GSTR 9 is an important document for businesses registered under the GST system in India. It is a form that needs to be filled out once every year and gives a complete summary of all sales (outward supplies) and purchases (inward supplies) that a business has made throughout the financial year.
This form helps to summarize the details already submitted through the monthly or quarterly returns, like GSTR-1 (which shows sales) and GSTR-3B (which summarizes the overall tax liability and payments). By the end of the year, businesses need to carefully review and correct any differences or mistakes made during the year in these returns before submitting GSTR 9.
Filing this form accurately is essential because it provides the final annual report for your GST transactions.
Types of GSTR-9 Forms
There are different types of GSTR-9 forms, depending on the kind of taxpayer you are:
GSTR-9: This is for regular taxpayers who file their GST returns monthly or quarterly. It covers the details of all the outward (sales) and inward (purchases) supplies made in the financial year.
GSTR-9A: This form is for taxpayers who have opted for the Composition Scheme. The Composition Scheme is a simpler and lower-tax option available to small businesses with a lower turnover. Since these businesses have fewer transactions and pay a lower tax rate, their GSTR-9A form is also simpler compared to the regular GSTR-9.
GSTR-9B: E-commerce operators who collect tax at source (TCS) need to file this form. It covers details about their collections and the tax paid on those transactions.
GSTR-9C: GSTR-9C is for businesses with an annual turnover exceeding Rs. 5 crore. It includes a reconciliation statement between the annual return (GSTR-9) and audited financial statements. However, as per the Union Budget 2021 amendments, from FY 2020-21 onwards, the requirement for certification by a Chartered Accountant (CA) or Cost Accountant (CMA) has been removed. Now, businesses can self-certify this form.
Each type of form caters to a different group of taxpayers, ensuring that the filing process is tailored to their specific needs and requirements.
Who Needs to File GSTR-9?
Most businesses registered under GST in India need to file GSTR-9. This includes regular taxpayers who file their monthly or quarterly returns through forms like GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B. Filing this annual return is mandatory, and it summarizes all your transactions and tax payments for the entire financial year.
However, there are a few exceptions. The following groups of taxpayers are not required to file GSTR-9:
- Input Service Distributors (ISD): These are businesses that distribute the credit of goods and services to other units within the same organization.
- Casual taxable persons: Individuals or businesses that occasionally undertake taxable transactions but don’t have a fixed place of business.
- Non-resident taxable persons: Individuals or entities based outside India but occasionally involved in taxable transactions within the country.
- Persons liable to deduct tax at source (TDS) under GST or collect tax at source (TCS).
Key Components of GSTR-9
GSTR-9 has several important sections that taxpayers need to fill out. These sections help summarize all the transactions, taxes paid, and credits claimed throughout the year. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
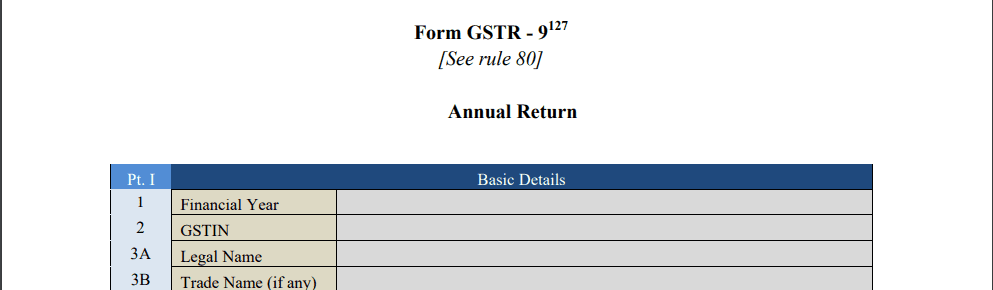
- Part I: Basic Information|
This section collects the basic details of the taxpayer, such as the GSTIN (GST Identification Number), the legal name of the business, and the financial year for which the return is being filed.
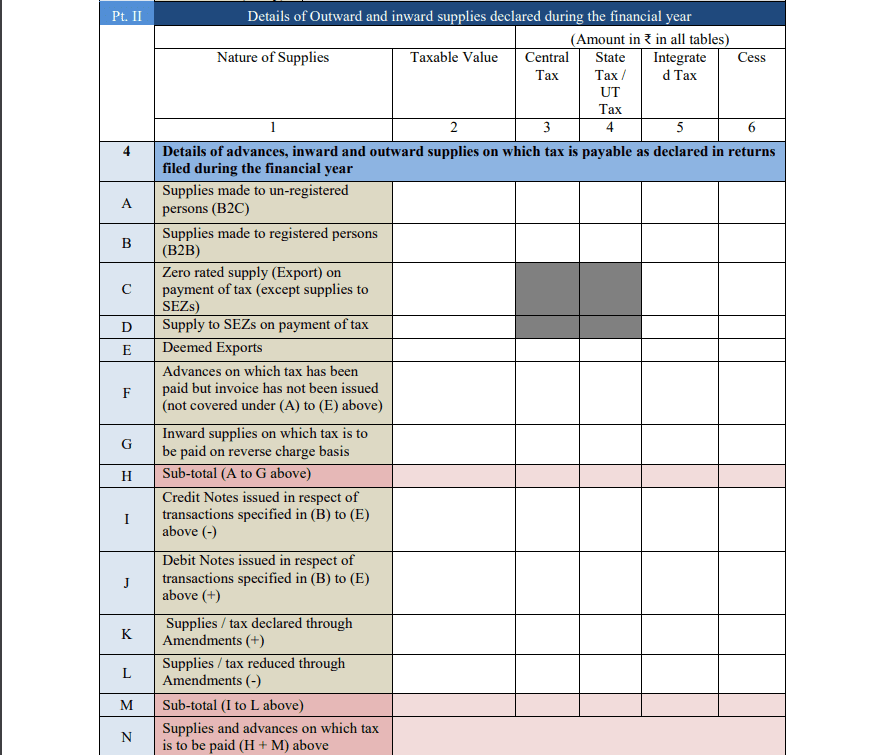
- Part II: Details of Outward and Inward Supplies
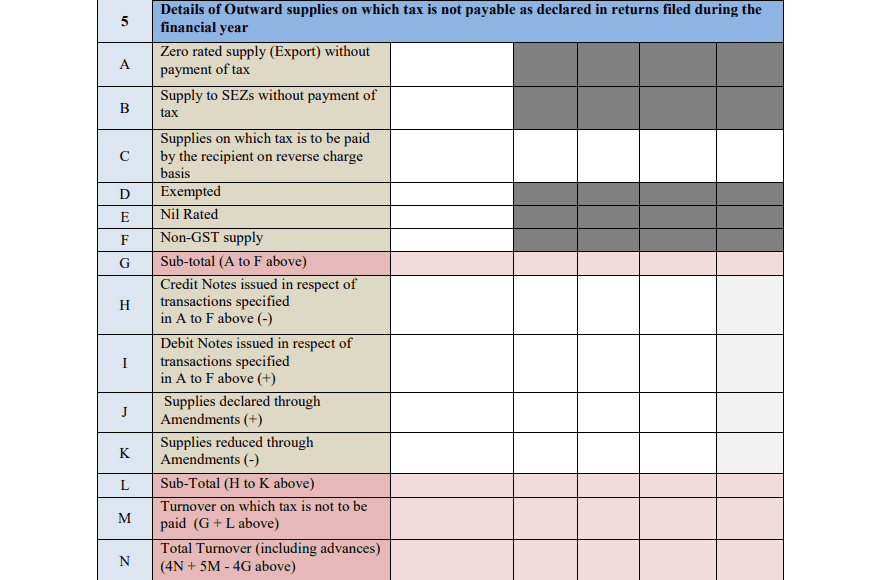
This part covers the summary of sales (outward supplies) and purchases (inward supplies) made during the year. It also includes taxable supplies, exempt supplies, and nil-rated supplies. All of these need to be correctly categorized so that the right amount of tax can be calculated.
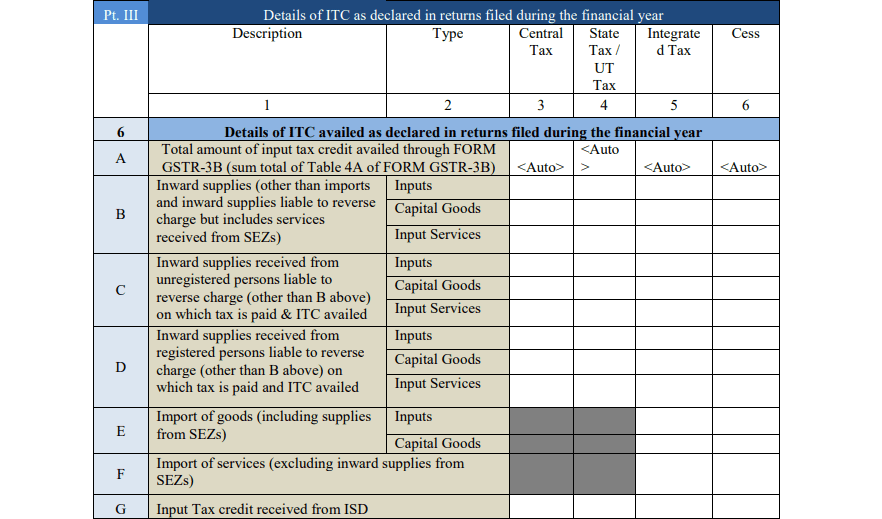
- Part III: Input Tax Credit (ITC)
This section is where taxpayers declare the Input Tax Credit (ITC) they claimed during the year. ITC is the tax paid on purchases that can be used to reduce the tax payable on sales. This section breaks down ITC into inputs (raw materials), capital goods
(machinery, equipment), and services.
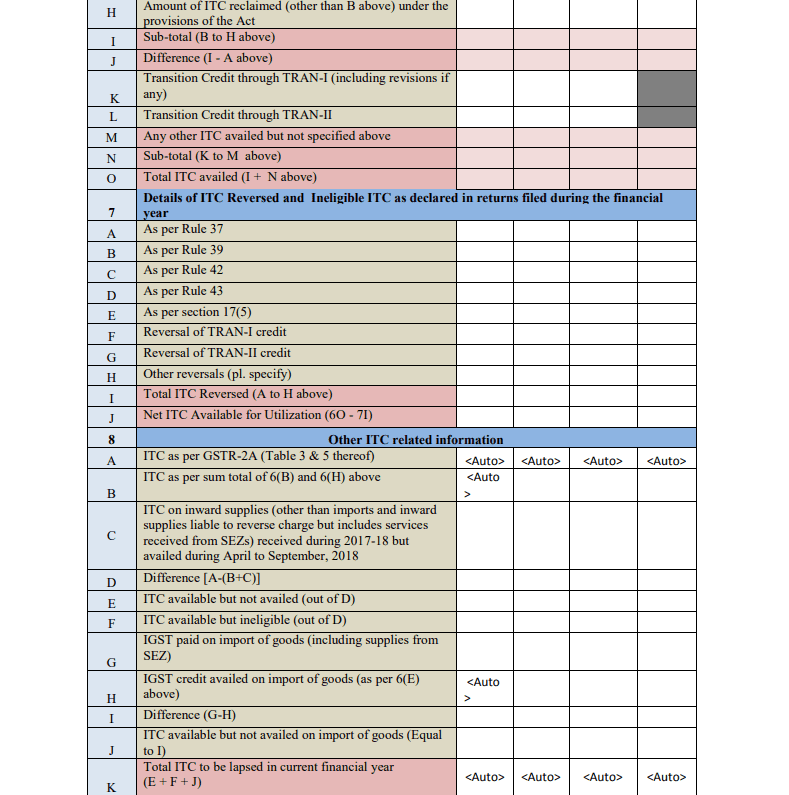
- Part IV: Tax Paid
This part summarizes all the taxes paid throughout the year, including CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess. It shows how much tax was paid through cash and how much was paid using the available ITC.
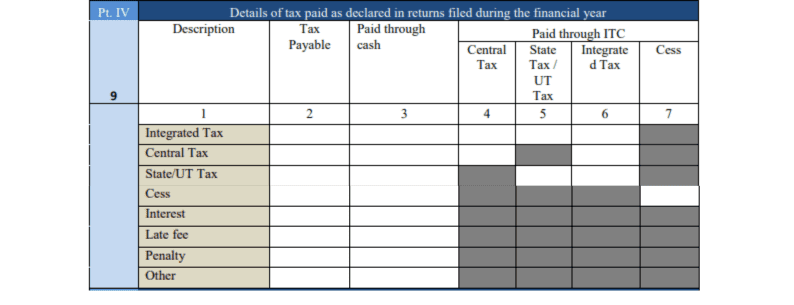
- Part V: Transactions from the Previous Period
Sometimes, businesses need to make corrections to transactions from the previous financial year that were reported in this year’s returns. This section helps to adjust such transactions.
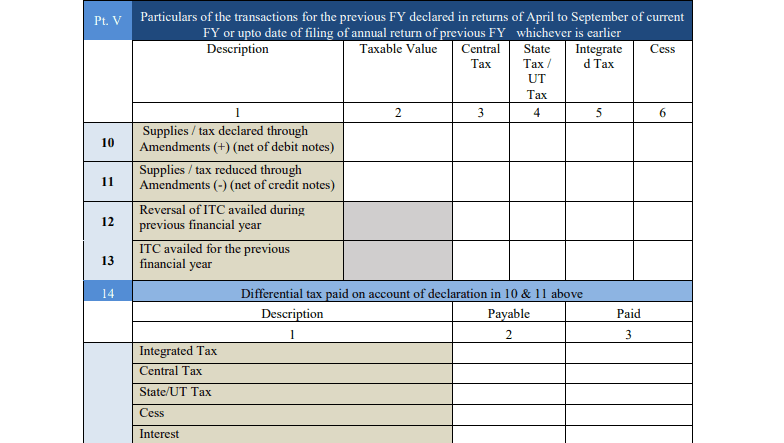
- Part VI: Other Information
This section includes miscellaneous details such as late fees, penalties, and any amendments made to earlier filed returns.
Each section of GSTR-9 helps ensure that all the business’s GST transactions for the year are accurately reported and reconciled. This detailed reporting is essential for avoiding mistakes and ensuring compliance with the GST law.
Due Date for Filing GSTR-9
The GSTR-9 form must be filed annually, and the due date is usually 31st December of the year following the financial year for which the return is being filed. For example, if you are filing for the financial year 2022-2023, the due date will be 31st December 2023.
Filing on time is crucial because failing to meet the deadline can result in late fees and penalties. These penalties are charged daily, so the longer you delay, the more you will have to pay.
While the due date is fixed, in some cases, the GST Council has extended the deadlines due to technical issues or to ease the compliance burden on taxpayers. However, it is always a good idea to file your returns as early as possible to avoid any last-minute rush or system glitches.
How to File GSTR-9? (Step-by-Step Guide)
Filing GSTR-9 is a straightforward process, but it’s important to follow each step carefully to ensure that all the details are correct. Here’s a simple guide to help you file your GSTR-9 on the GST portal:
Step 1: Log in to the GST Portal
- Go to the official GST portal (www.gst.gov.in) and log in using your GSTIN, username, and password.
- Once logged in, go to the ‘Returns Dashboard’ and select the financial year for which you are filing the return.
- Under the ‘Annual Return’ section, choose GSTR-9.
Step 3: Download Auto-Populated GSTR-9 Form
- The system will auto-populate certain details from your previously filed GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and other returns. Download the form to review the details.
Step 4: Enter Additional Details
- After reviewing the auto-filled details, fill in the missing or additional information such as:
- Details of sales (outward supplies) and purchases (inward supplies).
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) claimed during the year.
- Taxes paid under CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess.
Step 5: Review and Reconcile
- Before filing, cross-check all the entries in the GSTR-9 form with your monthly or quarterly returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B). Ensure that there are no discrepancies.
- You can use reconciliation tools or GST software to help identify any mismatches.
Step 6: Submit the Form
- After reviewing all details, click on ‘Compute Liabilities’ to calculate any tax dues.
- If there are any additional taxes to be paid, make the payment before submitting.
- Once you’re satisfied with the form, click on ‘Submit’ to file your GSTR-9.
Step 7: Download Filed GSTR-9
- After submission, download the filed GSTR-9 for your records. It’s essential to keep this as part of your tax documentation.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your GSTR-9 is filed correctly and on time. Filing the form accurately also helps in preventing future complications during GST audits or inspections.
Penalties for Late Filing of GSTR-9
Filing GSTR-9 on time is essential to avoid penalties and late fees. Here’s what happens if you miss the deadline:
Late Filing Fee
- If you do not file GSTR-9 by the due date, you will be charged a late fee. This fee is Rs. 200 per day (Rs. 100 for CGST and Rs. 100 for SGST) until the return is filed.
- There is no late fee for IGST returns, but the total penalty can accumulate up to 0.25% of your annual turnover in the respective state or union territory.
Interest on Outstanding Tax
- If you have any unpaid taxes at the time of filing GSTR-9, you will also be charged interest on the outstanding amount. The interest rate is 18% per annum and is calculated from the date the tax was due until the date of payment.
Impact on Future Filings
- Late filing of GSTR-9 can also affect your ability to file other returns. If GSTR-9 is not filed, you may face difficulties in claiming Input Tax Credit (ITC) in the future, and your compliance status could be affected, making it difficult to conduct business smoothly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing GSTR-9
Filing GSTR-9 requires careful attention to detail, and it’s easy to make mistakes if you’re not thorough. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
1. Incorrect Reporting of Input Tax Credit (ITC)
- One of the most frequent mistakes is inaccurately reporting the ITC. Ensure that the ITC you claim in GSTR-9 matches the ITC you claimed in your monthly or quarterly returns. Overclaiming or underclaiming ITC can lead to issues during audits and may result in penalties.
2. Mismatch with GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B
- GSTR-9 must be a summary of the returns you filed in GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B. Many taxpayers make the mistake of not reconciling these forms, which can lead to discrepancies. Always cross-check and ensure that the sales and purchases reported in GSTR-9 match the data in GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B.
3. Missing Out on Amendments
- If you’ve made any amendments to your returns during the year (such as corrections to GSTR-1 or GSTR-3B), ensure these are correctly reflected in GSTR-9. Forgetting to include amendments can result in inaccurate reporting.
4. Inaccurate Declaration of Tax Payments
- Ensure that the taxes paid, whether through cash or ITC, are correctly declared. Misreporting the amount of tax paid can lead to confusion and delays in reconciliation during audits.
5. Not Filing Even if There Are No Transactions
- Some businesses believe they don’t need to file GSTR-9 if they haven’t conducted any business during the year. However, nil returns are still required, even if no transactions took place. Failing to file a nil return will attract penalties.
6. Incorrectly Categorizing Transactions
- Transactions need to be categorized accurately as taxable, exempt, or nil-rated. Incorrect categorization can result in miscalculating the tax liability, which could later lead to additional payments or penalties.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your GSTR-9 is filed correctly and avoid potential fines, audits, or delays. Double-checking all details and using reconciliation tools can go a long way in ensuring smooth filing.
Challenges Faced During GSTR-9 Filing
While filing GSTR-9, many businesses face various challenges that can complicate the process. Here are some common difficulties and how to address them:
1. Data Reconciliation Issues
- One of the biggest challenges is reconciling data between GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-2A. Businesses often find differences between their sales data, purchase data, and ITC claims. This happens because of errors in monthly returns or delays in receiving invoices from vendors. To avoid this, it’s important to regularly reconcile your returns throughout the year, instead of waiting until the annual filing.
2. Technical Glitches on the GST Portal
- During peak filing periods, such as in December when GSTR-9 is due, the GST portal often experiences heavy traffic, leading to slow loading times and occasional errors in submissions. This can cause delays and last-minute stress. Filing early and avoiding the last-minute rush can help reduce the impact of such technical issues.
3. Lack of Proper Documentation
- Many businesses struggle with maintaining accurate records of all their sales, purchases, and tax payments throughout the year. Without proper documentation, it becomes difficult to complete GSTR-9 accurately. To overcome this challenge, businesses should adopt GST-compliant accounting software or maintain organized financial records, ensuring that all transactions are documented correctly.
4. Understanding Complex ITC Clauses
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) rules can sometimes be complicated, especially when dealing with reversals, ineligible credits, or supplies that are partially taxable and partially exempt. Misunderstanding these rules may lead to under or over-claiming ITC. Businesses should consult with a tax professional if they’re unsure about how to handle ITC in their GSTR-9.
5. Errors in Filing Amendments
- Amendments made in earlier returns throughout the year must be carefully reported in GSTR-9. Businesses sometimes overlook these corrections or report them incorrectly, leading to inaccurate filings. Proper tracking of amendments is essential to avoid errors.
By being aware of these challenges and preparing ahead of time, businesses can avoid many common issues and ensure a smoother filing process for GSTR-9.
Tips for Smooth GSTR-9 Filing
To avoid common mistakes and challenges while filing GSTR-9, here are some useful tips to ensure a smooth and hassle-free process:
1. Maintain Accurate Records Throughout the Year
- One of the most important tips is to keep your records accurate and up-to-date throughout the year. This includes tracking all sales, purchases, and taxes paid on a regular basis. Having well-organized financial records will make it easier to file GSTR-9 without errors or last-minute confusion.
2. Reconcile Your Data Regularly
- Instead of waiting until the end of the financial year to reconcile your returns, do it periodically. Make sure the details in your GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-2A match each other, and resolve any discrepancies immediately. Regular reconciliation will reduce the chances of errors when you’re ready to file GSTR-9.
3. Use GST-Compliant Software
- Using software that is specifically designed for GST compliance can help you track transactions, file returns, and reconcile data seamlessly. GST software can automatically pull data from your monthly returns, making the GSTR-9 filing process much easier and reducing manual errors.
4. Seek Professional Help
- If your business has complex transactions or if you are unsure about any part of the filing process, consider seeking help from a Chartered Accountant (CA) or GST professional. They can ensure that your returns are accurate, help you avoid mistakes, and guide you through reconciliation and ITC claims.
5. File Early to Avoid Technical Glitches
- Many taxpayers wait until the last minute to file their GSTR-9, which can lead to delays and frustration due to technical glitches on the GST portal. Filing your returns early ensures that you avoid peak traffic periods and gives you enough time to fix any issues that may arise during submission.
6. Review and Double-Check Your Data
- Before submitting your GSTR-9, review all the information thoroughly. Double-check the figures for sales, purchases, tax payments, and ITC claimed to ensure they match your monthly or quarterly returns. Any errors left unchecked could result in penalties or tax liabilities later.
By following these tips, businesses can ensure a smoother, more efficient filing process and minimize the risks of errors or delays. Proper preparation, regular reconciliation, and early filing are key to successful GSTR-9 compliance.
What if there’s a mismatch between GSTR-3B and GSTR-9?
If there’s a mismatch between GSTR-3B and GSTR-9, it’s important to identify the reasons for the discrepancy and take corrective steps:
- Identify the Mismatch: First, check where the differences are occurring—typically in output tax, input tax credit (ITC), or turnover. Review the returns filed for each month in GSTR-3B against the consolidated details in GSTR-9.
- Compare Key Figures: Make a detailed comparison of total turnover, tax liability, ITC claimed, and tax payments in both forms. This step helps you spot specific errors or omissions.
- Analyze Tax Liability and ITC: Differences often arise from incorrect ITC claims or tax liabilities. Ensure that ITC claims are valid and that all tax liabilities are accurately reported.
- Adjust in GSTR-9 or 9C: If you discover that errors are due to under-reporting or over-reporting in GSTR-3B, you may need to make adjustments while filing GSTR-9. Note that GSTR-9 allows you to report additional liabilities, which should be paid with interest (if applicable).
- Report Additional Liability: Any additional tax liability identified in GSTR-9 should be settled through the DRC-03 form. Ensure all dues are cleared before submission to avoid penalties.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: For complex mismatches, it’s advisable to consult a tax professional to ensure compliance with GST laws and avoid penalties.
Timely rectification of these mismatches can help maintain compliance and reduce the risk of penalties or future audits.
Impact of GSTR-9 on ITC Reconciliation
Filing GSTR-9 plays an essential role in reconciling your Input Tax Credit (ITC) for the financial year. ITC is the tax credit that businesses can claim on the purchases they made, and it helps reduce the overall GST liability. Here’s how GSTR-9 impacts ITC reconciliation:
1. Finalization of ITC for the Year
- GSTR-9 provides a complete summary of the ITC claimed throughout the financial year. It gives businesses a final opportunity to ensure that all eligible ITC has been claimed and that any discrepancies in monthly returns have been resolved.
2. Matching with GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B
- The ITC details reported in GSTR-9 need to match the auto-generated GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B forms, which show the ITC available based on supplier filings. If there’s a mismatch between what you’ve claimed and what is reflected in GSTR-2A or GSTR-2B, it could affect your ability to claim the credit.
3. Reversal of Ineligible ITC
- GSTR-9 requires businesses to reverse any ineligible ITC that was claimed during the year. This could happen if ITC was claimed for goods or services that are not eligible under GST rules. It’s important to ensure that any ineligible credits are identified and reversed to avoid penalties.
4. Correction of ITC Errors
- If you discover any mistakes in the ITC claimed during the year, such as missing credits or incorrect amounts, GSTR-9 provides an opportunity to correct these errors. However, the corrections must be made in subsequent returns (GSTR-3B) since GSTR-9 cannot be revised once filed.
5. Role of GSTR-9C in Auditing ITC Claims
- For businesses with an annual turnover exceeding a certain limit, GSTR-9C (the audit and reconciliation statement) must also be filed. This form ensures that ITC claims reported in GSTR-9 match with the audited financial statements. Any discrepancies between the returns and the audit must be explained and corrected.
Accurate ITC reconciliation through GSTR-9 is crucial because it directly affects your tax liabilities. By carefully reviewing your ITC claims and matching them with GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B, you can ensure that all eligible credits are correctly utilized and any errors are corrected in time.
Conclusion
Filing GSTR-9 is a crucial part of complying with the GST regulations for businesses in India. It serves as a summary of all your yearly transactions, including sales, purchases, tax payments, and Input Tax Credit (ITC) claims. Ensuring that the form is filled out accurately and on time is vital for avoiding penalties and maintaining smooth business operations.
Here are some key takeaways:
– GSTR-9 helps finalize your tax position for the financial year by summarizing monthly and quarterly returns (GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B).
– Regular reconciliation of data throughout the year will help reduce errors and ensure that your ITC claims are accurate.
– Avoid common mistakes like incorrect ITC claims, mismatches with previous returns, and missing amendments to ensure smooth filing.
– Filing the return on time will help you avoid penalties and late fees, and will ensure you stay compliant with GST regulations.
If your business has complex transactions or large turnovers, seeking professional help or using GST-compliant software can simplify the filing process.
In conclusion, filing GSTR-9 on time and with accurate data ensures you stay compliant with GST laws and avoid future tax-related complications. Take the time to review your records carefully, reconcile any discrepancies, and file early to prevent last-minute issues.
FAQs about GSTR-9
To clear any common doubts, here are some frequently asked questions about GSTR-9:
1. What happens if I miss the deadline for filing GSTR-9?
- If you miss the GSTR-9 filing deadline, you will be liable to pay a late fee of Rs. 200 per day (Rs. 100 for CGST and Rs. 100 for SGST). This fee will continue to accrue until the return is filed, with a maximum cap of 0.25% of your annual turnover. Interest may also be charged on any unpaid taxes.
2. Can I revise GSTR-9 after filing?
- No, GSTR-9 cannot be revised once it has been filed. This is why it is important to review all details carefully before submitting the form. If any corrections are needed, they must be reflected in the monthly or quarterly returns for the following financial year.
3. Do I need to file GSTR-9 if my business had no transactions during the year?
- Yes, even if your business had no transactions during the financial year, you are still required to file a nil return for GSTR-9. Not filing will result in penalties.
4. What is the difference between GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C?
- GSTR-9 is the annual GST return required for all regular taxpayers, mandatory for those with a turnover over Rs. 2 crore. GSTR-9C is a reconciliation statement between GSTR-9 and audited financials, applicable to taxpayers with a turnover above Rs. 5 crore. While GSTR-9 needs no certification, GSTR-9C required CA/CMA certification until FY 2020-21, after which self-certification suffices. Both forms are due by 31st December of the following financial year.
5. Can I claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) after filing GSTR-9?
- Once GSTR-9 is filed, you cannot claim any new ITC for the financial year you are filing for. Therefore, it’s important to ensure all eligible ITC is claimed and reconciled before filing the return. If you miss out, you may be able to claim ITC in subsequent returns, but only for eligible credits related to the next financial year.
6. What should I do if there’s a mismatch between GSTR-3B and GSTR-9?
- If there’s a mismatch between your monthly or quarterly return (GSTR-3B) and the annual return (GSTR-9), you must reconcile and correct the errors in your GSTR-9 before filing. Any additional tax liabilities found should be paid before submission.
These FAQs should help address the most common questions and concerns about filing GSTR-9, making the process smoother and easier to understand.


















