GSTR 9A is an annual return form that taxpayers under the GST Composition Scheme must file. It serves as a comprehensive summary of the quarterly returns filed throughout the financial year, consolidating key information like outward and inward supplies, tax liability, and payment details.
For businesses that opted for the Composition Scheme, GSTR-9A holds significant importance as it ensures compliance with GST regulations and provides a complete picture of their annual financial activity under GST. Filing this return accurately helps avoid penalties and ensures proper tax reporting, which is crucial for future assessments or audits.
The objective of this blog is to break down GSTR-9A into simple, understandable terms so that even those unfamiliar with GST processes can grasp the key aspects of this annual return and file it with ease. Let’s dive into everything you need to know about GSTR-9A.
What is GSTR-9A?
GSTR-9A is the annual return that taxpayers registered under the GST Composition Scheme are required to file. It is a consolidated form that summarizes all the quarterly returns (GSTR-4) submitted during the financial year. This return captures crucial details such as outward and inward supplies, tax liability, and taxes paid throughout the year. Essentially, it gives the government a comprehensive view of a composition taxpayer’s activity in a given financial year.
Why is GSTR-9A a part of the annual return filing under GST?
GSTR-9A serves as a critical document to ensure that taxpayers under the Composition Scheme adhere to GST regulations. While quarterly returns offer insights into business activities for specific periods, the annual return consolidates these activities, providing a full-year overview. Filing GSTR-9A ensures that there are no discrepancies between the quarterly returns and overall tax liability. It also serves as a compliance checkpoint for authorities to review the accuracy of returns and taxes paid.
Who Needs to File GSTR-9A?
Eligibility Criteria for Filing GSTR-9A
GSTR-9A is mandatory for businesses that have registered under the GST Composition Scheme. This scheme is designed for small taxpayers with a turnover of up to ₹1.5 crore, allowing them to pay a fixed percentage of their turnover as tax instead of following the regular GST rates. These businesses are required to file GSTR-9A annually, consolidating their quarterly GSTR-4 returns.
Taxpayers Under the Composition Scheme
The Composition Scheme is an option under GST that simplifies tax compliance for small businesses by reducing their tax liability and allowing them to file less frequent returns. The eligible taxpayers include:
- Small traders
- Manufacturers
- Restaurants not serving alcohol
- Service providers (with certain conditions)
These businesses can enjoy a lower tax rate and simplified tax procedures but are restricted from collecting tax from customers or claiming input tax credit (ITC). Since these taxpayers file GSTR-4 quarterly, they need to file GSTR-9A at the end of the financial year as a comprehensive summary.
Scenarios Where GSTR-9A is Applicable
GSTR-9A must be filed by all businesses who:
- Have been registered under the GST Composition Scheme at any point during the financial year.
- Even if the taxpayer opted out of the Composition Scheme midway through the year, they still need to file GSTR-9A for the period they were under the scheme.
- Businesses that have canceled their GST registration during the financial year but were registered under the Composition Scheme before cancellation are also required to file GSTR-9A.
In summary, GSTR-9A is applicable to any taxpayer who has availed the benefits of the Composition Scheme at any time during a given financial year.
Key Details Required for GSTR-9A Filing
When filing GSTR-9A, taxpayers need to consolidate key data from their quarterly returns (GSTR-4) and other relevant financial records to ensure accurate and compliant reporting. Below are the essential details required for GSTR-9A filing:
Part 1: Basic Details Provide basic details such as GSTIN, legal name, and trade name. Your financial year, GST registration number, and the period of your composition scheme enrollment will also be included.
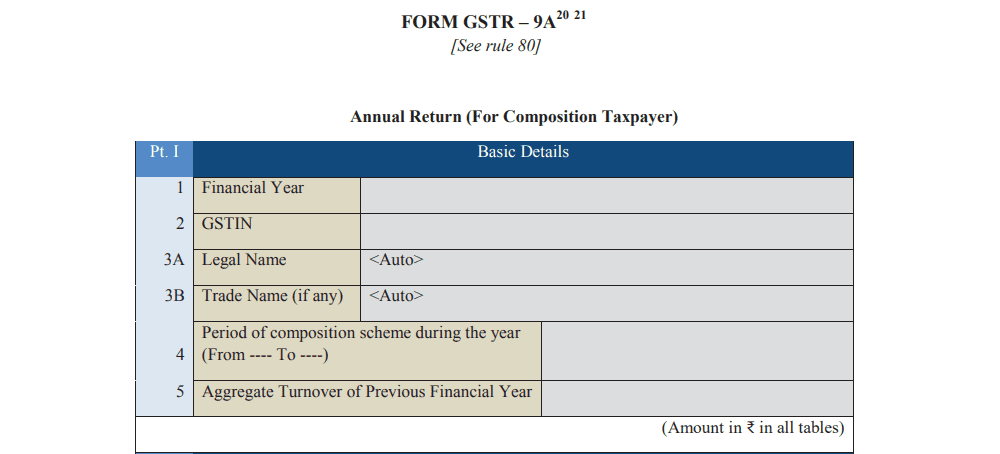
Part 2: Sales and Purchases Summary Enter details of all sales and purchases declared in your GSTR-4 returns. This includes taxable sales, inward supplies under reverse charge, and import of services or goods.
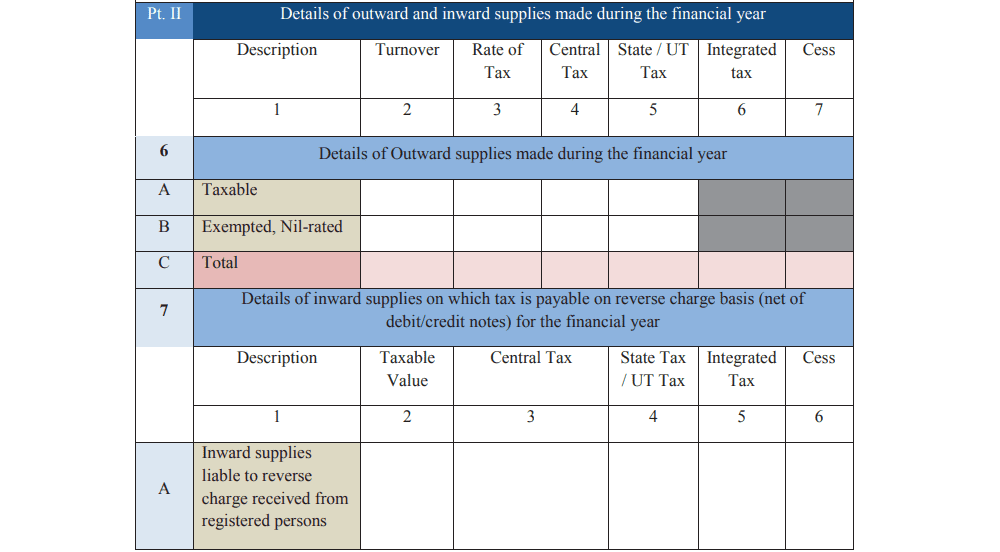
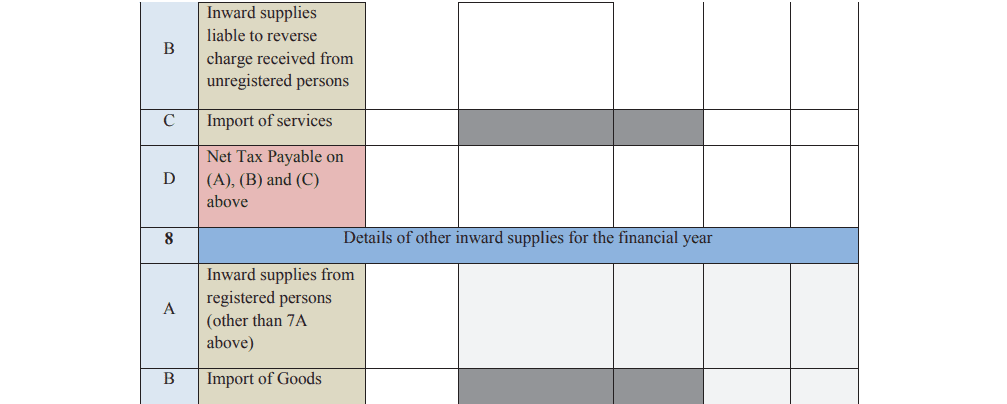
Part 3: Tax Paid Declare the tax paid during the financial year, split into categories like central, state, and integrated tax, as well as cess and penalties.
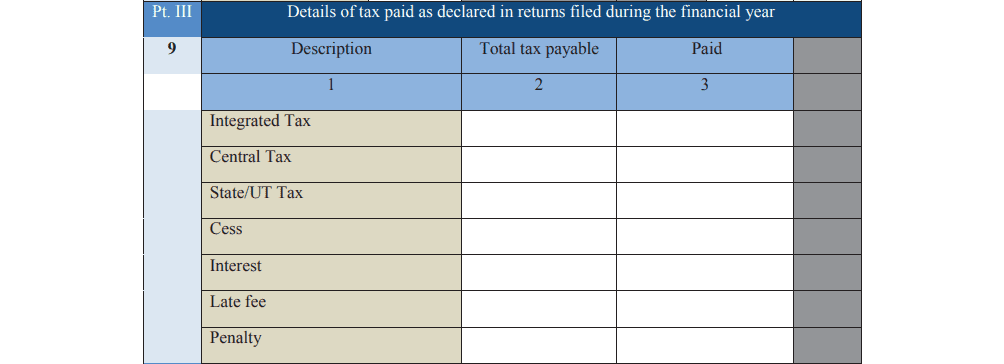
Part 4: Amendments Include any changes or corrections made to your returns, such as additional tax declared or adjustments made through debit and credit notes.
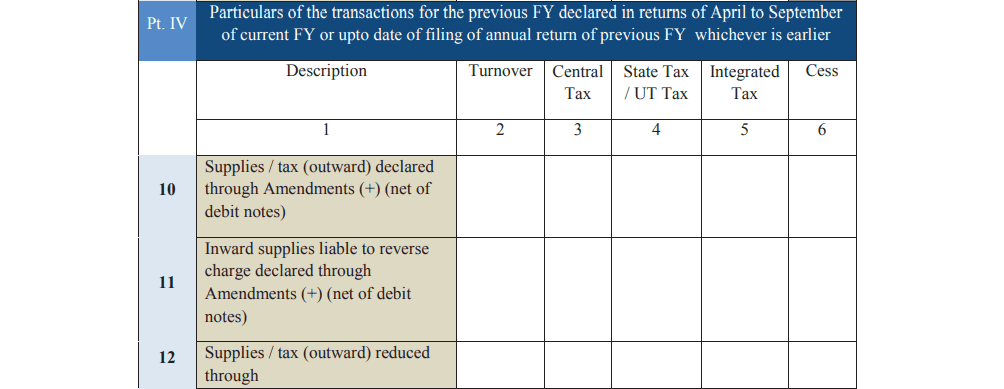
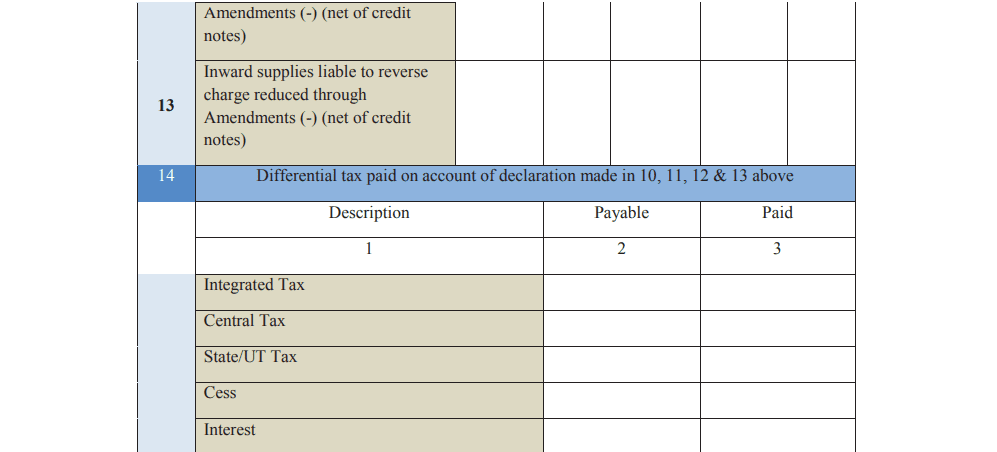
Part 5: Other Details Mention any refunds, credits, or late fees applicable during the year.
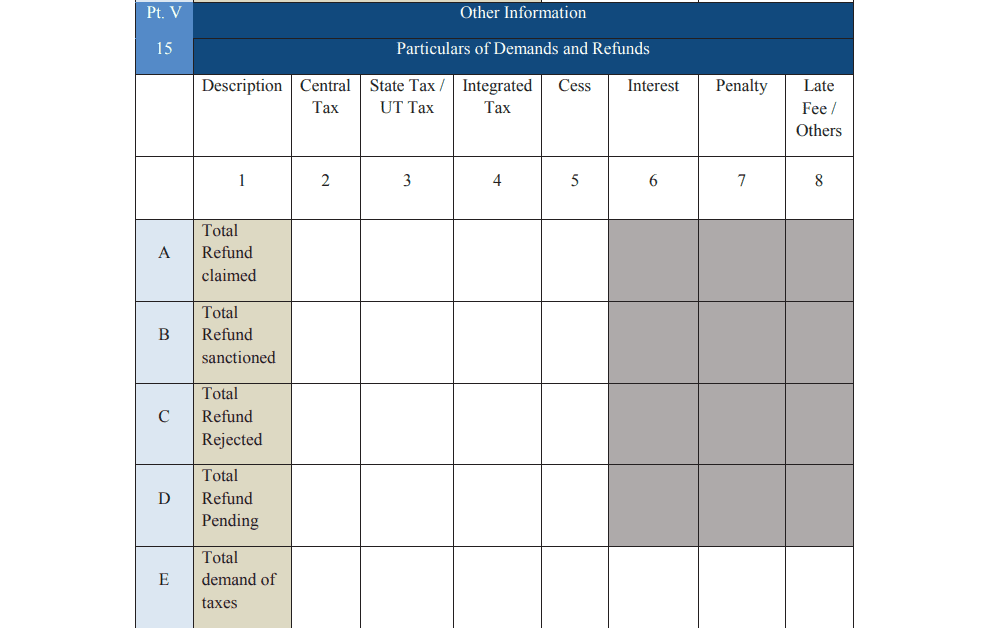
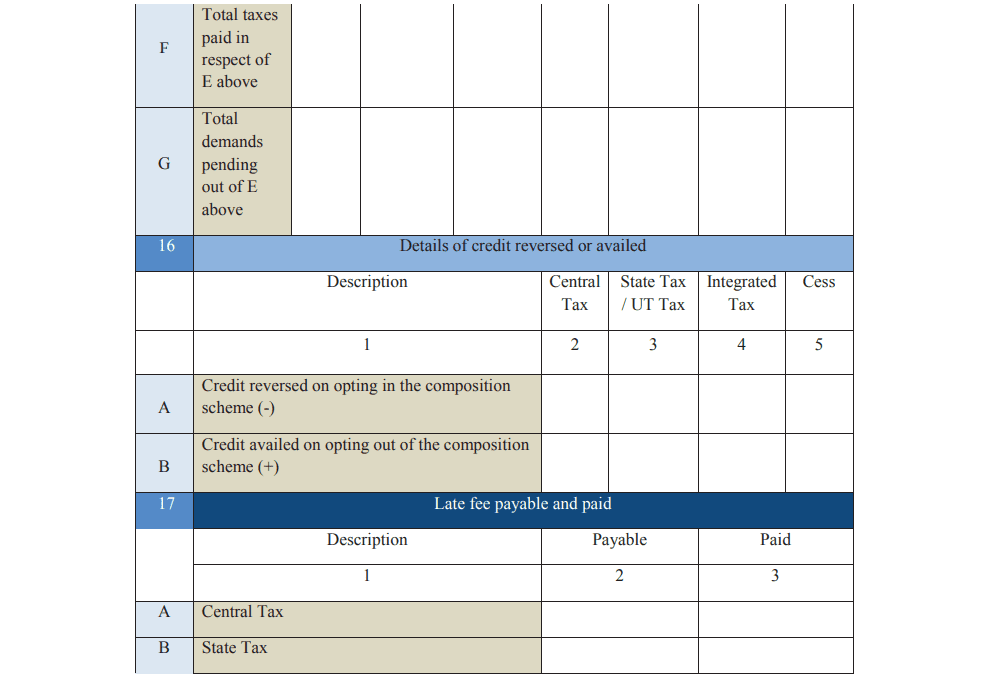
Declaration The form must be signed and verified using a digital signature certificate or an Aadhaar-based e-signature.
Due Dates for Filing GSTR-9A
1. Deadline for Filing
The due date for filing GSTR-9A is 31st December of the year following the financial year. For example, for the financial year 2023-2024, the last date to file GSTR-9A would be 31st December 2024. Taxpayers must ensure that they submit the return by this deadline to avoid late fees or penalties.
2. Importance of Timely Filing to Avoid Penalties
Filing GSTR-9A on time is crucial for several reasons:
- Avoiding Late Fees: A delay in filing GSTR-9A results in a late fee of ₹200 per day (₹100 for CGST and ₹100 for SGST) until the return is filed. The maximum penalty can be up to 0.5% of the taxpayer’s turnover in the relevant state or union territory.
- Compliance Rating: Timely filing contributes to the taxpayer’s GST compliance rating. A low rating can have negative consequences, such as increased scrutiny by tax authorities or difficulties in claiming refunds.
- Avoiding Further Legal Action: Consistent non-filing or late filing may attract further notices or actions from GST authorities, leading to more severe penalties or audits.
3. Process for Extension (if applicable)
In certain exceptional cases, the government may announce an extension of the due date for filing GSTR-9A. Taxpayers can check official notifications on the GST portal or through their tax consultants to stay updated on any extensions granted.
If no extension is provided and the taxpayer is unable to file by the deadline, they should ensure that the return is filed as soon as possible to minimize the late fee accrual. However, as of now, there is no individual request mechanism for extending the filing date on a case-by-case basis.
Timely filing of GSTR-9A ensures businesses maintain compliance and avoid the burden of additional fees or complications with the GST authorities.
Step-by-Step Guide to File GSTR-9A
Filing GSTR-9A is a straightforward process, provided you follow the steps correctly on the GST portal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you complete the filing efficiently:
1. Logging into the GST Portal
- Visit the official GST portal: www.gst.gov.in.
- Enter your valid username and password to log in.
- If you haven’t registered on the portal, you need to create an account by following the registration process.
2. Navigating to the GSTR-9A Form
- Once logged in, go to the ‘Services’ tab in the menu.
- Under the ‘Returns’ section, select ‘Annual Return’.
- You will see a list of available returns. Choose GSTR-9A for the relevant financial year.
3. Filling in the Relevant Details
- Auto-Populated Data: Some details, such as turnover and tax payment, will be auto-populated from the quarterly GSTR-4 returns filed during the financial year. Verify these details for accuracy.
- Supply Details: Enter any missing information related to outward and inward supplies, tax paid under different heads (CGST, SGST, IGST, Cess), and any demands or refunds during the year.
- Late Fees (if applicable): If you are filing after the due date, the portal will automatically calculate the late fees applicable, which you will need to pay before submitting the return.
4. Submitting the Form and Making Payment (if Required)
- After completing all sections, click on the ‘Preview’ button to review your form before submission. Make sure all the details are correct.
- Once you’ve confirmed everything is accurate, click ‘Proceed to File’.
- If any payment is required (such as late fees), you’ll be prompted to make the payment through the available online payment options (Net Banking, Credit/Debit Card, etc.).
- After successful payment (if applicable), the form will be submitted.
5. Downloading the Filed Return for Future Reference
- Once the GSTR-9A form is submitted, a confirmation message will appear on the screen.
- Download a copy of the filed return for your records. You can do this by clicking on the ‘Download Filed Return’ option on the portal.
- It is advisable to keep a copy of the filed return for future reference, audits, or compliance verification by tax authorities.
By following these steps, you can complete your GSTR-9A filing accurately and efficiently, ensuring compliance with GST regulations.
Late Fees and Penalties for GSTR-9A
Filing GSTR-9A after the due date can lead to financial penalties, which are levied on a per-day basis. Here’s what you need to know about the late fees and other consequences of missing the filing deadline:
1. Penalty for Late Filing (Per Day Basis)
If you fail to file GSTR-9A by the due date (typically 31st December of the following financial year), you will be charged a late fee. The late fee is calculated as follows:
- ₹200 per day (₹100 for CGST + ₹100 for SGST/UTGST).
- No late fee is applicable for IGST in case of delayed filing.
The late fee continues to accumulate until the return is filed.
2. Maximum Penalty Limits
To ensure that the late fees are not excessively burdensome, the government has set a maximum limit for the penalty:
- The total late fee cannot exceed 0.5% of the taxpayer’s turnover in the relevant state or union territory (0.25% CGST + 0.25% SGST).
This cap ensures that the penalty remains proportionate to the business’s size and operations.
3. Other Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Impact on Compliance Rating: Late filing or failure to file GSTR-9A can negatively impact your GST compliance rating. A poor compliance rating may result in increased scrutiny from tax authorities and may create challenges during audits or in claiming refunds.
- Legal Notices: Continuous failure to file GSTR-9A may result in the issuance of notices by GST authorities, which could lead to audits or assessments.
- Restrictions on Input Tax Credit (ITC): Inconsistent or delayed filing could result in issues related to Input Tax Credit (ITC) claims, making it harder for taxpayers to settle claims smoothly.
- Difficulty in Future Transactions: Non-compliance with GST return filing can lead to complications when trying to register for or cancel GST registration, file other returns, or process tax-related documents.
In summary, filing GSTR-9A on time not only helps avoid late fees but also ensures a good compliance rating and smoother tax processes in the future.
Amendments or Revisions in GSTR-9A
1. Can GSTR-9A be Revised After Filing?
Unfortunately, once GSTR-9A is filed, it cannot be revised. The GST system does not allow for any corrections or amendments after submission. Therefore, it is crucial to review all details thoroughly before filing the return to avoid errors or discrepancies.
If mistakes are identified after filing, they cannot be directly corrected in the same return. However, there are alternative ways to handle such issues, depending on the nature of the error.
2. How to Rectify Errors or Omissions in Filed GSTR-9A
If you realize that you’ve made an error or omission in your GSTR-9A, here are a few options to rectify the situation:
- Corrections in Subsequent Returns: If the mistake pertains to the current financial year, the corrections can be made in the next quarterly or annual return of the subsequent financial year. However, this option is not applicable for all errors, such as tax underpayment or misreported turnover.
- Consult with Tax Authorities: In case of significant errors, it is advisable to consult with a tax professional or reach out to the GST authorities. They may guide you on the next steps or any actions to take, depending on the error’s nature and implications.
- Pay Additional Tax with Interest (if applicable): If the error results in tax underpayment, you may need to pay the difference along with applicable interest. This can be done through the GST portal’s payment option, ensuring compliance despite the error.
- Use the GST Audit Process: In cases where errors or discrepancies are detected during a GST audit, the corrections may be noted in the audit process, and any tax liabilities, along with penalties, can be settled accordingly.
Since GSTR-9A does not allow amendments, double-checking all the figures and details before filing is essential. Taking extra care during the preparation and review process can help avoid the need for future corrections.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Filing GSTR-9A
Filing GSTR-9A requires attention to detail, as even small errors can lead to discrepancies, penalties, or complications later on. Here are some common mistakes taxpayers should avoid while filing GSTR-9A:
1. Mismatch of Data with GSTR-4
One of the most common errors in GSTR-9A filing is a mismatch between the data reported in the quarterly GSTR-4 returns and the annual GSTR-9A return. Since GSTR-9A consolidates the quarterly data, any discrepancies can raise red flags. Ensure that:
- The sales and purchase figures match the data reported in GSTR-4.
- The tax paid under various heads (CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess) aligns with the quarterly returns.
- Any amendments made during the year are accurately reflected in the annual return.
Double-checking the data from GSTR-4 before filing GSTR-9A helps avoid these mismatches.
2. Incorrect Tax Details or Claims
Another common mistake is entering incorrect tax amounts or making wrong claims. This can happen when:
- There is an error in reporting the tax liability, such as under-reporting or over-reporting the amount of tax paid.
- Incorrect tax rates or classification of supplies are applied.
- Tax deductions or exemptions are wrongly claimed, leading to discrepancies in total taxable turnover.
Always ensure that tax details are accurate, and cross-verify them with your business records and quarterly filings before final submission.
3. Ignoring the Section on Demand and Refund
Taxpayers often overlook or incorrectly fill in the section that asks for details on tax demands and refunds. This section requires accurate reporting of:
- Any outstanding tax demands raised by the authorities during the year.
- Refunds received due to excess tax paid, either during quarterly returns or through adjustments made later.
Filing incorrect details in this section can lead to compliance issues or delay future refund claims. It’s important to keep track of any demands or refunds issued by the GST authorities and report them accurately in GSTR-9A.
By avoiding these common mistakes and ensuring accuracy in the return, taxpayers can prevent issues with their filings and maintain smooth GST compliance.
Importance of Accurate Filing
Filing GSTR-9A accurately is crucial not only for meeting legal obligations but also for ensuring long-term business compliance under GST. Here’s why accurate filing is essential:
1. Impact of GSTR-9A on the GST Compliance Rating
The GST compliance rating is an important measure used by tax authorities to assess a taxpayer’s adherence to GST regulations. Timely and accurate filing of GSTR-9A contributes positively to this rating. A higher compliance rating brings several advantages, including:
- Reduced scrutiny: Businesses with a good compliance rating are less likely to be audited or subjected to detailed investigations by GST authorities.
- Faster refunds and smoother processes: A high rating can expedite the processing of refunds and facilitate easier tax compliance in the future.
- Positive reputation: Having a good compliance record reflects well on the business, fostering trust with both tax authorities and potential clients.
Filing GSTR-9A correctly is key to maintaining a high GST compliance rating.
2. Ensuring No Discrepancies for Smooth Audits
Accurate filing ensures that the data reported in GSTR-9A matches your quarterly GSTR-4 returns and other financial records. When there are no discrepancies:
- GST audits can be completed smoothly without raising additional concerns or queries from tax authorities.
- Accurate filings prevent penalties and assessments due to mismatches in reported turnover, tax paid, or claims made.
- The business is less likely to face legal notices, delayed processes, or further investigations due to filing errors.
Ensuring consistency in data across all returns not only helps avoid audits but also keeps your business running smoothly.
Although taxpayers under the Composition Scheme cannot claim Input Tax Credit (ITC), accurate GSTR-9A filing still impacts future transactions:
- Errors in GSTR-9A can lead to complications when a taxpayer opts out of the Composition Scheme and becomes eligible for ITC. Any past discrepancies might delay or block future ITC claims.
- Reconciliation of purchases and sales with proper tax payments ensures that there are no outstanding tax liabilities that could affect ITC calculations in future filings.
- Accurate filing prevents disputes or rejection of claims by the authorities if the business transitions from the Composition Scheme to a regular taxpayer scheme.
By filing GSTR-9A correctly, taxpayers can prevent future compliance issues, ensuring smooth GST operations and a hassle-free tax experience.
Exemptions from Filing GSTR-9A
While GSTR-9A is mandatory for most taxpayers under the GST Composition Scheme, there are certain scenarios where filing GSTR-9A is not required. Understanding these exemptions can help businesses ensure they are compliant without unnecessary filings.
There are specific cases where taxpayers are exempt from filing GSTR-9A:
- Businesses Opting Out of the Composition Scheme: If a business transitions from the Composition Scheme to the regular taxpayer regime during the financial year, they are not required to file GSTR-9A for the portion of the year when they were not under the Composition Scheme. Instead, they will file GSTR-9 for the entire year, covering both their composition and regular taxpayer periods.
- GST Cancellation: Taxpayers who cancel their GST registration before the financial year-end are exempt from filing GSTR-9A. However, if the taxpayer was registered under the Composition Scheme for any portion of the year, they must still file GSTR-9A for the period they were registered.
- Turnover Below Threshold for Composition Scheme: Taxpayers whose annual turnover falls below the threshold required for GST registration (₹20 lakh for most states, ₹10 lakh for North-Eastern and certain other states) are not required to file GSTR-9A if they are not liable to register for GST in the first place.
In summary, businesses under the Composition Scheme are generally required to file GSTR-9A unless they have opted out, canceled their registration, or have turnover below the GST registration threshold. Understanding these exemptions can help businesses avoid unnecessary filings and remain compliant with GST regulations.
Difference between GSTR-9 and GSTR-9A
| Feature | GSTR-9 | GSTR-9A |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Annual return for regular taxpayers registered under GST. | Annual return for composition scheme taxpayers under GST. |
| Applicable To | Regular taxpayers who file GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-9C (if applicable). | Composition scheme taxpayers who file GSTR-4. |
| Frequency | Annually | Annually |
| Components | Consists of details of outward and inward supplies, tax paid, input tax credit (ITC), and amendments. | Consists of summarized details of turnover, tax paid, and amendments, without detailed itemization. |
| Filing Deadline | 31st December of the following financial year | 31st December of the following financial year |
| Format Complexity | More detailed and complex, requiring extensive data reconciliation. | Simpler compared to GSTR-9 with fewer sections. |
| Late Fees & Penalties | Penalty for late filing as per GST regulations | Penalty for late filing as per GST regulations |
| Amendment Capability | Amendments or corrections for previous years cannot be made in GSTR-9. | Amendments or corrections for previous years cannot be made in GSTR-9A. |
| Audit Requirement | Required for taxpayers with turnover exceeding ₹5 crore (through GSTR-9C). | No audit requirement for composition scheme taxpayers. |
Conclusion
GSTR-9A is an essential part of the GST compliance process for businesses registered under the Composition Scheme. Filing this annual return accurately consolidates your quarterly filings, provides a complete summary of your business activities for the year, and helps avoid future compliance issues. While the process may seem complex, understanding the key details, eligibility criteria, and deadlines can ensure smooth filing and prevent penalties.
Accurate and timely filing of GSTR-9A not only maintains your GST compliance rating but also helps in avoiding legal complications, audits, and potential delays in future transactions. By following the step-by-step guide and being mindful of common mistakes, taxpayers can ensure they remain compliant and free from penalties.
Ultimately, GSTR-9A is an opportunity to ensure your business has met all GST obligations for the year, giving you peace of mind as you continue operating within the GST framework.


















