serve multiple purposes that make them indispensable in international trade. Here’s why they are essential:
- Customs Clearance: Export invoices provide customs authorities with the necessary information to assess the shipment’s value, determine applicable duties or taxes, and ensure compliance with regulations. Without this document, goods may be detained or delayed at the border.
- Legal Proof of Transaction: An export invoice acts as a binding document confirming the transaction between the exporter and the buyer. It is a key piece of evidence in case of disputes or claims.
- Facilitates Payment: Banks and financial institutions often require export invoices to process payments under international payment methods like letters of credit or bank guarantees.
- Taxation and Accounting: Export invoices are necessary for filing taxes, availing input tax credits, and maintaining accurate financial records.
- Buyer and Seller Assurance: By detailing all agreed-upon terms, export invoices ensure clarity and prevent misunderstandings between the buyer and seller.
Export invoices are, therefore, much more than a billing tool—they are a cornerstone of smooth, compliant international trade operations.
Importance of Raising an Export Invoice
Raising an export invoice is not just a legal formality; it holds significant importance for all stakeholders in the export process:
- Ensures Legal Compliance: Many countries mandate the issuance of an export invoice as part of their export-import regulations. Non-compliance can lead to penalties or shipment delays.
- Simplifies Customs and Logistics: Accurate export invoices streamline customs procedures, as they serve as the basis for export declarations, shipping manifests, and other documentation.
- Facilitates Smooth Transactions: By detailing every aspect of the sale, an export invoice minimizes the chances of disputes over payment terms, product specifications, or delivery conditions.
- Acts as a Financial Record: Export invoices serve as critical records for both exporters and importers. They help track revenue, manage cash flow, and analyze trade performance.
- Builds Credibility and Trust: A well-structured and accurate invoice reflects professionalism, which strengthens relationships with international buyers and partners.
Raising an export invoice is, therefore, a fundamental step in ensuring smooth, lawful, and efficient trade processes.
When Should You Raise an Export Invoice?
Timing is critical when raising an export invoice to ensure compliance with legal regulations and avoid delays in the export process. Generally, an export invoice is issued at specific points in the transaction, depending on the nature of the goods and the terms agreed upon between the exporter and the buyer. Here are the key scenarios:
- Before Shipment: Most exporters issue the invoice after confirming the purchase order and finalizing the terms of sale but before the goods are shipped. This allows the buyer to arrange payment or secure necessary documentation, such as letters of credit.
- After Shipment: In some cases, the invoice is raised once the goods have been shipped, and the shipping documents (such as the Bill of Lading or Airway Bill) are available. This method is often used for transactions involving deferred payments or credit terms.
- As Per the Agreement: Export invoices can also be raised at a pre-agreed stage in the transaction, such as after the production of goods, in cases of custom orders, or after specific milestones in service contracts.
- Complying with Legal Timeframes: Under Indian laws, for example, an export invoice must be raised within a stipulated timeframe, usually within 15 days from the date of shipment of goods or the completion of services.
Why Timely Invoicing Matters
– Customs Clearance: Delays in issuing an invoice can lead to shipment holds at customs.
–Buyer Compliance: The buyer might face delays in customs clearance on their end without the invoice.
– Payment Delays: Late invoicing can postpone payment processing, affecting cash flow.
– Regulatory Penalties: Missing legal deadlines for issuing invoices can result in fines or penalties.
Exporters should aim to align invoice issuance with the agreed-upon trade terms and legal requirements to ensure a seamless export process.
Types of Export Invoices
Export invoices come in different forms, each serving a specific purpose in international trade. Choosing the right type of export invoice depends on the nature of the transaction, the trade agreement, and the legal requirements. Let’s dive into the common types of export invoices with detailed explanations and examples for each:
1. Proforma Invoice
A proforma invoice is a preliminary document issued before the actual shipment of goods. It acts as a quotation or a commitment from the exporter to the buyer, providing a detailed estimate of the costs involved. This invoice is not legally binding but helps the buyer understand the terms of the deal and make arrangements for payment or import documentation.
Key Features:
- Provides an itemized list of goods with approximate costs.
- Includes terms of sale, delivery date, and payment methods.
- Often used during the negotiation stage of a trade agreement.
Example: A textile exporter in India provides a proforma invoice to a buyer in Germany detailing 1,000 meters of cotton fabric at $10 per meter. The invoice includes an estimated shipping cost of $500, making the total value $10,500. The buyer uses this document to seek approval from their customs authority or arrange financing.
2. Commercial Invoice
The commercial invoice is the most commonly used export invoice and serves as a legally binding document. It provides a complete record of the goods or services sold, their value, and the agreed terms of sale. This invoice is essential for customs clearance, as it helps authorities assess the shipment’s value for tax and duty purposes.
Key Features:
- Legally binding and required for customs clearance.
- Includes detailed product descriptions, quantity, price, and total value.
- Specifies trade terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight).
Example: An electronics manufacturer in China exports 500 smartphones to a retailer in the UAE. The commercial invoice lists each smartphone at $200, with a total value of $100,000. The invoice also states the trade term as CIF, meaning the cost of insurance and freight is included.
3. Consular Invoice
A consular invoice is required by certain countries to verify the authenticity and value of goods being imported. It must be certified by the consulate of the importing country in the exporter’s location. This type of invoice ensures compliance with the importing country’s regulations.
Key Features:
- Certified by the consulate of the importing country.
- Helps prevent undervaluation or fraud in international trade.
- Required for goods shipped to specific countries, such as Argentina or Egypt.
Example: An agricultural machinery exporter in the US ships equipment to Argentina. The consular invoice, certified by the Argentine consulate in the US, details the shipment’s value at $50,000. This certification helps the Argentine customs authority validate the import.
4. Customs Invoice
A customs invoice is a simplified version of the commercial invoice, tailored for use by customs authorities. It contains essential details to calculate duties and taxes and ensures the shipment meets the importing country’s requirements.
Key Features:
- Simplified format for customs use.
- Includes product descriptions, value, and country of origin.
- Focuses on information relevant to duty assessment.
Example: A Canadian exporter ships maple syrup to Japan. The customs invoice lists the quantity as 1,000 bottles, the value as $20,000, and the country of origin as Canada. This document ensures a smooth customs clearance process in Japan.
5. Packing List Invoice
The packing list invoice is not a financial document but an auxiliary one that details the packaging and contents of the shipment. It complements the commercial invoice and helps customs authorities verify the shipment.
Key Features:
- Lists packaging details, such as dimensions, weight, and container numbers.
- Assists in customs checks and inventory management.
- Does not include financial information.
Example: An Indian furniture exporter ships 50 wooden chairs to the UK. The packing list invoice specifies that the chairs are packed in five crates, each weighing 100 kg, with dimensions of 2m x 1m x 1m. This document helps UK customs verify the shipment’s contents against the commercial invoice.
6. Service Export Invoice
This invoice is used for exporting intangible services instead of physical goods. It outlines the nature of the service provided, its duration, and the payment terms.
Key Features:
- Highlights the type of service (e.g., consulting, software development).
- Includes hourly rates or project costs.
- Specifies timelines and payment milestones.
Example: A software development firm in India exports a custom app to a US-based client. The service export invoice states the project cost as $25,000, with payment terms of 50% upfront and 50% on delivery. It also includes a description of the app’s features and delivery timeline.
Understanding the various types of export invoices and their applications ensures exporters meet their legal obligations, avoid errors, and facilitate smooth international trade. By using the appropriate invoice type for each transaction, businesses can build credibility and trust with global partners.
Legal Regulations for Export Invoices
Export invoices are governed by stringent legal regulations to ensure compliance with international trade laws and local government requirements. Understanding these laws is critical for exporters to avoid penalties, shipment delays, or rejection by customs authorities. Below, we discuss the legal framework surrounding export invoices, with a specific focus on Indian regulations.
1. Regulatory Authorities Governing Export Invoices in India
- Customs Department: Ensures that export shipments comply with customs regulations.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Laws: Govern tax implications for exports.
- Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA): Regulates foreign currency transactions.
- Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT): Issues guidelines on export documentation, including invoices.
2. Mandatory Requirements for Export Invoices
In India, the following are mandatory details that an export invoice must include to comply with legal requirements:
- Exporter Details: Name, address, and GSTIN (if applicable).
- Importer Details: Name and address of the buyer, including the country of import.
- Invoice Number and Date: A unique, sequential invoice number and the date of issue.
- Description of Goods/Services: Detailed specifications, including Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) codes.
- Value of Goods/Services: Itemized and total value, including any applicable taxes.
- Currency: The currency in which the transaction is conducted, e.g., USD, EUR.
- Terms of Trade (INCOTERMS): Specifies delivery terms like FOB, CIF, or EXW.
- Shipping and Transport Details: Method of shipment, carrier details, and shipping date.
- Bank Details: Exporter’s bank account details for receiving payments.
- Declaration: A statement affirming the accuracy of the information and compliance with export laws.
3. Time Limit to Raise an Export Invoice Under Indian Law
Indian law mandates strict timelines for raising export invoices based on the nature of goods or services:
- For Goods: An export invoice must be raised within 15 days of the date of shipment.
- For Services: The invoice must be raised within 30 days of rendering the service.
Non-compliance with these timelines can attract penalties under GST laws and delay payment processing.
4. Export Under Bond or Letter of Undertaking (LUT)
Exports in India are considered zero-rated under GST, meaning no GST is charged. However, exporters must meet specific conditions:
- Bond: Required if the exporter does not intend to pay GST upfront.
- LUT: Allows exporters to ship goods without paying GST, subject to certain conditions. The export invoice should clearly state “Supply meant for export under LUT without payment of IGST.”
5. Documentation for Customs Clearance
An export invoice forms part of the essential documentation required for customs clearance in India:
- Invoice Copy: Customs authorities use this to verify the value and description of goods.
- Shipping Bill: Generated by customs based on the export invoice.
- Packing List: Accompanies the invoice to detail packaging and shipment contents.
6. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with legal regulations for export invoices can result in:
- Customs Penalties: Fines for incorrect or incomplete documentation.
- Shipment Delays: Detainment of goods at ports or borders.
- Tax Liabilities: Loss of benefits like input tax credit (ITC) or zero-rated GST status.
Can export invoices be canceled?
Yes, export invoices can be canceled, but the process depends on the stage of the transaction and the regulations in your country. Here’s a general outline:
1. Before Shipment/Export:
- If the goods have not been shipped and the export procedure is still in the documentation stage, the invoice can typically be canceled without significant complications.
- You may need to issue a credit note to reverse the transaction and record the cancellation in your accounting system.
2. After Shipment/Export:
- If the goods have already been shipped and the invoice has been submitted to customs, canceling the invoice becomes more complicated.
- You may need to work with customs authorities and amend or cancel the export declaration, depending on the rules in your jurisdiction.
3. GST or Tax Implications:
- In countries like India, where GST applies, canceling an export invoice may involve reversing the GST filing (if applicable) or making adjustments in the relevant returns (e.g., GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B).
- It’s crucial to reflect the cancellation in your GST returns accurately.
4. E-Invoicing or Digital Filing:
- If an e-invoice was generated, you might need to cancel it through the same e-invoicing platform. Most systems allow cancellation within a specified timeframe (e.g., 24 hours in India). Beyond this window, amendments may be required.
5. Record Maintenance:
- Always maintain a record of the canceled invoice, along with the reasons and any supporting documentation, for audit and compliance purposes.
Tips for Compliance
To ensure compliance with legal regulations:
– Use professional invoicing software that automatically incorporates required fields.
– Stay updated on regulatory changes through DGFT or customs notifications.
– Double-check all details on the invoice for accuracy and completeness.
– Consult a legal or trade expert for complex export scenarios.
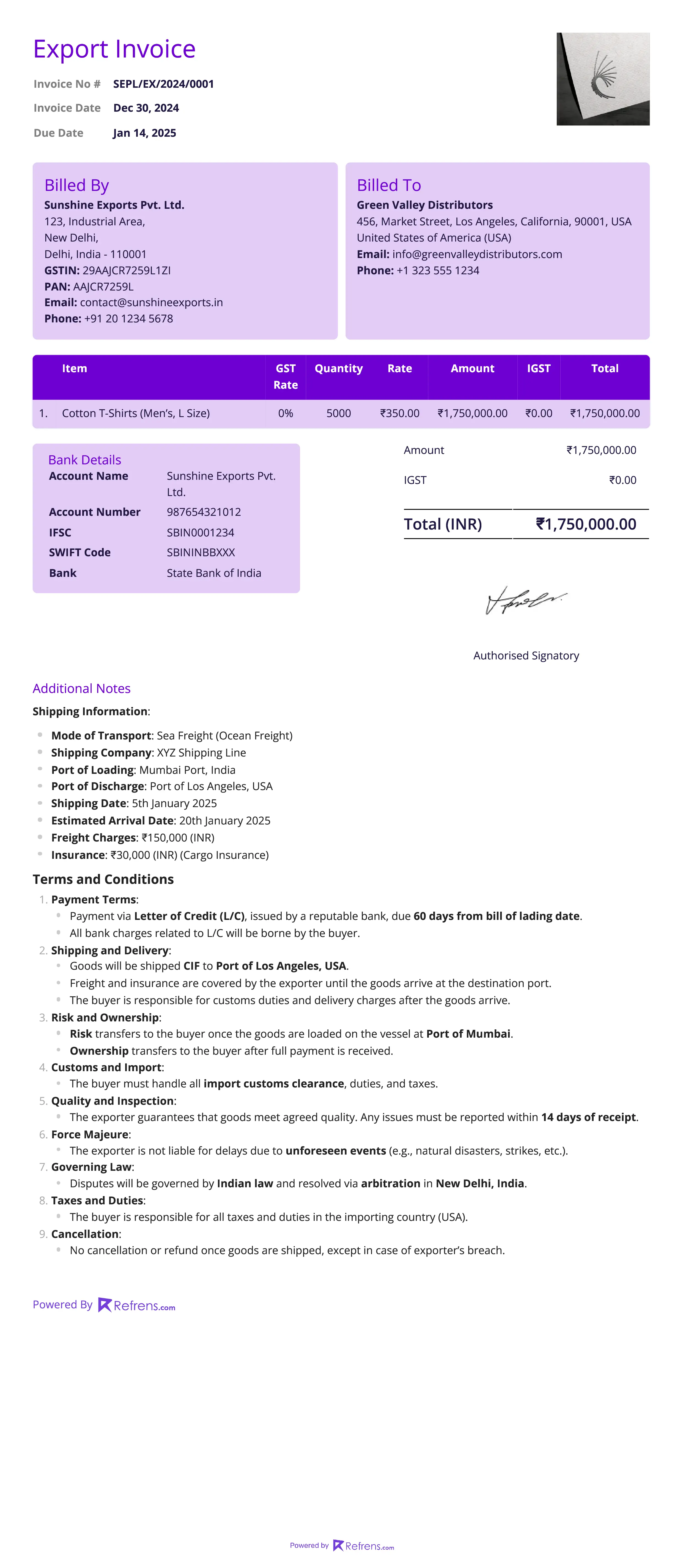
Sample Format of an Export Invoice
This sample format can be customized based on specific business and buyer requirements. Using invoicing software like Refrens can help ensure accuracy and consistency in creating professional export invoices.
How Are Packing and Shipping Dealt With in an Export Invoice?
Packing and shipping details are integral to an export invoice, as they directly influence customs clearance, logistics, and the buyer’s understanding of the shipment. Including accurate and detailed information about packing and shipping ensures a seamless export process and minimizes the risk of disputes or delays. Here’s how packing and shipping are managed in an export invoice:
1. Packing Details
Packing details help customs authorities and buyers verify the shipment’s content and ensure the goods are packed appropriately for transit. These details are often included in a separate packing list or integrated within the export invoice.
Key Packing Information to Include:
- Type of Packaging: Specifies whether the goods are packed in boxes, crates, pallets, or other materials.
- Number of Packages: Total number of packages or containers in the shipment.
- Dimensions and Weight: The size (length x width x height) and weight (gross and net) of each package.
- Markings and Labels: Identifying marks, such as barcodes, batch numbers, or product labels, to distinguish the goods.
- Description of Contents: A brief summary of what each package contains.
Example of Packing Details:
- Number of Packages: 10 wooden crates
- Gross Weight: 1,200 kg
- Net Weight: 1,000 kg
- Dimensions: 2m x 1m x 1m per crate
- Contents: 1,000 units of cotton shirts (500 Size L, 500 Size M)
2. Shipping Details
Shipping details in an export invoice provide essential information about the transport and delivery of the goods. These details ensure transparency and help both parties track and manage the shipment.
Key Shipping Information to Include:
- Mode of Transport: Specifies whether the goods are transported by sea, air, road, or rail.
- Carrier Details: The name of the shipping line, airline, or courier company handling the shipment.
- Shipping Date: The date the goods are dispatched from the port of origin.
- Port of Loading and Destination: The departure and arrival ports for the shipment.
- Bill of Lading (BOL) or Airway Bill Number: A unique identifier for the shipment.
Example of Shipping Details:
- Mode of Transport: Sea
- Carrier: Maersk Line
- Port of Loading: Mumbai, India
- Port of Destination: Rotterdam, Netherlands
- Shipping Date: 15 December 2024
- Bill of Lading Number: BL2024123456
3. Role of Packing and Shipping in Customs Clearance
Both packing and shipping details are critical for customs authorities to assess the shipment:
- Customs Duties and Taxes: Packing and shipping details help customs calculate duties based on the weight, value, and type of goods.
- Verification: Customs authorities cross-check the invoice details with the actual shipment to ensure accuracy.
- Compliance: Accurate documentation ensures compliance with international shipping regulations.
Why Packing and Shipping Details Matter to Buyers
Buyers rely on packing and shipping details for multiple reasons:
– Logistics Planning: Ensures they are prepared to handle the shipment upon arrival.
– Damage Claims: Clear packing details help in assessing liability for any damages during transit.
– Inventory Management: Accurate packaging details allow buyers to plan their storage and inventory needs.
Including detailed packing and shipping information in your export invoice is not just a requirement—it is a critical step toward building trust with buyers and ensuring compliance with international trade standards.
Use of Currency in an Export Invoice
The choice and accurate representation of currency in an export invoice are crucial for ensuring clarity and avoiding disputes in international trade. Since exporters and buyers are often based in different countries with distinct currencies, a well-documented approach to handling currency is essential. Here’s how currency is addressed in an export invoice:
1. Specifying the Transaction Currency
The currency used for the transaction must be clearly stated in the export invoice. This is typically decided during the negotiation stage and reflects the terms agreed upon by both parties.
Commonly Used Currencies in Export Invoices:
- US Dollar (USD): Widely used in international trade due to its global acceptability.
- Euro (EUR): Common in trade involving European countries.
- British Pound (GBP): Frequently used in transactions with the UK.
- Japanese Yen (JPY): Popular in trade with Japan.
- Indian Rupee (INR): Occasionally used for exports to countries with strong trade relations with India.
Example of Currency Declaration:
Currency: USD
2. Conversion Rates
If the currency of the invoice differs from the exporter’s domestic currency, the exchange rate should be mentioned. This helps in accounting and compliance with tax regulations.
Key Points:
- The exchange rate on the date of invoice issuance should be used.
- Mention the source of the exchange rate, such as a central bank or a recognized financial institution.
Example:
Conversion Rate: 1 USD = 83 INR (As per Reserve Bank of India on 12 December 2024)
3. Multicurrency Transactions
In some cases, transactions may involve multiple currencies:
- The invoice might be issued in one currency, but payments are received in another.
- Freight charges, insurance, or taxes might be quoted in a different currency.
To avoid confusion, specify the primary transaction currency and provide a breakdown for any additional charges in other currencies.
Example of Multicurrency Details:
- Goods Value: USD 10,000
- Freight Charges: EUR 500
- Total Amount Payable: USD 10,500 (converted at the prevailing exchange rate)
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
In countries like India, export invoices must comply with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). Under these regulations:
- Exporters must report the transaction value in a freely convertible currency.
- RBI guidelines require exporters to repatriate the foreign exchange earnings within the prescribed timeframe.
5. Handling Currency Fluctuations
Currency fluctuations can impact the final payment value, especially in long-term transactions. To mitigate risks:
- Incorporate Currency Clauses: Add a clause in the invoice to address exchange rate differences.
Example Clause: “The buyer shall bear any exchange rate fluctuations beyond 2% from the date of this invoice.” - Use Hedging Tools: Financial instruments like forward contracts can lock in exchange rates, protecting against currency volatility.
6. Why Accurate Currency Representation Matters
- Avoids Payment Delays: Clear currency details ensure buyers remit the correct amount.
- Ensures Tax Accuracy: Proper currency declaration simplifies GST or VAT calculations.
- Prevents Disputes: Precise currency details reduce misunderstandings over payment values.
By specifying currency details clearly and adhering to international and local regulations, exporters can enhance transparency, facilitate smoother transactions, and protect themselves from financial risks.
How to Create an Export Invoice: A Comprehensive Guide
An export invoice is a vital document in international trade, detailing the transaction between the exporter and the buyer. To create an accurate and legally compliant export invoice, follow this step-by-step process that includes all essential components:
1. Exporter Details
Include the name, address, and contact information of the exporting company. For Indian exporters, add GSTIN, PAN, and IEC Code to comply with regulatory requirements.
Example:
Exporter: ABC Textiles Pvt. Ltd.
123 Industrial Lane, New Delhi, India
GSTIN: 07AAACA1234F1Z1 | IEC Code: 0512345678
2. Buyer (Importer) Details
Provide the buyer’s name, address, and country of import. Include tax identification numbers if required by the destination country.
Example:
Buyer: XYZ Trading Co.
45 High Street, London, UK
VAT Number: GB123456789
3. Unique Invoice Number and Date
Assign a unique and sequential invoice number for tracking and include the issuance date.
Example:
Invoice Number: EXP/2024/001
Invoice Date: 12 December 2024
4. Description of Goods or Services
List the goods or services being exported with detailed descriptions, including product name, specifications, HSN/SAC codes, quantity, unit price, and total value for each line item.
Example:
| Item No. | Description | HSN Code | Quantity | Unit Price (USD) | Total Price (USD) |
| 1 | Cotton Shirts (Size L) | 6109 | 500 | 10.00 | 5,000.00 |
5. Terms of Trade (INCOTERMS)
Specify trade terms to clarify responsibilities for costs and risk transfer.
Example:
Terms of Trade: FOB Mumbai
6. Currency and Exchange Rate
Mention the transaction currency and the conversion rate if applicable.
Example:
Currency: USD
Conversion Rate: 1 USD = 83 INR (as of 12 December 2024).
7. Shipping and Packing Details
Provide shipping information, including mode of transport, carrier details, shipment date, and ports of loading and destination. Add packing details such as the number of packages, weight, and dimensions.
Example:
Mode of Transport: Sea
Carrier: Maersk Line
Packing: 10 wooden crates, each weighing 100 kg
8. Payment Terms
Clearly define payment methods and timelines, such as advance payment or post-shipment credit.
Example:
Payment Terms: 50% advance, 50% upon receipt of goods
9. Bank Details
Include the exporter’s bank account information for payment, such as account number, SWIFT/BIC code, and bank address.
Example:
Bank Name: State Bank of India
Account Number: 1234567890
SWIFT Code: SBININBB123
10. Declaration
Add a statement confirming the accuracy of the information and compliance with export regulations.
Example:
“We hereby certify that the above-stated information is true and correct, and the goods mentioned are of Indian origin and free from any encumbrances.”
11. Final Review
Double-check all details for accuracy to avoid errors or delays in processing. Use a standardized export invoice template or invoicing software to ensure all components are included.
Use Invoicing Software
To save time and reduce errors, use invoicing software like Refrens or similar platforms that provide ready-made export invoice templates. These tools can automatically include fields required for compliance and generate professional invoices.
Conclusion
Export invoices are essential for smooth international trade, ensuring transparency, compliance, and efficient operations. By understanding their components, legal requirements, and types, businesses can avoid disputes and streamline processes. Accurate and timely invoicing builds trust, ensures compliance, and supports global growth. Using professional invoicing tools can simplify the process, helping businesses focus on expanding their international presence.
FAQs on Export Invoices
Are export invoices the same as commercial invoices?
Yes, a commercial invoice is the primary type of export invoice used in international trade. It includes detailed information about the transaction and is required for customs clearance and payment processing.
What is the difference between proforma and export invoices?
A proforma invoice is a preliminary document used to provide a cost estimate and terms before the sale is finalized. An export invoice, on the other hand, is a legally binding document issued after the sale agreement.
What are INCOTERMS, and why are they important in export invoices?
INCOTERMS (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of the buyer and seller in terms of shipping, risk, and costs. Including INCOTERMS in an export invoice clarifies trade terms and prevents misunderstandings.
Are there penalties for errors in export invoices?
Yes, errors in export invoices can lead to customs delays, fines, or rejection of goods at the destination. Ensure thorough checks to avoid such issues.
Is an export invoice required for drop shipments?
Yes, even for drop shipments (where goods are shipped directly from a third country to the buyer), an export invoice from the seller to the buyer is necessary to document the transaction.
Do I need to issue an export invoice for samples?
Yes, even for samples, an export invoice must be issued. You can declare the goods as “Samples – Not for Sale” and assign a nominal value for customs purposes.
Are export invoices necessary for free trade agreements (FTAs)?
Yes, export invoices are crucial for FTAs as they provide proof of goods’ origin, enabling buyers to claim tariff reductions or exemptions.
Can export invoices be canceled?
Once issued, an export invoice cannot be canceled outright. Instead, you must issue a credit note to nullify or adjust the invoice value.
Are there any tools available to create export invoices?
Yes, invoicing platforms like Refrens that offer export invoice templates and are compliant with trade regulations, making the process easier and more accurate.
How does an export invoice differ for goods and services?
For goods, the invoice includes physical product details, packing, and shipping information. For services, it highlights the type of service, duration, and payment terms.
Is an export invoice required for e-exports?
Yes, export invoices are required for e-exports, especially for tax and customs compliance, even when the transaction involves digital goods or services.


















