GSTR 8 is a monthly tax return that e-commerce operators in India need to file under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system. If you run a platform like Amazon, Flipkart, or any online marketplace where other sellers use your platform to sell products, GSTR-8 is essential for you.
The key purpose of GSTR 8 is to track and report the Tax Collected at Source (TCS). TCS is a small percentage of the sale amount that e-commerce platforms must collect from their sellers and then deposit with the government. This tax ensures that the sales made through online platforms are taxed properly and are part of the larger GST system.
For e-commerce operators, filing GSTR-8 is important because it helps them comply with GST regulations. By collecting and depositing TCS, operators not only stay within the law but also ensure that the sellers on their platforms can claim an input tax credit (ITC), which is basically the credit sellers can use to reduce their overall GST liability. This makes the entire tax process smoother for everyone involved.
Who Needs to File GSTR-8?
Eligibility Criteria for Filing GSTR-8
GSTR-8 must be filed by every e-commerce operator who is registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system and is responsible for collecting Tax Collected at Source (TCS). If you own or manage a platform where other sellers list and sell their products, such as an online store or marketplace, you are required to file GSTR-8.
The basic eligibility criteria include:
- You must be registered under GST and have a valid GST Identification Number (GSTIN).
- You should be collecting TCS from the sales made through your platform.
- Your business turnover should exceed Rs. 20 lakhs (Rs. 10 lakhs for businesses in northeastern states of India).
Who is Considered an E-commerce Operator under GST?
An e-commerce operator is defined under GST as any person or company that owns, operates, or manages a digital or electronic platform through which the sale of goods or services takes place. This means platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, and similar online marketplaces where sellers can offer their products to consumers. The key role of an e-commerce operator is to facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers and collect TCS on behalf of the government.
Exemptions and Special Cases
Not all online businesses need to file GSTR-8. Here are a few exemptions and special cases:
- Suppliers or sellers on e-commerce platforms: They do not need to file GSTR-8. They only need to file their regular GST returns like GSTR-1 or GSTR-3B.
- Non-resident taxpayers: If you are a non-resident, you are not required to file GSTR-8.
- E-commerce operators who have no TCS liability: If you have not collected any TCS in a particular tax period or there are no supplies made through your platform, you may not need to file GSTR-8 for that period.
By understanding who needs to file GSTR-8 and meeting the eligibility requirements, e-commerce operators can ensure they are staying compliant with GST regulations and avoid penalties.
Why GSTR-8 is Important?
GSTR-8 plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency and compliance in e-commerce transactions under the GST system. Here are some key reasons why it’s important:
Verification of TCS by the Government
GSTR-8 allows the government to verify the Tax Collected at Source (TCS) collected by e-commerce operators. Since e-commerce platforms are required to collect a 1% TCS on all taxable supplies made through their platform, the information provided in GSTR-8 helps ensure that the correct amount of TCS is being deposited with the government. This helps prevent tax evasion and ensures that the tax system remains fair.
Monitoring of E-commerce Transactions
As the demand for e-commerce continues to rise, the government needs a way to monitor these transactions effectively. GSTR-8 provides detailed information about all the supplies made through e-commerce platforms. This data helps the government keep track of the volume of online sales and ensures that e-commerce operators are complying with GST rules.
Contribution to GST Revenue Collection
GSTR-8 is essential for ensuring that the government collects the appropriate amount of GST revenue from e-commerce transactions. By filing GSTR-8, e-commerce operators report the total value of sales and the TCS collected. This information is critical for the government to maintain an accurate picture of revenue inflows from the rapidly growing e-commerce sector.
Integration with Suppliers’ GSTR-2A for Input Tax Credit (ITC)
One of the most significant advantages of GSTR-8 is that it allows suppliers to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) for the TCS collected on their behalf. Once the e-commerce operator files GSTR-8, the TCS details appear in the supplier’s GSTR-2A form. The supplier can then use this information to claim ITC, which helps reduce their overall GST liability. This integration ensures that the tax system operates smoothly, and businesses can maximize their tax benefits without any delays.
In summary, GSTR-8 plays a vital role in verifying TCS, ensuring transparency in e-commerce transactions, contributing to GST revenue collection, and facilitating ITC for suppliers. It is an essential part of the compliance framework for e-commerce operators under GST.
Prerequisites for Filing GSTR-8
Before filing GSTR-8, e-commerce operators need to meet certain requirements. These prerequisites ensure that the filing process is smooth and compliant with GST regulations. Here’s a breakdown of the key requirements:
GST Registration Requirements for E-commerce Operators
To file GSTR-8, the e-commerce operator must be registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. The operator should have a valid GST Identification Number (GSTIN), which is a 15-digit number based on the PAN of the business. Without GST registration, the operator cannot collect TCS or file GSTR-8.
Revenue Threshold for Filing
E-commerce operators must file GSTR-8 if their aggregate turnover exceeds a certain threshold. Specifically, if the business’s annual turnover exceeds ₹20 lakhs, or ₹10 lakhs for operators in northeastern states, they are required to file GSTR-8 monthly. This revenue threshold ensures that small e-commerce operators with lower revenues are exempt from this filing.
Maintaining TCS Records
E-commerce operators must maintain detailed records of all TCS (Tax Collected at Source) collected on taxable supplies made through their platform. These records should include the value of supplies, the amount of TCS collected, and the GSTIN of suppliers. Proper record-keeping is essential for filing an accurate GSTR-8 return and avoiding penalties for non-compliance.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or EVC for Filing
For e-commerce operators to file GSTR-8 on the GST portal, they must authenticate the return using either a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or the Electronic Verification Code (EVC).
- DSC: A Digital Signature Certificate is a secure digital key that verifies the identity of the operator. It is mandatory for companies and LLPs to file using DSC.
- EVC: For individual taxpayers or partnerships, an Electronic Verification Code (EVC) can be used as an alternative to DSC. It generates an OTP sent to the registered mobile number for verification.
Ensuring that these prerequisites are in place before filing GSTR-8 helps streamline the compliance process, avoids delays, and minimizes the chances of errors.
GSTR-8 Format & Details
When filing GSTR-8, e-commerce operators are required to provide specific details about their transactions, tax collection, and other important information. Let’s take a detailed look at each section of the GSTR-8 form:
- GSTIN
- Legal Name
The first section of GSTR-8 asks for the GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) and the legal name of the e-commerce operator. This information is auto-populated once you log into the GST portal, making it easier to ensure that your details are correctly entered.
- GSTIN: A unique 15-digit identification number assigned to the e-commerce operator.
- Legal Name: The registered business name associated with the GSTIN, auto-filled based on the registration.
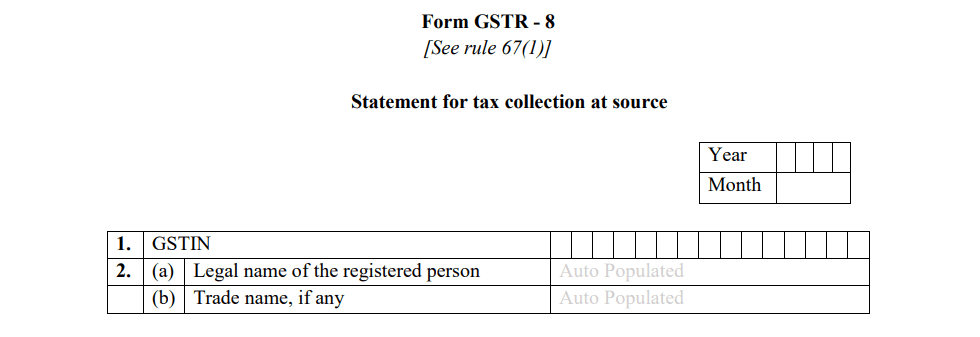
- Supply Details Made Through the E-commerce Platform
This section covers the key details of the taxable supplies made through the e-commerce platform. Here, the operator needs to provide:
- Gross value of supplies: This includes the total value of goods or services supplied to both registered and unregistered persons through the platform.
- Value of supplies returned: If any goods or services are returned during the month, this value needs to be reported.
- Net taxable value: The difference between the total supplies and the returns is the net amount on which Tax Collected at Source (TCS) is applicable.
The net taxable value forms the basis for calculating TCS, which the e-commerce operator must collect and report.
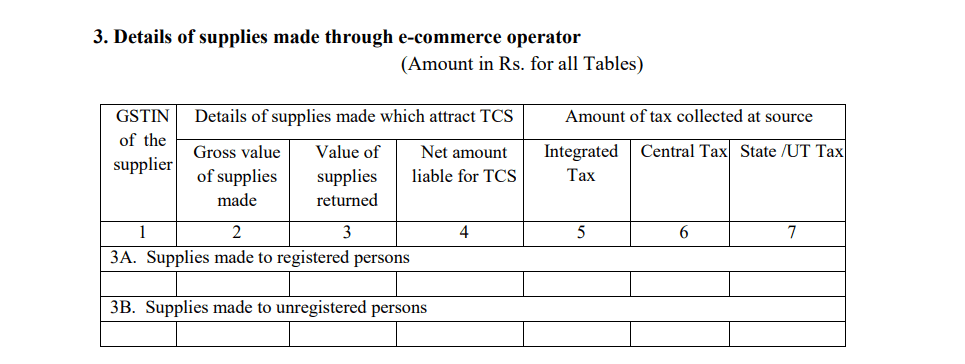
- Amendments to Previous Returns
If there were any errors or omissions in the GSTR-8 returns filed for earlier periods, they can be corrected in this section.
- Amendment details: This includes corrections to the taxable value, TCS amount, or any other information reported incorrectly in earlier months.
By providing accurate amendments, e-commerce operators can rectify discrepancies and avoid future compliance issues.
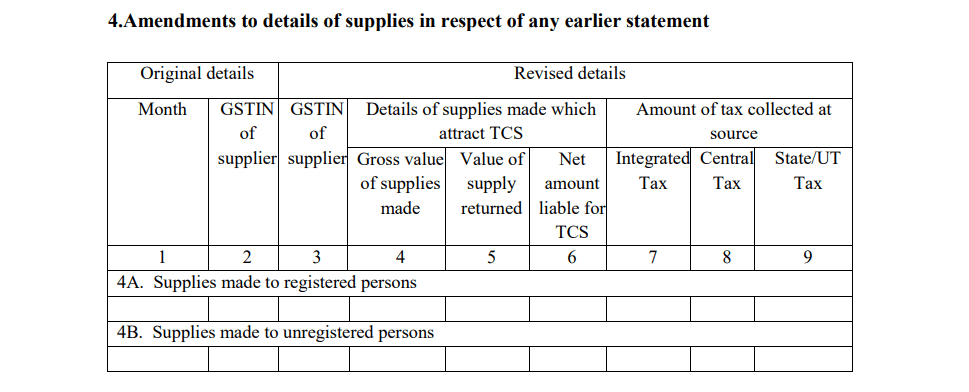
- Details of Interest on Delayed Payments
If there is any delay in paying the TCS collected, the operator is required to pay interest. The interest rate is set at 18% per annum and must be calculated on the outstanding amount.
- Interest details: This section will include the interest due and payable for the delayed payment of TCS. Timely filing and payment of TCS can help avoid accumulating interest.
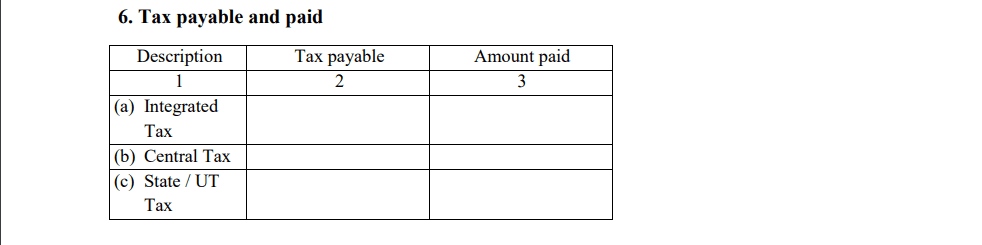
- Tax Paid and Payable
This section requires the operator to report the total amount of tax that has been paid and any remaining tax liability that is still payable.
- Tax paid: The total amount of TCS already remitted to the government.
- Tax payable: The outstanding TCS amount that is yet to be paid.
This breakdown ensures that the government is aware of the operator’s tax remittance status.
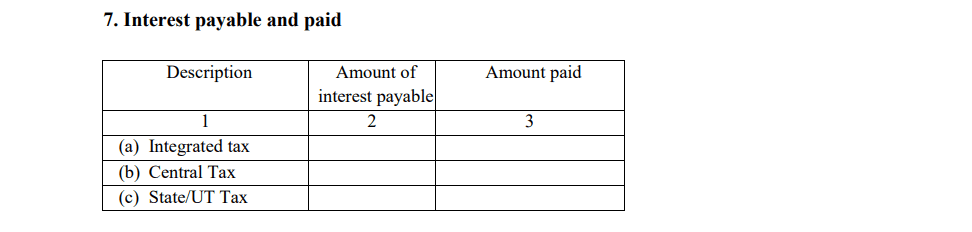
- Interest Payable and paid
This section captures details of any interest that is either payable or has already been paid due to late payment of TCS (Tax Collected at Source). It includes a breakdown of interest owed on the delayed remittance of taxes and any interest that has been settled. This ensures transparency and compliance with tax regulations regarding late payments.
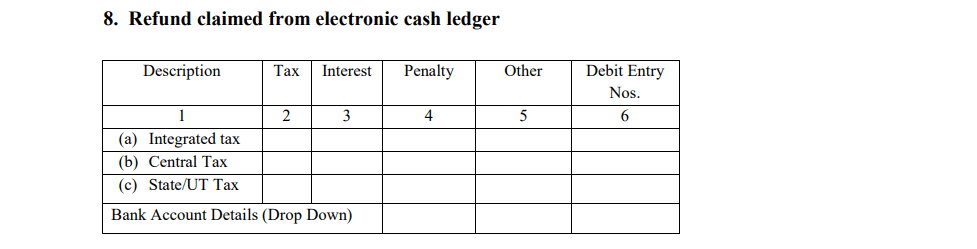
- Refund Claimed from the Electronic Cash Ledger
E-commerce operators can claim a refund if there is excess money in their electronic cash ledger after fulfilling their TCS liability for a particular tax period.
- Refund details: This section will show any refund claims made from the electronic cash ledger, ensuring transparency in financial transactions.
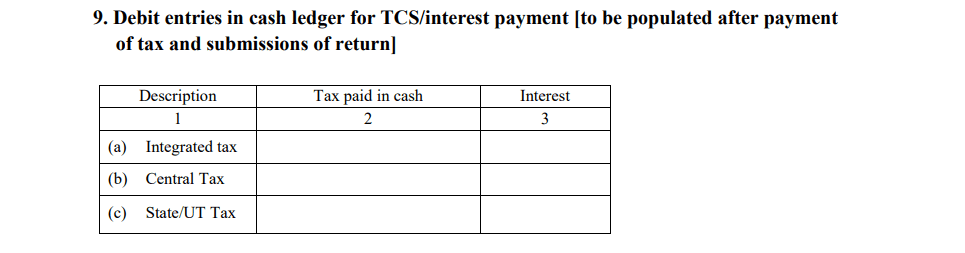
- Debit Entries in the Cash Ledger for TCS/Interest Payments
After filing GSTR-8, the amounts collected as TCS are automatically reflected in the cash ledger. This section displays any debit entries made from the cash ledger for paying TCS or interest on delayed payments.
- Debit entries: This includes details of payments made to clear TCS liabilities or interest dues, ensuring all liabilities are settled accurately.
By understanding and filling out these sections of GSTR-8 correctly, e-commerce operators can ensure that they remain compliant with GST regulations, avoid penalties, and streamline the overall tax filing process.
How to File GSTR-8?
Filing GSTR-8 is a crucial task for e-commerce operators to remain compliant with GST regulations. There are two main ways to file the return: directly on the GST portal or by using the offline utility tool. Below is a simple step-by-step guide to help you navigate the filing process.
Step-by-step Guide to Filing GSTR-8 on the GST Portal
- Log in to the GST Portal
Visit the official GST portal at www.gst.gov.in.
Use your credentials (Username and Password) to log in.
- Access the Returns Dashboard
Once logged in, go to the “Services” section in the top menu.
Click on “Returns” and then select “Returns Dashboard.”
Select the financial year and the tax period (month) for which you are filing GSTR-8.
- Select Form GSTR-8
From the list of returns, select “GSTR-8” to begin filing the return for e-commerce operators.
- Enter the Required Details
GSTIN and legal name: Auto-populated based on your login credentials.
Supply details: Fill in the gross value of supplies made, the value of supplies returned, and the net taxable value.
Amendments: If necessary, enter any corrections for previously filed returns.
Interest: Provide details of any interest due for late TCS payments.
Tax Paid/Payable: Fill in the details of the tax already paid and any remaining liability.
Refunds: Include details if you are claiming any refunds from the electronic cash ledger.
Debit entries: Update the debit entries for TCS and interest payments made.
- Preview the Return
After filling out all the required information, click on “Preview” to view a summary of your GSTR-8 form before submission.
- Submit and Validate
Once satisfied with the details, click on “Proceed to File.” You will be prompted to validate the data.
DSC or EVC: You can file GSTR-8 using either a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or an Electronic Verification Code (EVC) sent to your registered mobile number.
- Confirmation
After successful submission, you will receive an Application Reference Number (ARN) as confirmation of your filing.
You will also receive an SMS and email notification confirming the successful submission.
Using the Offline Utility Tool for GSTR-8 Filing
- Download the GSTR-8 Offline Utility Tool
Go to the GST portal and download the GSTR-8 Offline Utility tool under the “Downloads” section.
Install the tool on your computer (Windows 7 or higher).
- Enter the Required Details Offline
Open the GSTR-8 Offline Utility tool and fill in the required details, including supply information, amendments, interest, tax payable/paid, etc.
The tool offers built-in validations to help avoid errors before uploading.
- Generate the JSON File
After filling out all the information, click on “Generate JSON” to create a file that can be uploaded to the GST portal.
- Upload the JSON File on the GST Portal
Log in to the GST portal and navigate to the Returns Dashboard.
Select “GSTR-8” and choose the option to upload the JSON file.
Once uploaded, the data will be processed, and you can proceed to validate and submit the return.
Key Details to Be Filled in Each Section
- GSTIN and Legal Name: Auto-populated after logging in.
- Supply Details: Enter the gross and net value of supplies made through your platform.
- Amendments: Make any corrections to previously filed returns.
- Interest: Include details of interest applicable for delayed payments.
- Tax Paid/Payable: Update the status of the tax already paid and any remaining liabilities.
- Refunds: Provide refund details from the electronic cash ledger, if applicable.
- Debit Entries: Report any debit entries made for paying TCS or interest.
Submission and Validation Process
- Submission: After entering all the details and previewing the return, click on “Submit.” The return will be filed after validation.
- Validation: Choose between using a DSC or EVC for verification. Once validated, your GSTR-8 form will be officially submitted.
- Acknowledgment: You will receive an Application Reference Number (ARN) as proof of successful filing, along with an SMS and email confirmation.
Filing GSTR-8 on time helps e-commerce operators avoid penalties and stay GST-compliant. Whether you file it online or use the offline utility tool, ensure all sections are accurately filled to prevent any future discrepancies.
Due Date for Filing GSTR-8
Filing Deadline for GSTR-8
The due date for filing GSTR-8 is the 10th day of the month following the tax period. For example, if you are filing for the transactions made in October, you must submit GSTR-8 by the 10th of November. This deadline ensures that the government receives timely reports on the supplies made through e-commerce platforms and the amount of TCS collected.
Impact of Missing the Due Date
If GSTR-8 is not filed on or before the 10th of the following month, the e-commerce operator may face consequences such as penalties, interest on the outstanding amount, and disruption in claiming input tax credits by the suppliers who sell through the platform. This can also create compliance issues and add extra costs to the business due to the late filing charges.
Penalty and Late Fees for GSTR-8
Filing GSTR-8 after the deadline can lead to financial penalties and interest charges. Here’s a breakdown of the penalty structure and its implications.
Penalty Structure for Late Filing (Rs. 200/day up to Rs. 5,000)
- Late Fee: A penalty of Rs. 100 per day under CGST and Rs. 100 per day under SGST is levied for each day the filing is delayed. This totals Rs. 200 per day.
- Maximum Penalty: The late fee is capped at Rs. 5,000, meaning the total penalty will not exceed this amount, no matter how long the delay is.
- No Penalty on IGST: No late fees are imposed under IGST.
Interest Rate of 18% on Outstanding Tax
In addition to the daily penalty, an interest charge of 18% per annum is applicable on the outstanding TCS amount. The interest is calculated from the day following the due date (the 11th of the month) until the actual payment date. This interest needs to be paid by the e-commerce operator along with the outstanding tax amount.
Implications of Non-filing or Incorrect Filing
- Inability to Claim Input Tax Credit (ITC): Suppliers who sell through the e-commerce platform will not be able to claim the TCS amount as an Input Tax Credit (ITC) until the e-commerce operator files GSTR-8. This can affect the suppliers’ compliance and cash flow.
- Audit and Scrutiny: Persistent non-filing or incorrect filing may result in an audit or scrutiny from the GST authorities, leading to further penalties and legal complications.
- Blocking of Compliance Ledger: In extreme cases, continued non-compliance can result in the blocking of the compliance ledger for the e-commerce operator, which restricts their ability to file returns or claim refunds under GST.
It is essential for e-commerce operators to file GSTR-8 on time and ensure accuracy in their returns to avoid these penalties and interest charges.
Can GSTR-8 Be Revised?
Process for Correcting Errors in GSTR-8
Unfortunately, once GSTR-8 is filed, it cannot be revised for the same tax period. If you discover any errors or omissions after filing the return, the corrections must be made in the subsequent month’s return. This means any incorrect or missing details from the previous month can only be updated when you file GSTR-8 for the next month.
How to Handle Mistakes in the Next Return
If a mistake is made in one GSTR-8 filing, it can be corrected in the next return by:
- Amending supply details in Table 4 (Amendments to supplies attracting TCS).
- Correcting the taxable value or the TCS amount that was incorrectly reported.
The corrected details will be reflected in the subsequent month’s GSTR-8 return, and the changes will also be passed on to the concerned suppliers in their GSTR-2A.
Limitations on Revising TCS Details
Revisions to TCS details can only be made once for any given tax period. Additionally, if the supplier has already accepted the original TCS details, no further changes are allowed. This is to ensure that there is no back-and-forth on the details, which could cause confusion for both the e-commerce operator and the suppliers.
Common Issues and Best Practices for Filing GSTR-8
Dealing with Rejected Documents and Supplier Issues
One of the common challenges while filing GSTR-8 is dealing with rejected documents or discrepancies flagged by suppliers. When the supplier rejects the TCS details provided in GSTR-8, it leads to mismatches in their GSTR-2A. To handle this, the e-commerce operator needs to:
- Amend the details in the following month’s GSTR-8 return.
- Communicate with suppliers to resolve disputes about the TCS collected.
- Ensure that any corrections are reflected in both the e-commerce operator’s and the supplier’s records to avoid future discrepancies.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
To avoid issues and ensure seamless GSTR-8 filing, follow these best practices:
- Timely Filing: Always file GSTR-8 before the 10th of the following month to avoid penalties and interest.
- Accurate Data Entry: Ensure that all details related to taxable supplies, TCS collected, and amendments are correctly entered into the system.
- Review Before Submission: Double-check all details before submission to avoid errors, especially in the TCS amount and supply details.
Importance of Regular Reconciliation of TCS and Transaction Data
A major component of filing GSTR-8 is ensuring that the TCS data matches the actual transactions made on the e-commerce platform. Regular reconciliation of:
- Sales data from the platform,
- TCS collected, and
- Returns and refunds processed,
will ensure accurate filing and reduce the chances of errors, penalties, or discrepancies flagged by suppliers. This practice also helps in maintaining compliance with GST regulations and avoiding legal complications.
Automation Tools and GST Software Integration for Error-Free Filing
Utilizing automation tools and integrating GST software into your e-commerce system can significantly reduce manual errors and streamline the GSTR-8 filing process. Benefits of using these tools include:
- Automatic data capture: The software can capture transaction data in real-time, ensuring accurate and up-to-date records.
- Error detection: GST software often has built-in error-checking features, helping to identify discrepancies before submission.
- Simplified reconciliation: Integration of GST software with e-commerce platforms allows seamless reconciliation of sales, returns, and TCS collected, ensuring compliance with minimal manual intervention.
By following these best practices and leveraging automation tools, e-commerce operators can ensure compliance with GST laws, avoid penalties, and maintain accurate records of their TCS liabilities.
Key Takeaway
- Understanding GSTR-8: GSTR-8 is a mandatory GST return for e-commerce operators in India, primarily used to report Tax Collected at Source (TCS).
- Who Must File: All registered e-commerce operators who collect TCS are required to file GSTR-8, except in cases of no TCS liability.
- Purpose of GSTR-8: It ensures transparency, aids in tax compliance, and supports sellers in claiming Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- Filing Prerequisites: Operators need a valid GSTIN, maintain TCS records, and authenticate using DSC or EVC.
- Filing Process: GSTR-8 can be filed online on the GST portal or through the offline utility tool, following detailed steps.
- Due Date and Penalties: The filing deadline is the 10th of the following month, with penalties for late filing and interest on outstanding TCS.
- Revisions and Corrections: Errors can’t be directly revised; amendments must be filed in the next month’s return.
- Best Practices: Timely filing, accurate data entry, and regular reconciliation help avoid penalties and compliance issues.
- Automation Benefits: GST software integration and automation tools can reduce manual errors, ensuring smoother GSTR-8 filing.
FAQs about GSTR-8
- Can GSTR-8 be filed after the due date?
Yes, GSTR-8 can be filed after the due date, but a late fee of Rs. 200 per day (Rs. 100 under CGST and Rs. 100 under SGST) will be levied, up to a maximum of Rs. 5,000. Additionally, an interest rate of 18% per annum will be charged on any outstanding tax amount until the payment is made. - What happens if TCS details are rejected by the supplier?
If the TCS details are rejected by the supplier, the e-commerce operator can amend the information in the following GSTR-8 return. The corrections can be made only once, and the revised details will be sent back to the supplier for approval. - Is GSTR-8 mandatory for all e-commerce operators?
GSTR-8 is mandatory for all e-commerce operators registered under GST who are required to collect Tax Collected at Source (TCS). If no TCS is collected during a specific tax period, then filing GSTR-8 for that period is not required, unless there are amendments or corrections from previous filings. - What to do if there is no TCS collected in a particular tax period?
If no TCS is collected in a specific tax period and there are no amendments to be made from previous filings, the e-commerce operator is not required to file GSTR-8 for that period. However, it is important to ensure that any auto-populated details in Table 4 are checked for accuracy.


















