Invoices are a fundamental part of every business transaction. Simply put, an invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer, outlining the goods or services provided and the payment due. They help businesses keep track of their sales, ensure payments are received on time, and provide a legal record for tax and financial purposes.
You might think all invoices are the same, but there are actually many different types. Each type serves a unique purpose and can be used depending on the situation. In this blog, we’ll explore different types of invoices, explaining when to use them, what they should include, and why they are important for keeping your business running smoothly.
Why Different Types of Invoices Matter
You might be wondering, “Why do I need so many types of invoices?” The answer is simple: different situations call for different types of invoices. Each invoice type is designed to meet specific business needs and legal requirements. Using the right one can save time, prevent mistakes, and even protect your business in case of a dispute.
Each type ensures that the proper details are included in a way that suits the transaction, whether it’s a one-time service, recurring payments, or a long-term contract. By using the correct invoice type, you can:
- Improve payment clarity: Customers will know exactly what they owe and when.
- Meet legal obligations: Some invoices are required by law to include certain details.
- Simplify accounting: Different invoice types help track income and expenses accurately for better accounting.
In short, choosing the right invoice ensures smooth transactions and protects both you and your customers.
How Invoices Benefit Businesses
Invoices do much more than just request payment—they are vital tools that help businesses stay organized and run smoothly. Here’s how:
1. Clear Record-Keeping
Invoices provide a detailed record of every sale or service provided. This helps businesses keep track of what has been sold, how much is owed, and when payments are due. Whether you’re a small business or a large corporation, having clear records is essential for managing cash flow and taxes.
2. Improved Cash Flow
Issuing invoices on time helps ensure you get paid on time. By clearly stating the payment terms (like “due in 30 days”), you set expectations for when payment should be made. This helps prevent delays and keeps your cash flow steady, so you can pay your own bills and grow your business.
3. Legal Protection
Invoices are also a legal document that protects your business. If there’s ever a dispute about a payment or transaction, an invoice serves as evidence of the terms agreed upon. It can also help with tax filing, as it clearly shows what was sold and when.
4. Professionalism
A well-written invoice enhances your business’s image. It shows customers that you are organized and professional, which builds trust and encourages prompt payment. This professionalism can lead to repeat customers and positive reviews.
5. Tax and Compliance Benefits
Invoices are key for tax purposes. Having a record of all your transactions makes it easier to file taxes, claim deductions, and stay compliant with local regulations.
In summary, invoices help with organization, cash flow, legal protection, professionalism, and tax compliance. Using the right invoice type ensures that all these benefits are maximized!
Legal Requirements for Invoices
When it comes to invoicing, there are several legal aspects to keep in mind to ensure that your invoices are compliant and protect both you and your customers. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know:
1. What Must Be Included in Every Invoice
In many countries, there are certain details that are legally required to be on every invoice you issue. These include:
- Invoice Number: A unique number for each invoice to keep things organized and trackable.
- Date of Issue: The date when the invoice is created.
- Seller’s and Buyer’s Information: Your business name, address, and contact details, as well as your customer’s.
- Description of Goods or Services: A clear description of what was sold or provided.
- Amount Due: The total amount the customer owes.
- Payment Terms: How and when the payment is expected (e.g., within 30 days, late fees apply, etc).
- Tax Information: If applicable, include VAT or sales tax and your tax identification number.
2. Country-Specific Regulations
Different countries have different invoicing rules. For example:
- In the European Union, invoices for businesses must include VAT details if the business is VAT-registered.
- In the United States, certain states have specific sales tax regulations that require businesses to show taxes separately on invoices.
3. Digital Invoices and E-Invoicing
Many countries are moving toward digital invoicing and e-invoicing systems, especially for businesses dealing with larger transactions or international sales. Some regions may even require invoices to be submitted electronically, particularly for government contracts. By automating invoicing, these systems streamline the process, ensuring compliance and minimizing human error.
4. Retention of Records
Legally, businesses are required to keep copies of invoices for a certain period (typically 5-7 years, depending on local regulations). This is important for accounting purposes and in case of audits or disputes.
5. Penalties for Non-Compliance
If you fail to include the required information or follow local invoicing rules, you could face fines or penalties. Ensuring your invoices are legally sound is crucial to avoiding these risks.
In short, understanding and following the legal requirements for invoices can save your business from potential headaches and ensure smooth, compliant operations.
Types of Invoices
Commercial Invoice
Definition:
A commercial invoice is a document used in sales transactions to provide detailed information about the goods or services sold. It serves as an official record of the sale and may be required for customs clearance in international shipments. The commercial invoice includes key details like the product description, quantity, price, and terms of the sale.
When is it used?
Commercial invoices are used for both domestic and international sales transactions. For international shipments, it is particularly important as it is used by customs authorities to assess duties and taxes. It is typically required when goods are being exported or imported across borders.
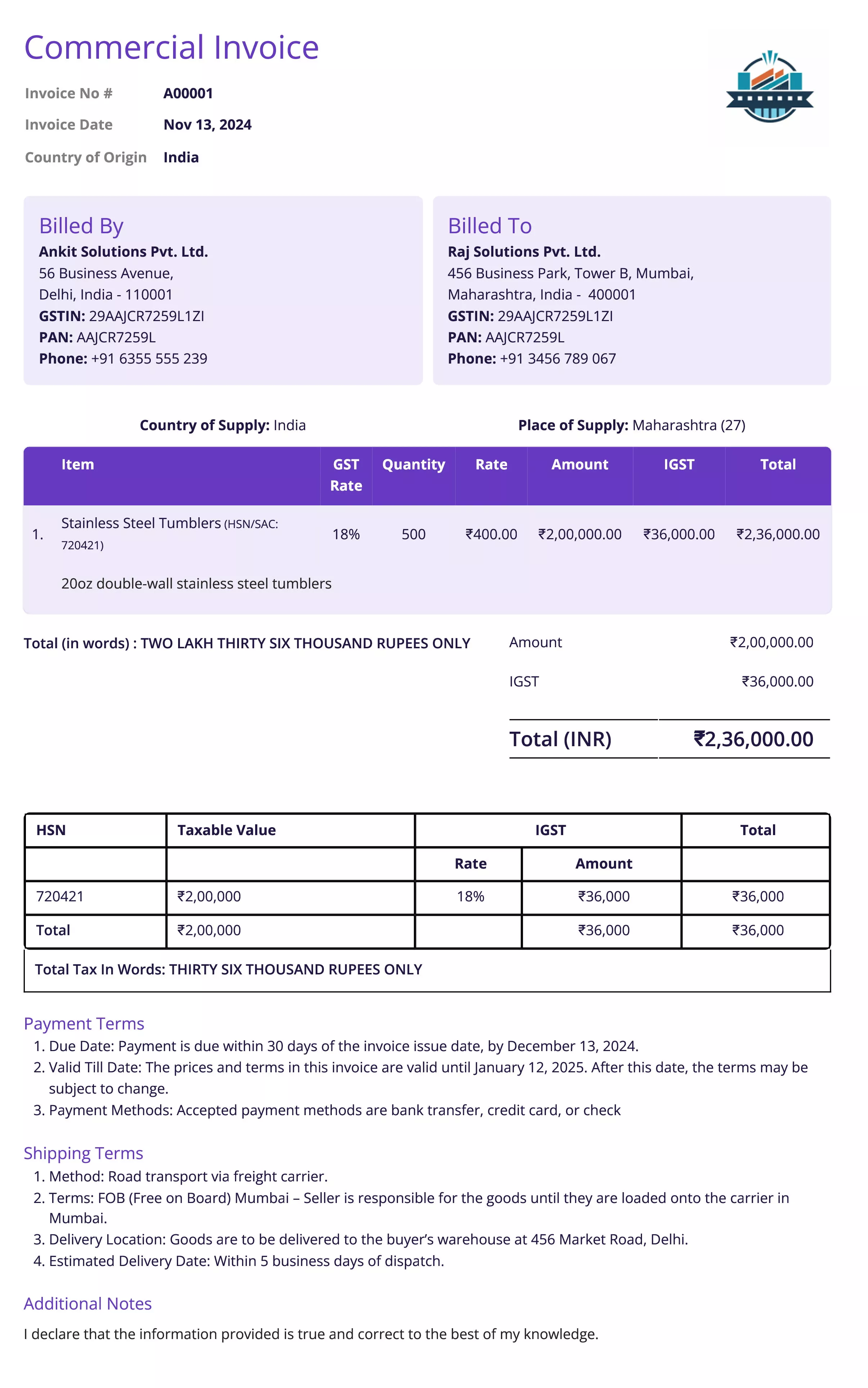
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the commercial invoice.
- Company Logo: A logo helps with brand recognition and adds a professional touch.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details of both the seller and the buyer, including business names, addresses, contact details and tax identification numbers.
- Description of Goods/Services: A detailed list of the items sold, including product descriptions, quantities, unit prices, and total amounts.
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: An international product classification code used for customs purposes (especially in international shipments).
- Country of Origin: The country where the goods were produced or manufactured, which is crucial for customs clearance.
- Shipping Terms: The agreed shipping method, terms (e.g., FOB, CIF), and the location where goods are to be delivered.
- Payment Terms: The terms of payment, including due dates, payment methods, and any early payment discounts or penalties for late payment.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount of the sale, including the cost of goods and any applicable taxes or fees.
- Customs Declaration: A statement declaring that the details provided are accurate, required for customs processing.
- Currency: The currency in which the payment will be made (e.g., USD, EUR).
- Invoice Date and Shipping Date: The date the invoice was issued and the date the goods were shipped or delivered.
Importance of Commercial Invoice:
A commercial invoice is crucial for both the seller and the buyer in completing a sales transaction, especially when goods are being shipped internationally. For businesses, it serves as the official record of the sale, helping with accounting, inventory management, and taxation. For customs authorities, the commercial invoice is a key document used to assess tariffs, duties, and taxes on imported goods.
It provides a clear and detailed breakdown of the transaction, preventing delays in customs clearance. For buyers, it ensures transparency in the pricing and terms of the sale, making it easier to track purchases and process any claims for damages or discrepancies. Additionally, it can serve as evidence in case of disputes regarding the goods or services provided.
Expense Report or Expense Reimbursement Invoice
Definition:
An expense report or Expense Reimbursement invoice is a document used by employees, contractors, or freelancers to request reimbursement for business-related expenses incurred during the course of their work. These invoices summarize all out-of-pocket expenses for which reimbursement is being sought.
When is it used?
Expense report invoices are used when an individual has paid for work-related expenses, such as travel, meals, supplies, or other business-related costs, and needs to submit those expenses for reimbursement from their employer or client.
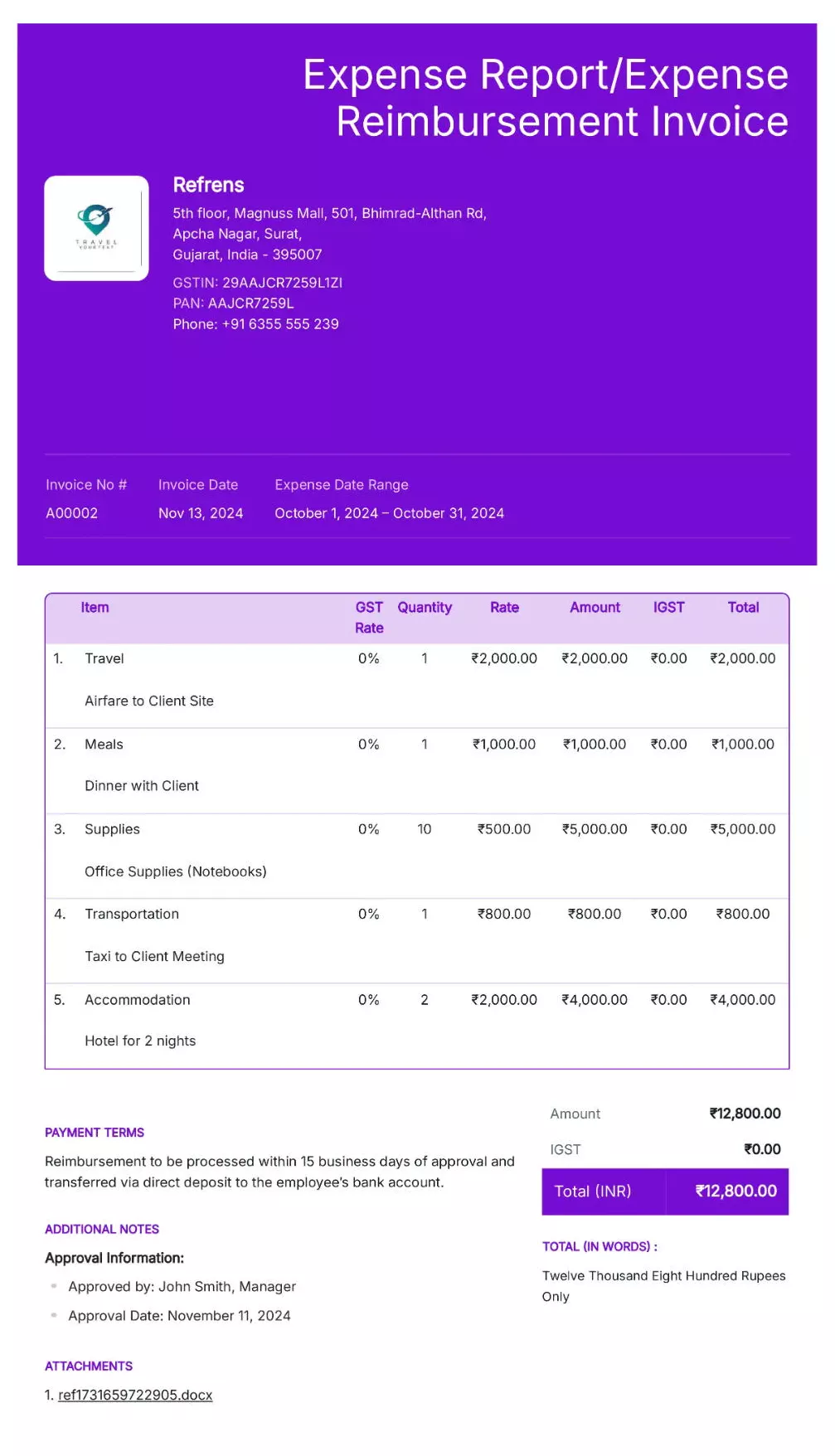
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the expense report invoice.
- Employee/Contractor Information: The name, contact details, and employee or contractor ID (if applicable) of the individual requesting reimbursement.
- Company Information: The name, address, and contact details of the employer or client responsible for reimbursing the expenses.
- Date of Report: The date the expense report is submitted or the date range for the expenses being reported.
- Description of Expenses: A detailed breakdown of the expenses being claimed, including dates, items or services purchased, quantities, and cost per item (e.g., travel, meals, supplies).
- Receipts/Proof of Purchase: Copies of receipts or other supporting documents for each expense item to verify the claimed amount.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount being requested for reimbursement.
- Payment Terms: Information on how and when the reimbursement will be processed and paid.
- Approval Information: Any necessary approval from supervisors or managers to confirm the expenses were authorized.
Importance of Expense Report Invoice:
Expense report Expense Reimbursement invoices are essential for ensuring that employees and contractors are reimbursed for business-related expenses in a timely and accurate manner. They help businesses track and control costs related to employee spending, ensuring that only authorized and legitimate expenses are reimbursed.
For employees and contractors, submitting an expense report invoice ensures they receive compensation for out-of-pocket costs incurred while performing their duties. These invoices also help businesses maintain accurate financial records, support tax compliance, and ensure that budgets are properly managed. Additionally, they provide a transparent record of expenses, making it easier to resolve any disputes or discrepancies.
Proforma Invoice
Definition:
A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice sent to a customer before the actual delivery of goods or services. It provides an estimated cost of the goods or services to be supplied and outlines the terms of the sale.
When is it used?
Proforma invoices are typically used when a business needs to provide a quote or estimate to a potential customer before finalizing the transaction. They are often used in international trade to provide a formal offer and are useful for customs purposes, especially when goods are shipped across borders.
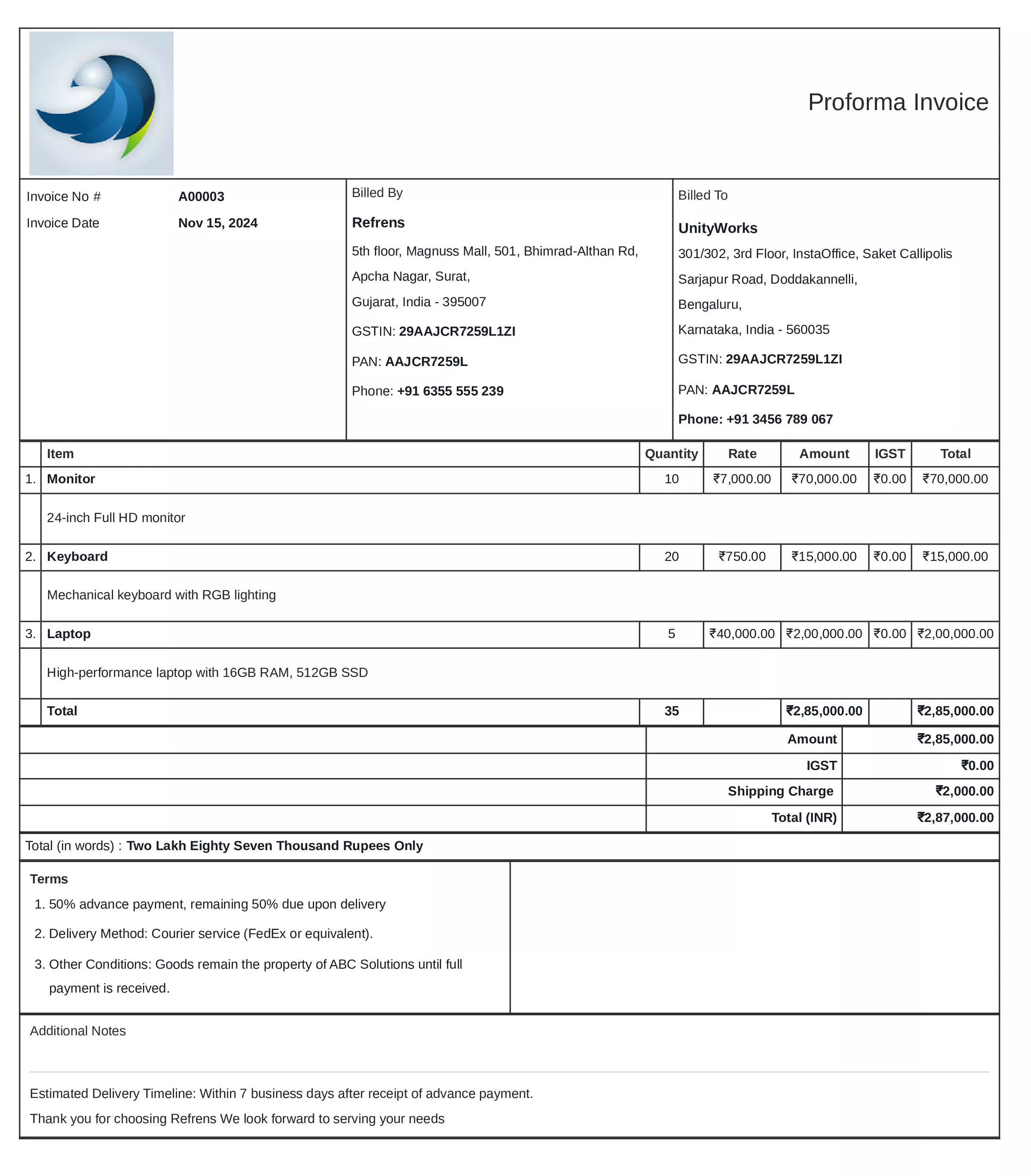
What All is Included in this Format:
- Seller and Buyer Information: Names, addresses, contact details.
- Description of Goods/Services: Details about the items or services being provided, including quantities, specifications, and unit prices.
- Total Estimated Cost: A breakdown of the total cost, including any applicable taxes or shipping charges.
- Terms of Sale: Payment terms, delivery method, and any additional conditions.
- Proposed Delivery Date: Expected delivery timeline for the goods or services.
- Currency: Currency in which the payment is to be made.
- Validity Period: The time frame in which the quoted prices and terms are valid.
Importance of Proforma Invoice:
Proforma invoices are essential for setting clear expectations between the buyer and seller before a transaction is finalized.
They help in obtaining approvals, securing funding (if necessary), and ensuring transparency in pricing. This invoice type also helps in managing international shipments by providing an estimated value for customs clearance and tax purposes.
Note: Learn how to create a proforma invoice with ease by following our step-by-step guide, designed to help you provide accurate estimates and ensure smooth transactions.
Sales Invoice
Definition:
A sales invoice is a formal request for payment sent by a seller to a buyer for goods or services provided. It outlines the details of the transaction and serves as a legal document that confirms the sale.
When is it used?
Sales invoices are used after goods or services have been delivered, typically for immediate or future payment. They are the standard invoice type issued for most commercial transactions, ensuring that the buyer is aware of the amount due for the products or services provided.
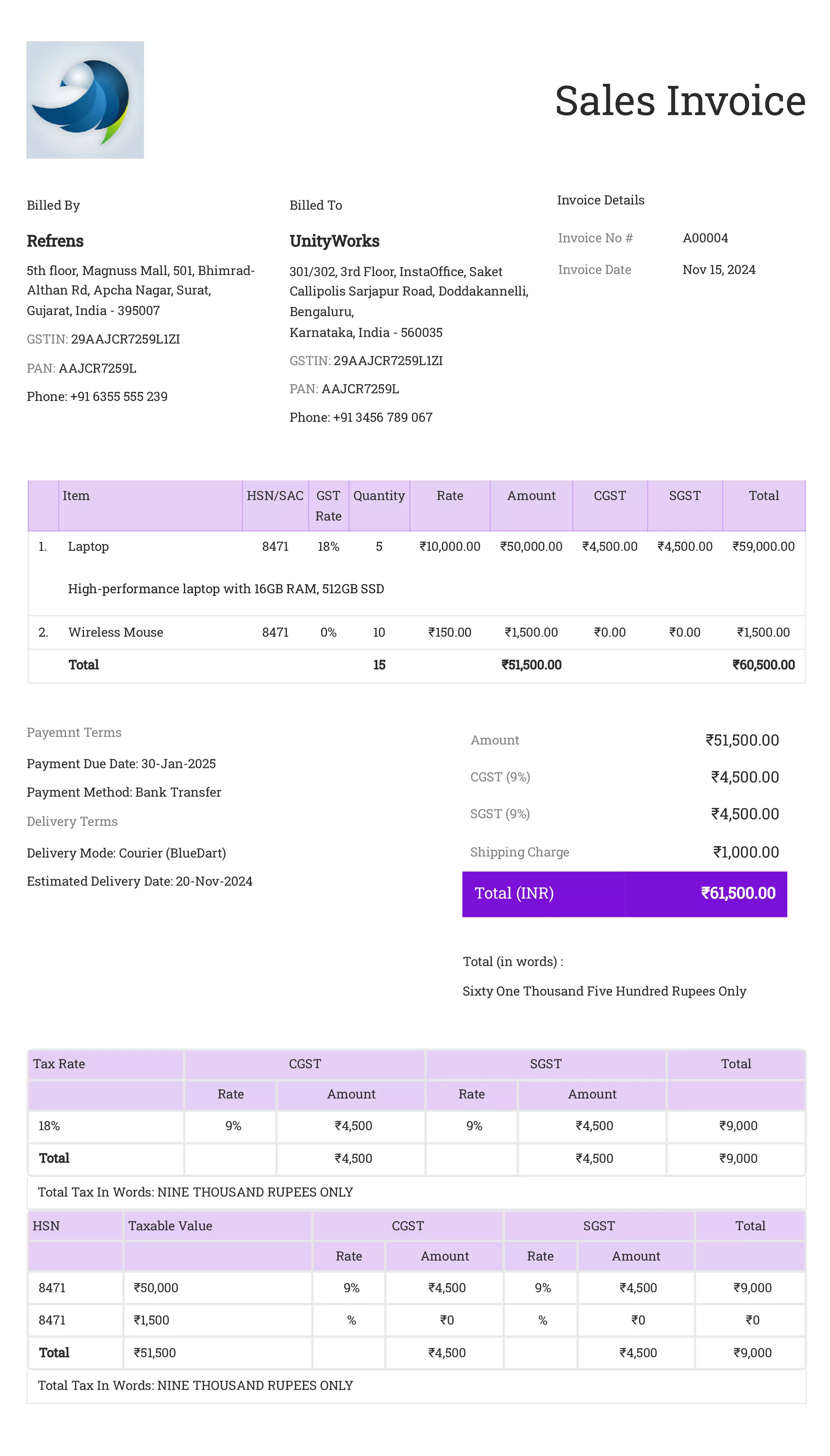
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the transaction.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Full contact details, including name, address, and business registration numbers.
- Description of Goods/Services: A detailed list of the products or services provided, including quantities, unit prices, and any applicable product codes.
- Total Amount Due: The total cost, including taxes, shipping fees, and any applicable discounts.
- Payment Terms: Specific payment instructions, such as due date, method of payment, and late fees if applicable.
- Invoice Date: The date the invoice was issued.
- Tax Information: Details about any taxes, including VAT or sales tax, depending on jurisdiction.
- Delivery Terms: Delivery method and timeline for goods or services.
Importance of Sales Invoice:
A sales invoice is a critical document for both the seller and the buyer. It serves as proof of the transaction, helps in record-keeping, and ensures that payment is collected for goods or services rendered.
It is also important for financial reporting, as it helps businesses track sales revenue and manage cash flow. Sales invoices are often required for tax reporting and serve as legal evidence in case of disputes.
Looking for the best software to manage your sales and purchase invoices? Check out our comprehensive list of top invoice tools that can streamline your invoicing process.
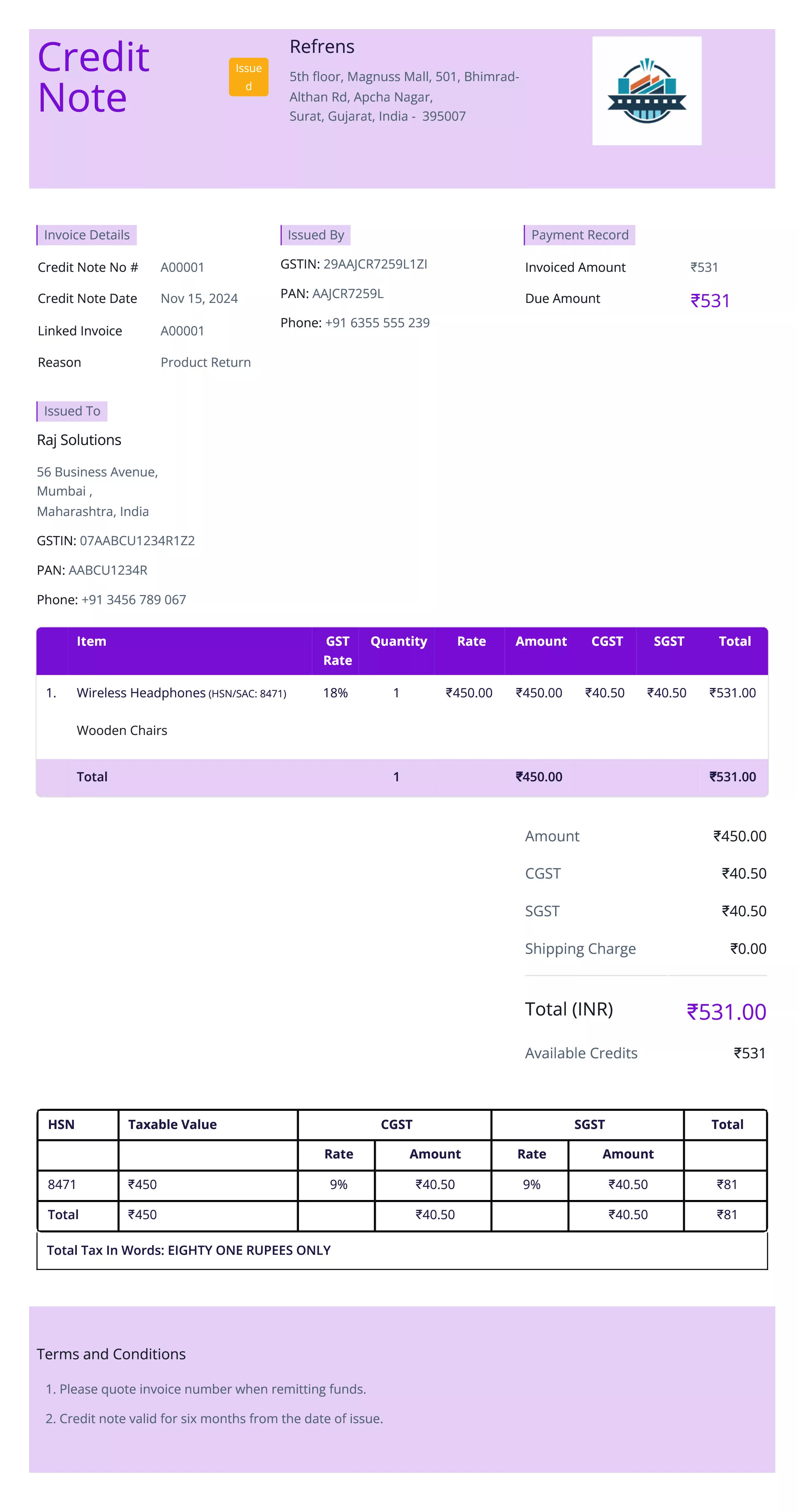
Credit Invoice
Definition:
A credit invoice, also known as a credit memo, is issued by a seller to reduce or cancel a previously issued sales invoice. It is typically used when a buyer is entitled to a discount, refund, or when there has been an error in the original invoice (such as overcharging).
When is it used?
Credit invoices are used when there is a need to correct or adjust a previous invoice. This can occur in cases such as returns, pricing errors, or an agreement to provide a discount after the original invoice was issued.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the credit invoice, which may reference the original sales invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details of both parties.
- Original Invoice Reference: The number of the original invoice being adjusted.
- Reason for Credit: Explanation for the reduction or adjustment, such as a returned item, discount granted, or billing error.
- Amount Credited: The specific amount being credited to the buyer’s account, including taxes if applicable.
- Date of Credit: The date the credit invoice is issued.
- Terms of Refund or Adjustment: If applicable, details on how the credit will be applied or refunded.
Importance of Credit Invoice:
Credit invoices are important for maintaining accurate accounting records. They ensure that any errors in pricing or transactions are corrected in a timely manner and that the buyer is properly credited for returns or discounts.
It also ensures transparency in financial transactions and is required for tax purposes, as it impacts the amount of tax to be paid. Credit invoices help protect both parties in case of disputes by providing a clear and formal acknowledgment of adjustments made.
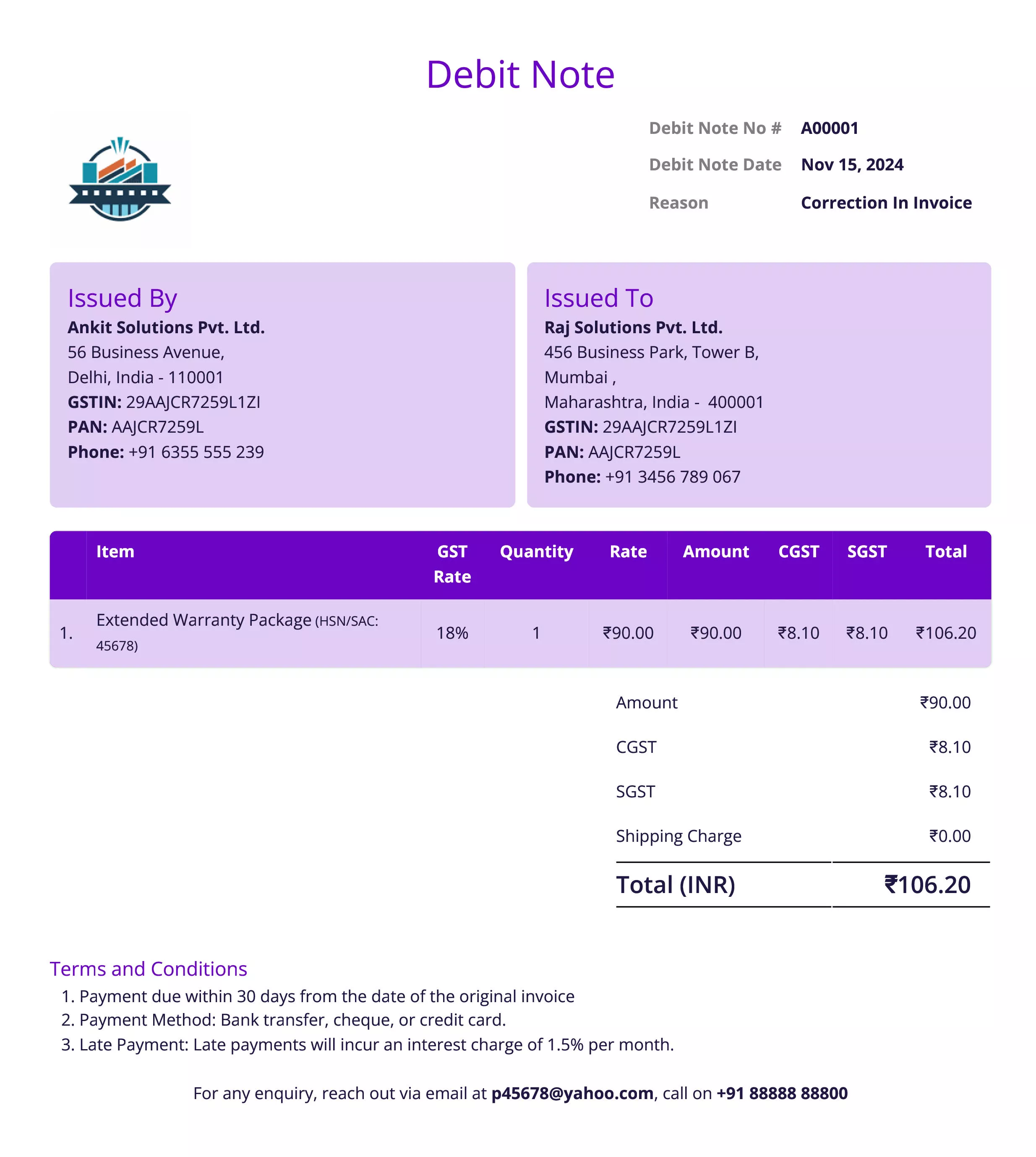
Debit Invoice
Definition:
A debit invoice is issued by a seller to increase the amount a buyer owes, often due to additional charges or corrections on an earlier invoice. It serves as an official request for the buyer to pay more than originally invoiced.
When is it used?
Debit invoices are used when additional charges need to be applied to a previous invoice. This can occur if there was an undercharge, additional costs were incurred after the initial sale, or if the buyer agreed to extra services or products not included in the original invoice.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the debit invoice, which may reference the original sales invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Names, addresses, and contact details for both parties.
- Original Invoice Reference: The number of the original invoice being adjusted, if applicable.
- Reason for Debit: An explanation for why the amount due has increased (e.g., additional services, late fees, shipping costs, etc.).
- Additional Charges: The specific amount being added, including any taxes or fees.
- Total Amount Due: The new total after the debit is applied.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how and when the additional payment should be made.
Importance of Debit Invoice:
A debit invoice is essential for ensuring that the seller receives full payment for goods or services provided, especially when unforeseen costs arise after the initial sale. It allows businesses to correct mistakes or add charges that were omitted or not accounted for earlier.
For the buyer, a debit invoice provides a clear breakdown of the additional costs, promoting transparency and preventing misunderstandings. It is also crucial for proper financial accounting, ensuring that both parties have accurate records for tax reporting and payment tracking.
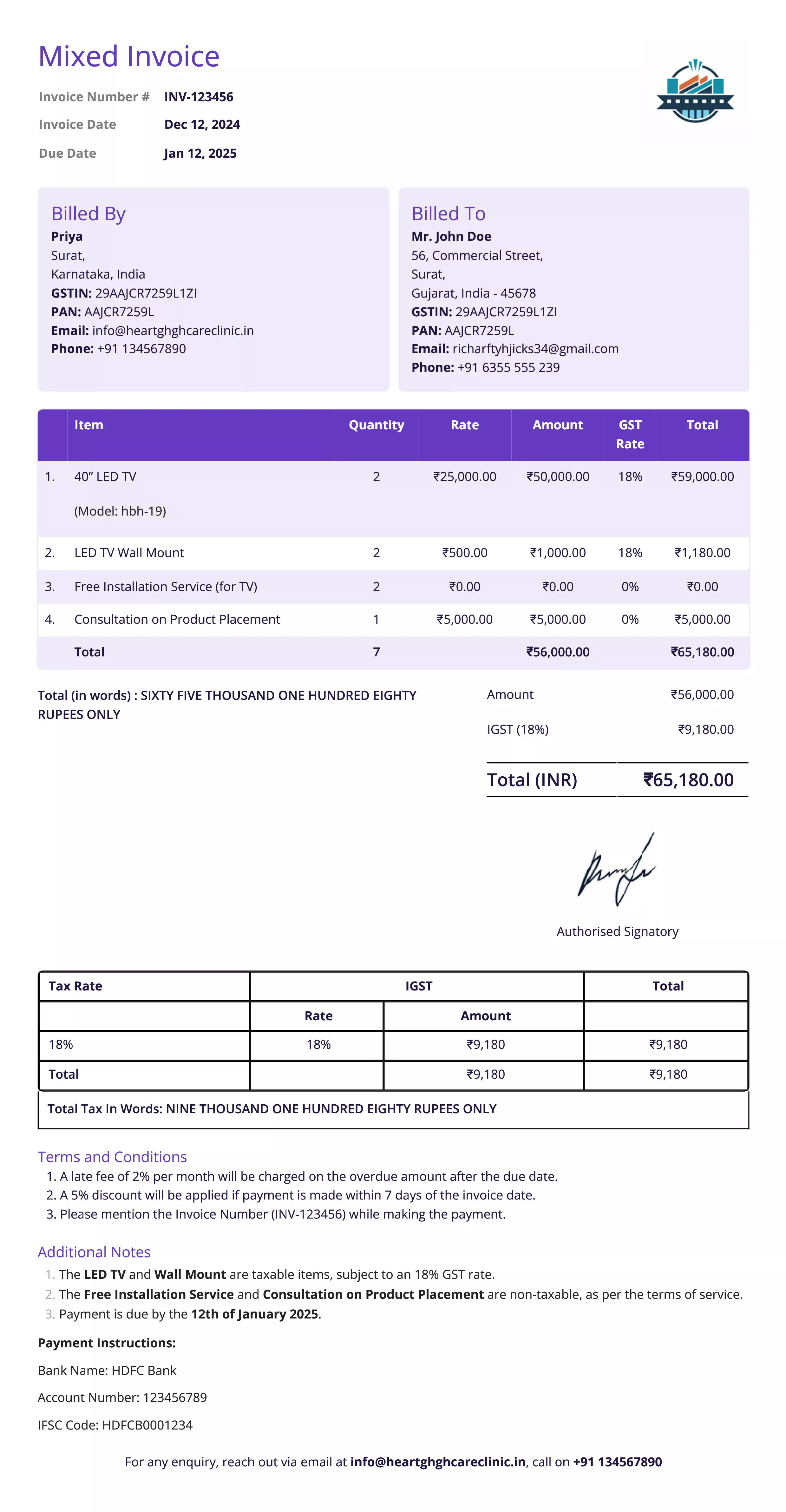
Mixed Invoice
Definition:
A mixed invoice refers to an invoice that includes both taxable and non-taxable items or services. This type of invoice is commonly used in businesses that offer a combination of taxable products (like goods or services subject to GST or VAT) and exempt or non-taxable items.
When is it used?
A mixed invoice is used when a business provides both taxable and non-taxable goods or services. It clearly separates taxable items (subject to tax) from non-taxable ones (exempt from tax). This ensures accurate tax calculation and compliance with tax laws.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Taxable Goods/Services: Items or services that are subject to tax, with the applicable tax rate (e.g., GST, VAT) specified.
- Tax Rate and Amount: The tax rate applied to taxable items, with the total tax amount calculated separately.
- Itemized List: A detailed breakdown of all items/services provided, distinguishing between taxable and non-taxable components.
- Total Amount: The total amount due, with taxes added only for taxable items, showing a clear distinction between taxable and non-taxable charges.
- Invoice Number and Date: Unique identifier and date of issuance for record-keeping and tracking purposes.
- Business Details: The seller’s name, contact information, and tax identification number.
- Customer Details: The buyer’s name, address, and other necessary details for invoicing purposes.
Importance of Mixed Invoice:
Mixed invoices are important for businesses to handle complex transactions where both refunds and additional charges occur within the same billing cycle. They streamline the accounting process, reduce the number of invoices to be managed, and provide a clear, consolidated view of what is owed or refunded.
This helps improve cash flow management, enhances transparency, and simplifies financial record-keeping. For both the seller and buyer, a mixed invoice offers clarity and ensures that all adjustments are accurately accounted for in a single document.
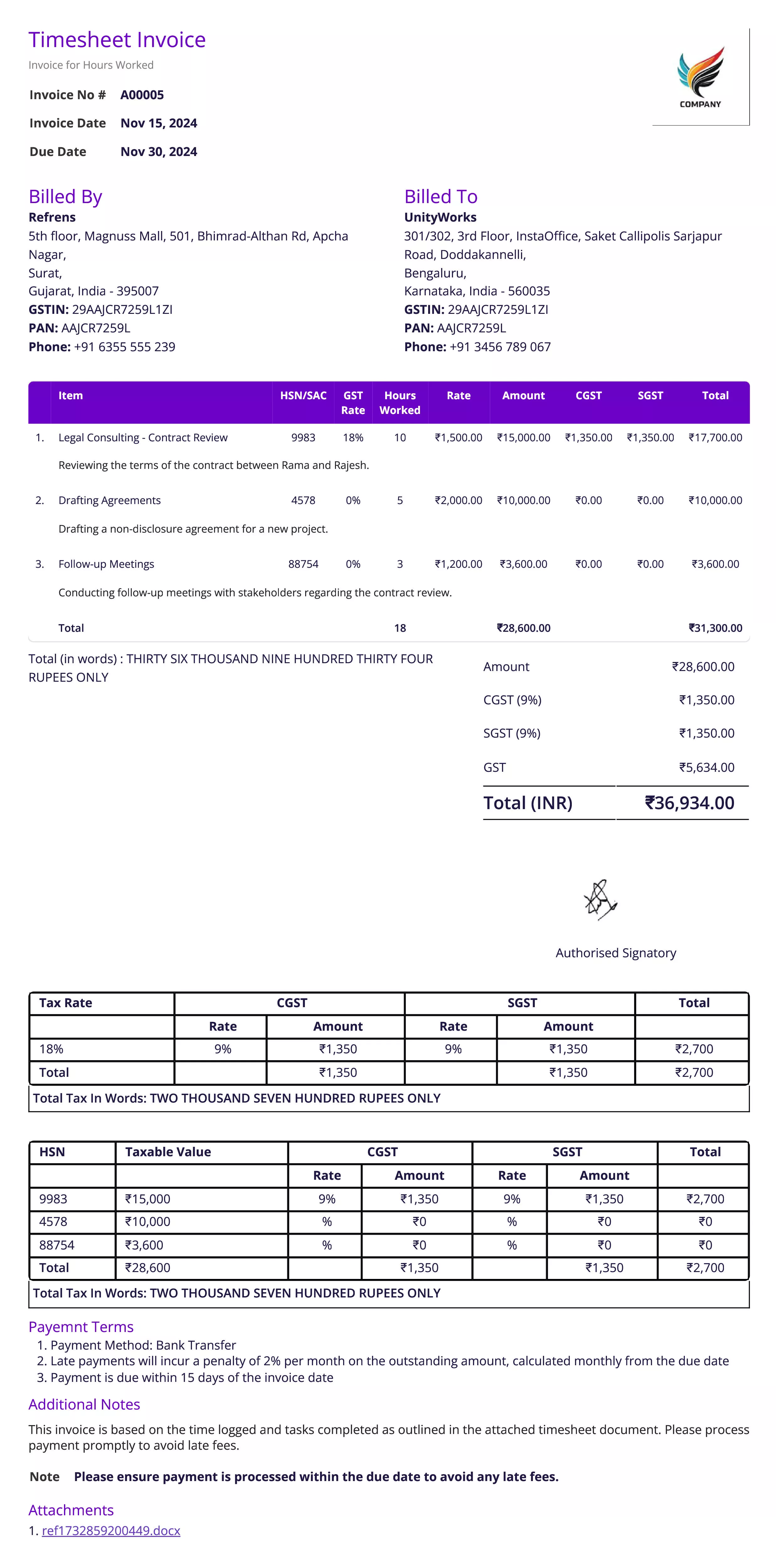
Timesheet Invoice
Definition:
A timesheet invoice is an invoice based on the number of hours worked, typically for services rendered on an hourly basis. It details the time spent on a project or task and the corresponding charges.
When is it used?
Timesheet invoices are commonly used in service-based industries such as consulting, legal, or freelance work, where clients are billed based on the hours worked. It is issued after the work has been completed and is based on an agreed hourly rate or time unit.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the timesheet invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details of both the service provider and client.
- Description of Services: Details about the work performed, including task descriptions or project milestones.
- Hours Worked: The number of hours worked, including a breakdown if different tasks took varying amounts of time.
- Hourly Rate or Fee: The agreed-upon rate per hour or unit of time.
- Total Amount Due: The total charges calculated by multiplying the hours worked by the hourly rate, with any applicable taxes or additional costs.
- Timesheet Reference: A reference to the timesheet document or log showing the hours worked.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on payment methods, due dates, and any penalties for late payment.
Importance of Timesheet Invoice:
Timesheet invoices provide transparency and clear documentation for both parties, ensuring that the client is billed accurately for the time spent on their behalf. It helps maintain a clear record of work done, which is especially important in hourly-based or project-based work.
For service providers, timesheet invoices are crucial for getting paid fairly for the time spent on a project or task, and for clients, they provide a detailed breakdown of the services provided, ensuring that no overcharging occurs. Additionally, they help in budgeting and financial tracking for both parties.
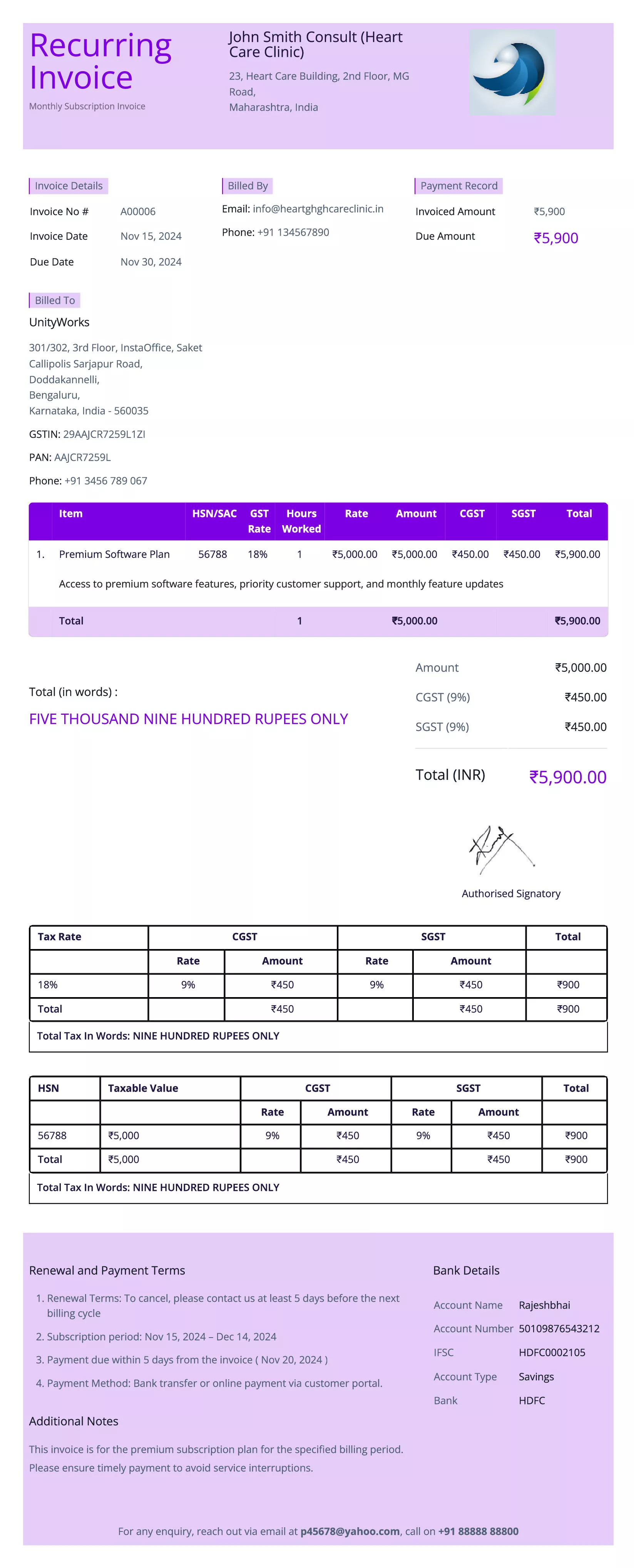
Recurring/Subscription Invoice
Definition:
A recurring or subscription invoice is issued regularly for ongoing services or subscription-based products. This type of invoice is used for customers who subscribe to a service or product on a regular basis, such as monthly or annually.
When is it used?
Recurring or subscription invoices are used when a business provides services or products that require regular payments over a period of time. Common examples include software subscriptions, membership fees, magazine subscriptions, or utility services that are billed on a periodic basis.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique number for each recurring invoice, often with a system that auto-generates sequential numbers.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both parties.
- Subscription Details: Description of the service or product being subscribed to, including any features or options selected.
- Billing Period: The specific period covered by the invoice (e.g., monthly, annually).
- Amount Due: The subscription fee for the period, which may include taxes, discounts, or any additional charges.
- Payment Terms: Information on payment methods, due dates, and whether the payment is automatic or requires manual action.
- Renewal Terms: If applicable, details about renewal options and any changes to the service or pricing upon renewal.
- Next Billing Date: The next scheduled invoice date, particularly in subscription services that automatically renew.
Importance of Recurring/Subscription Invoice:
Recurring invoices are vital for businesses offering subscription-based models or services that require ongoing payments. They ensure that the client is billed consistently and on time for the duration of the subscription, promoting steady cash flow for the business. For the client, this type of invoice provides clarity on their regular financial commitment and helps them track service or product usage over time.
Recurring invoices are particularly useful in managing long-term relationships with customers, providing automated and predictable billing that saves time for both the business and the customer.
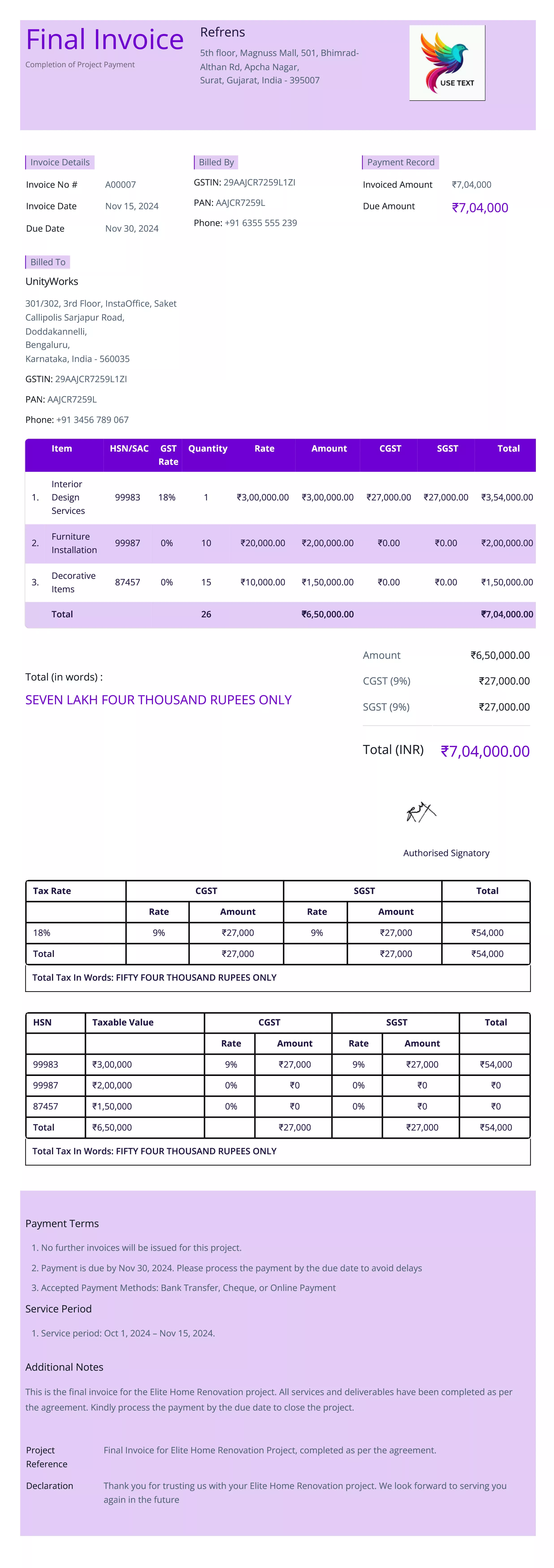
Final Invoice
Definition:
A final invoice is issued after the completion of a project or delivery of services, requesting the remaining balance due for the entire transaction. It marks the conclusion of the transaction between the buyer and seller.
When is it used?
A final invoice is used when all the goods or services have been delivered, and there are no further outstanding amounts to be billed. It is typically issued at the end of a project, after an interim invoice or progress payments have already been made.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the final invoice, often marked as “Final” or similar.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Full contact details for both the business and the client.
- Description of Goods/Services Delivered: A comprehensive list of all goods or services provided, including any relevant project details.
- Total Amount Due: The final amount due for the transaction, subtracting any prepayments or interim payments already made.
- Payments Already Made: A summary of previous payments or partial payments made before the final invoice.
- Taxes and Additional Charges: Any applicable taxes, fees, or additional charges that apply to the final amount.
- Payment Terms: Details on how and when the payment should be made, including the due date.
- Completion Date: The date when the project or service was fully completed.
Importance of Final Invoice:
The final invoice serves as the official and conclusive request for payment after all goods or services have been delivered. It ensures that the seller receives the full amount for the completed transaction and provides the buyer with a clear summary of the entire project or purchase.
Final invoices are crucial for financial reporting, allowing businesses to close out accounts for specific projects or transactions. For the buyer, it offers a final accounting of all costs, ensuring that all previous payments are accounted for and that the correct amount is paid.
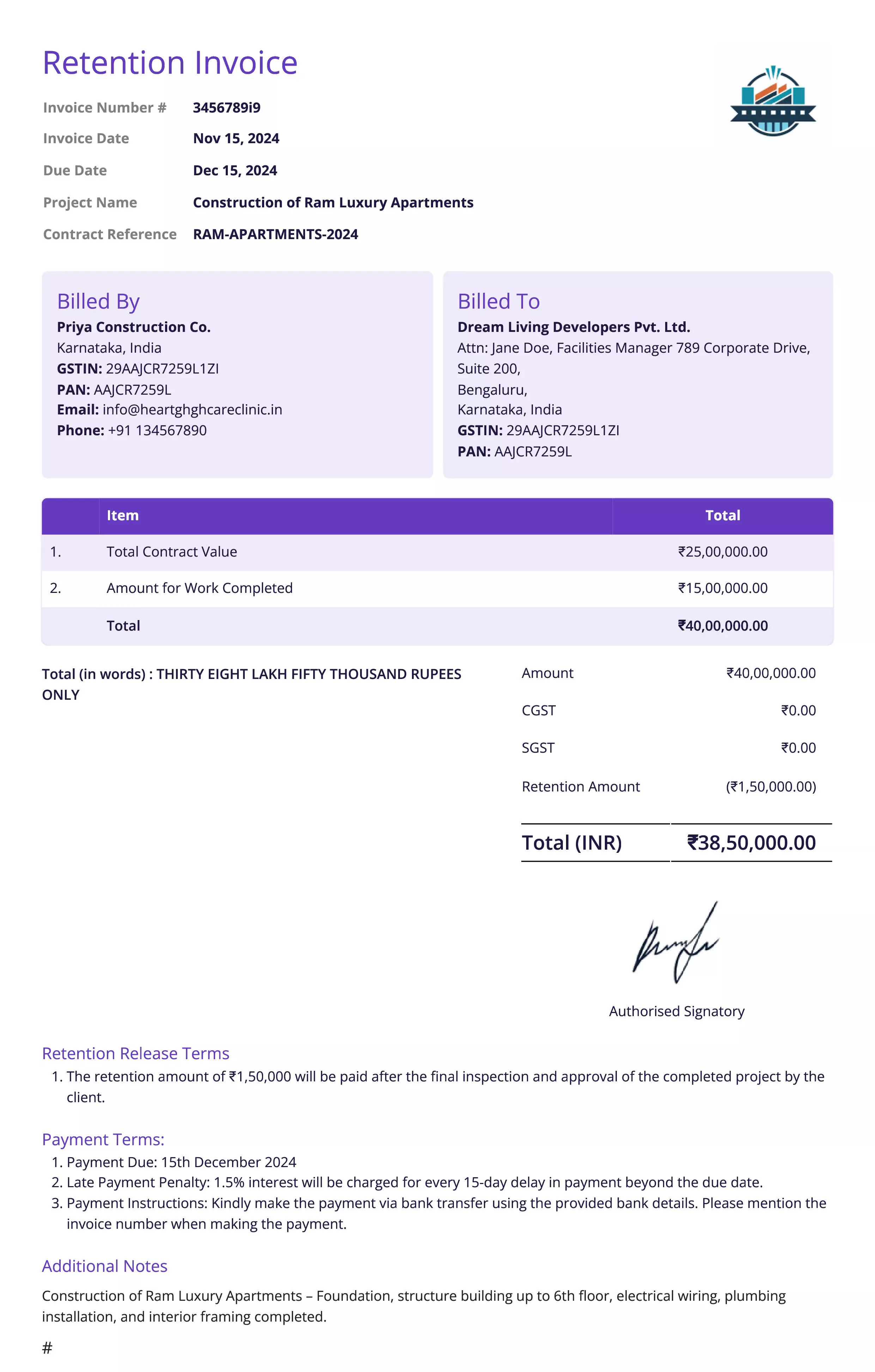
Retention Invoice
Definition:
A retention invoice is issued to withhold a portion of payment from the total amount due for a project until certain conditions are met, typically until the completion of the project or until the client is satisfied with the final deliverables. This is often used in construction, real estate, and large-scale projects.
When is it used?
Retention invoices are used in industries where work is completed in stages or over extended periods, and the client or project owner wants to ensure that the contractor or service provider finishes the work to their satisfaction. The retained amount is usually a percentage of the total payment, withheld until the project is finished or specific performance criteria are met.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the retention invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: The contact details of both the seller (contractor/service provider) and the buyer (client).
- Project Details: The name or description of the project or work being completed.
- Total Project Cost: The overall cost of the project, with the portion retained clearly indicated.
- Amount Retained: The specific percentage or amount withheld from the payment until completion or satisfaction (e.g., 10% of the total amount).
- Payment Terms: The terms under which the retained amount will be released, usually after project completion or after satisfying specific conditions (e.g., approval from the client, final inspection).
- Completion Date or Milestones: The expected date of completion for the project or the milestones that need to be met to release the retained amount.
- Remaining Balance: The amount still due after the retention has been withheld, along with any other pending payments.
- Conditions for Release: Any conditions or inspections required for the release of the retained amount (e.g., completion of final inspection, client approval).
Importance of Retention Invoice:
Retention invoices are important for clients or project owners to ensure that contractors or service providers meet all contractual obligations and quality standards before full payment is made. For businesses, retention invoices help ensure that the customer is satisfied with the work before the final payment is made, minimizing the risk of non-payment after the project is completed.
These invoices also help businesses manage cash flow by allowing for incremental payments while retaining an amount that can be used as leverage to ensure completion. Retention invoices establish clear terms regarding payment withholding and release, helping avoid disputes and ensuring the satisfaction of both parties involved in the project.
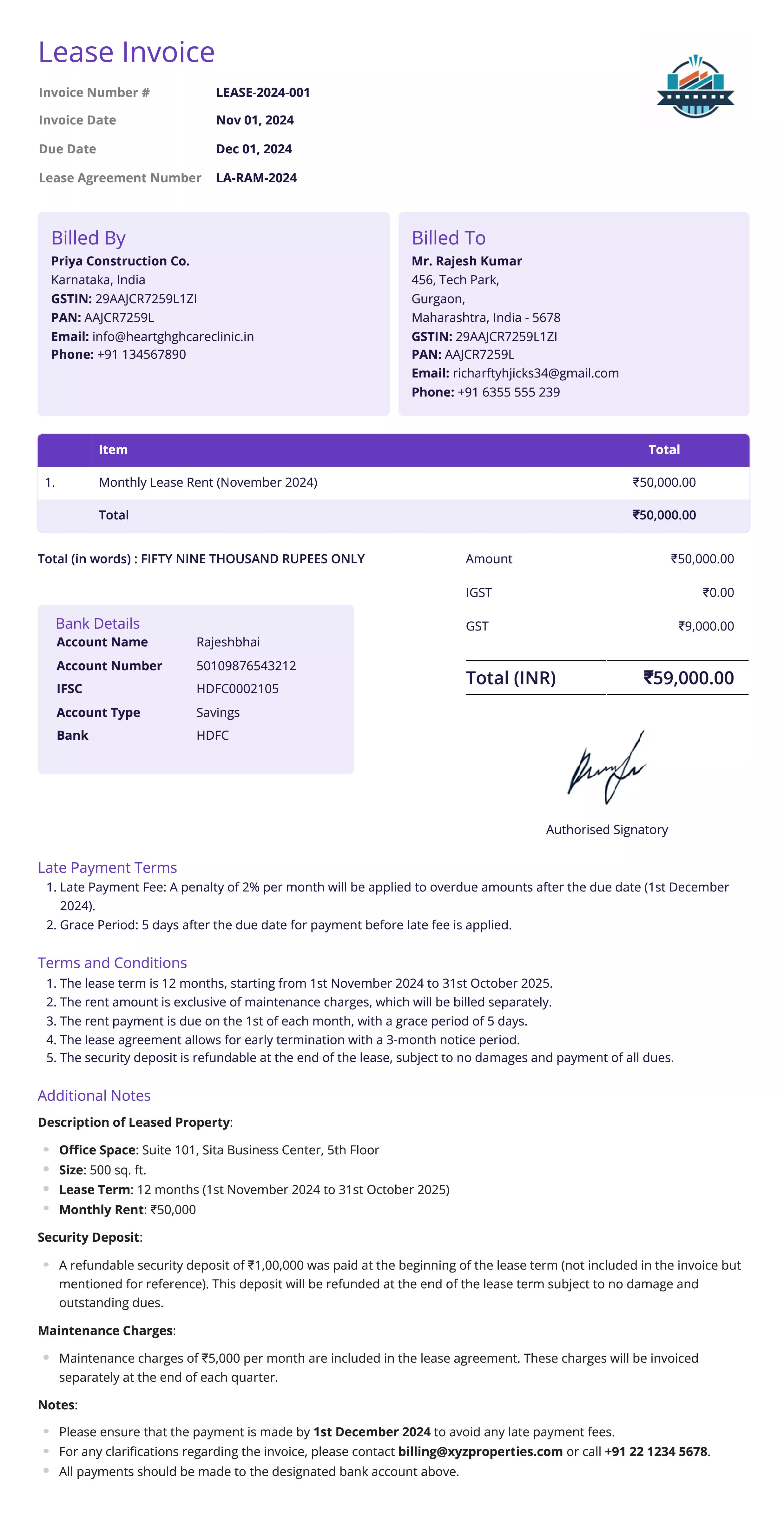
Lease Invoice
Definition:
A lease invoice is issued for periodic payments that are due under a lease agreement. It details the amount to be paid, the frequency of payments, and the terms of the lease, such as the lease duration and the items or property being leased.
When is it used?
Lease invoices are used in lease agreements for properties, equipment, or vehicles where the lessee (tenant) agrees to make periodic payments to the lessor (owner). These invoices are commonly issued for real estate leases, car leases, or equipment leasing.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the lease invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: The contact details of both the lessor (landlord/owner) and lessee (tenant).
- Lease Agreement Details: A reference to the lease agreement number or terms of the lease, including the start and end dates of the lease.
- Description of Leased Property: A description of the property or item being leased, including model, serial number, or location for physical assets (e.g., apartment address, equipment type).
- Amount Due: The payment due for the current lease period, including any applicable taxes, insurance, or additional charges (e.g., maintenance fees).
- Payment Period: The frequency of payment (e.g., monthly, quarterly), along with the due date for the current period’s lease payment.
- Outstanding Balance (if applicable): If there are any past-due payments or adjustments, they should be reflected in the invoice.
- Late Fees (if applicable): Any charges for late payments, based on the terms outlined in the lease agreement.
- Payment Terms: The method of payment (e.g., bank transfer, check) and any late payment penalties.
- Security Deposit (if applicable): Any security deposit required, which may be listed separately from the periodic payment if the deposit is part of the lease terms.
Importance of Lease Invoice:
Lease invoices are important for businesses and individuals to track payments related to leased property or equipment. For the lessor, these invoices ensure that payments are collected on time and according to the lease terms, helping maintain cash flow. For the lessee, lease invoices provide a clear and structured reminder of payment obligations, helping them stay on track with their financial commitments.
These invoices also serve as a formal record of the transaction, which can be important for accounting and tax purposes. Additionally, lease invoices often clarify any additional costs, such as maintenance fees, taxes, or insurance, ensuring transparency between the parties involved.
Escrow Invoice
Definition:
An escrow invoice is issued in transactions where an escrow service is used to hold funds on behalf of the buyer and seller until the conditions of the agreement are met. The invoice details the fees associated with the escrow service and any other relevant terms, including the conditions for releasing the funds.
When is it used?
Escrow invoices are used in transactions that require third-party mediation to protect both the buyer and seller. Commonly used in real estate deals, mergers and acquisitions, high-value goods, and online marketplaces, escrow invoices outline the services provided by the escrow company and any associated costs, such as fees for holding the funds or disbursing payments upon completion of contract terms.

What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the escrow invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details of both the buyer and seller, as well as the escrow service provider.
- Escrow Account Details: Reference to the escrow account or agreement number that holds the funds for the transaction.
- Escrow Service Fees: A breakdown of the fees charged by the escrow service provider for holding and managing the funds during the transaction.
- Transaction Details: A brief description of the transaction being facilitated through escrow, including the nature of the goods or services being exchanged.
- Amount Held in Escrow: The total amount of funds being held in escrow for the transaction.
- Payment Terms: The terms under which the funds will be released, such as upon fulfillment of specific conditions (e.g., delivery of goods, completion of inspections).
- Escrow Release Conditions: A detailed explanation of the conditions that must be met for the release of the escrowed funds (e.g., satisfactory inspection, signed documents).
- Payment Due for Escrow Services: The amount the buyer or seller needs to pay for escrow services, usually as a percentage of the total transaction value or a flat fee.
- Due Date for Escrow Fees: The due date for the payment of escrow service fees.
- Transaction Completion Date: The anticipated or actual date when the transaction will be completed, and funds will be disbursed.
Importance of Escrow Invoice:
Escrow invoices are critical for transactions that involve a third-party intermediary to ensure the protection of both the buyer and seller. They provide transparency regarding the costs and terms associated with using escrow services. For buyers and sellers, the escrow invoice outlines the fees and conditions for the release of funds, offering reassurance that the transaction will be completed according to the agreed-upon terms.
For escrow service providers, the invoice serves as a formal record of the fees charged for their services and helps ensure that payment for escrow-related activities is collected promptly. Additionally, the escrow invoice contributes to the overall security of the transaction by ensuring that the funds will only be released when the specified conditions are met, protecting all parties involved.
Overdue Invoice
Definition:
An overdue invoice is issued when a payment is not made by the due date specified in the original invoice. It serves as a reminder and often includes a request for immediate payment, along with any additional fees or penalties for late payment.
When is it used?
An overdue invoice is used when the buyer has not paid by the agreed-upon due date. It is typically sent after the original invoice’s due date has passed and serves as a formal reminder to encourage prompt payment, often with added penalties or interest if stipulated in the original agreement.
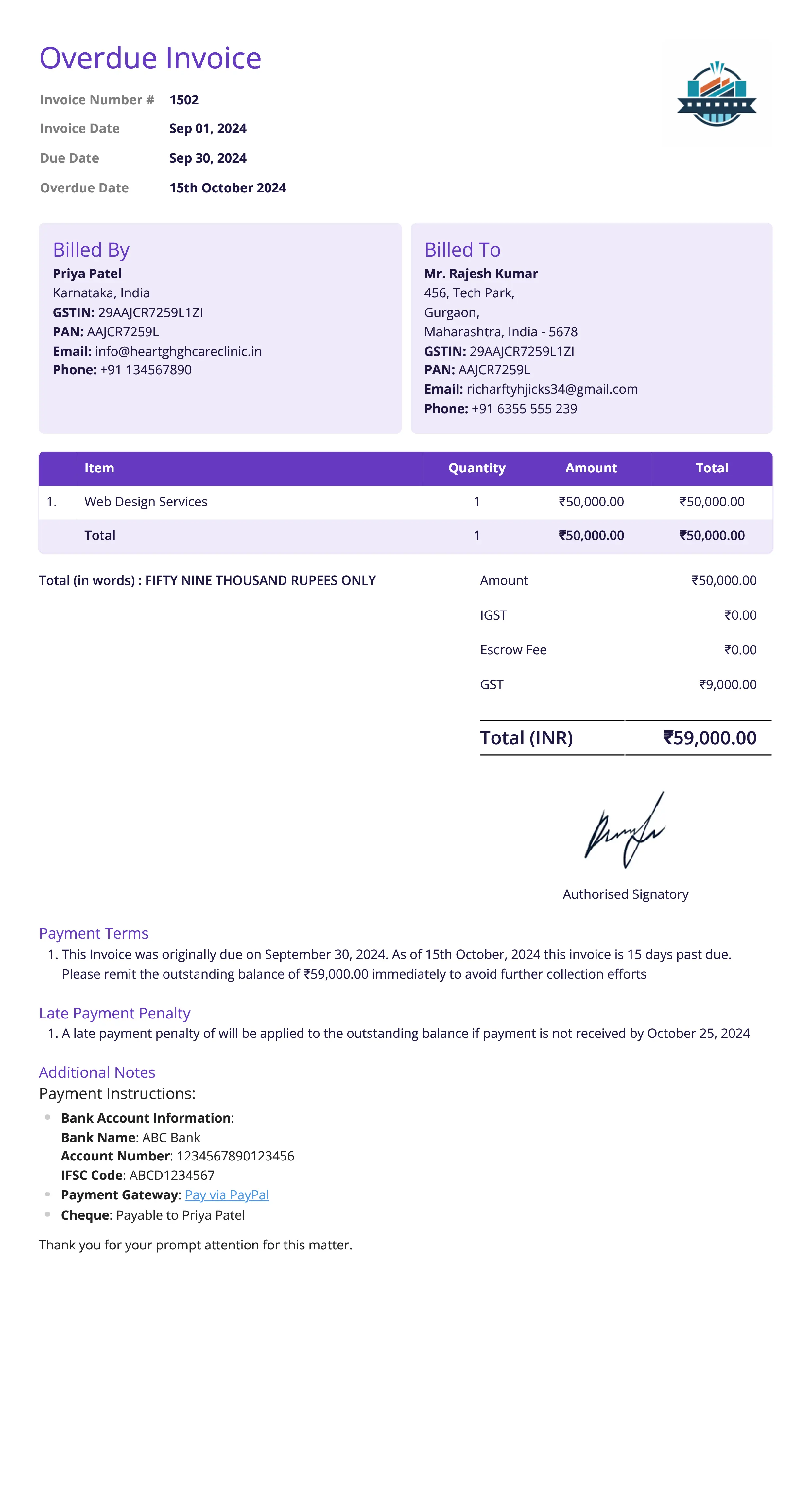
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the overdue invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both parties.
- Original Invoice Reference: The number of the original invoice that is now overdue.
- Due Date: The original payment due date from the original invoice.
- Outstanding Amount: The amount still owed by the buyer, including any applicable late fees or interest.
- Late Fees or Interest: Details on any penalties or interest charges for the overdue payment, as specified in the original terms.
- Payment Terms: Instructions for how and when the overdue payment should be made, and any consequences for continued non-payment.
- New Due Date: A revised date by which the payment must be made (if applicable).
Importance of Overdue Invoice:
An overdue invoice is important for maintaining cash flow and ensuring timely payments. It serves as an official reminder to the buyer that payment is late and provides a clear statement of what is owed, including any additional charges.
Overdue invoices help businesses recover funds quickly and reduce the risk of bad debt by formally addressing non-payment. For the buyer, it serves as a prompt to resolve the outstanding balance and avoid further penalties or legal consequences. Overdue invoices are also crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and helping businesses manage collections.
Struggling with overdue invoices? Discover the best invoice reminder software that can help automate follow-ups and ensure timely payments
Purchase Invoice
Definition:
A purchase invoice is issued by a seller to a buyer for goods or services received. It represents the buyer’s obligation to pay for the items or services that have been delivered or provided.
When is it used?
A purchase invoice is used when a business or individual purchases goods or services. It is issued by the supplier to the buyer once the goods or services have been delivered, and it details the amount the buyer owes for the transaction.
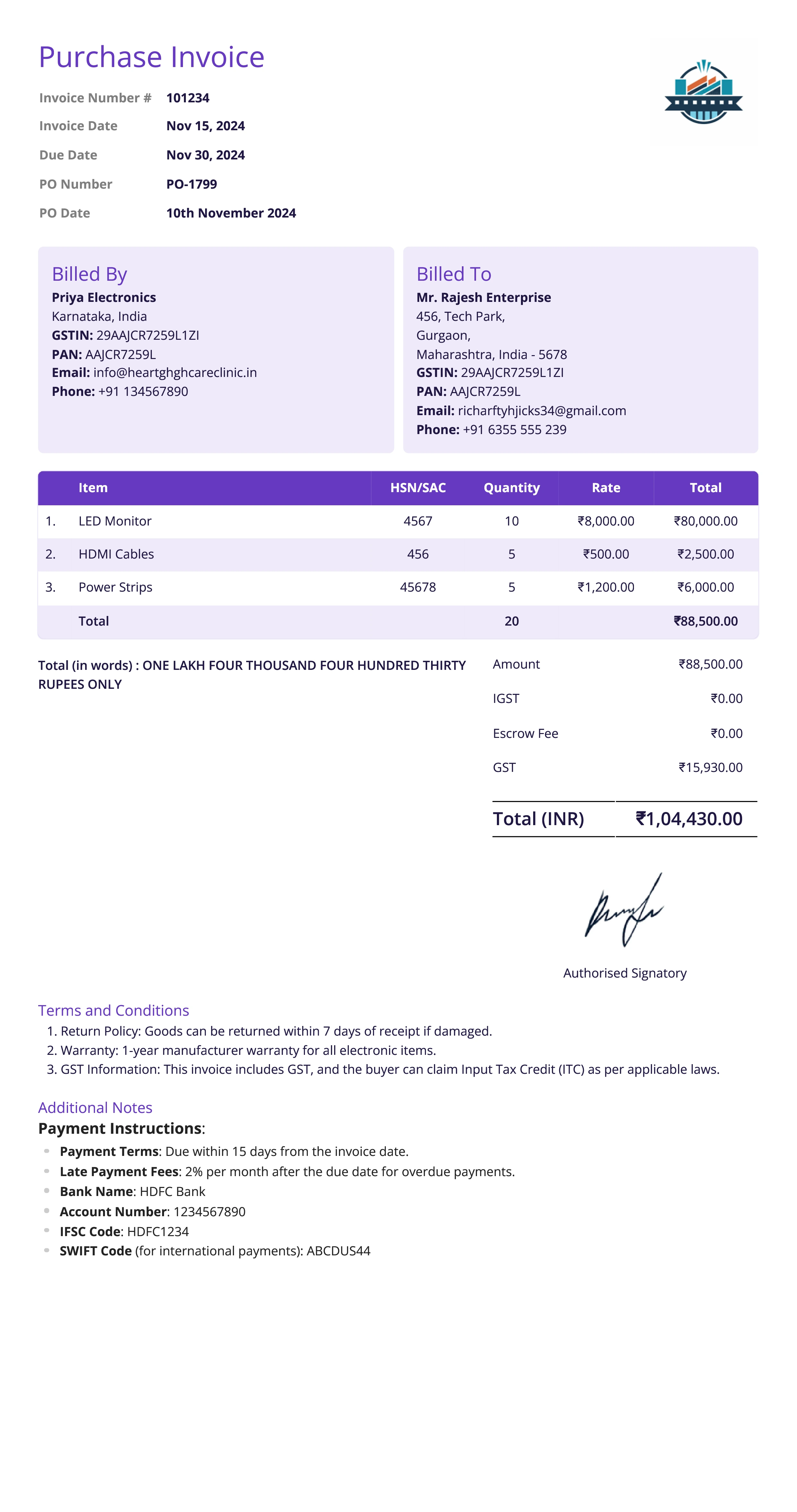
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the purchase invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details of both the supplier (seller) and buyer.
- Description of Goods/Services: A detailed list of items or services purchased, including quantities, unit prices, and any relevant product or service codes.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount payable, including taxes, delivery fees, and any other applicable charges.
- Payment Terms: Information on the payment method, due date, and any early payment discounts or penalties for late payment.
- Purchase Order Reference: The purchase order number (if applicable), which links the purchase invoice to a prior order placed by the buyer.
- Delivery Information: Date of delivery or performance, and delivery method (if applicable).
Importance of Purchase Invoice:
A purchase invoice is important for the buyer’s accounting records, as it serves as proof of the transaction and is used to verify expenses for financial reporting and tax purposes. It is essential for maintaining accurate records of inventory, costs, and cash flow. For the seller, the purchase invoice is crucial for tracking the sale, ensuring payment, and managing accounts receivable. This invoice type also plays a role in inventory management and auditing, helping businesses reconcile their purchases and ensure that what was ordered is what was received.
Progress Invoice
Definition:
A progress invoice is issued during the course of a project to request partial payment based on the work completed at specific milestones or stages. It is commonly used for long-term projects where the total payment is divided into multiple phases.
When is it used?
Progress invoices are used in projects that involve multiple stages of work, such as construction, large consulting projects, or custom orders. These invoices are issued periodically (e.g., after completing certain phases or milestones) to ensure the business receives payment for work completed before the project is fully finished.
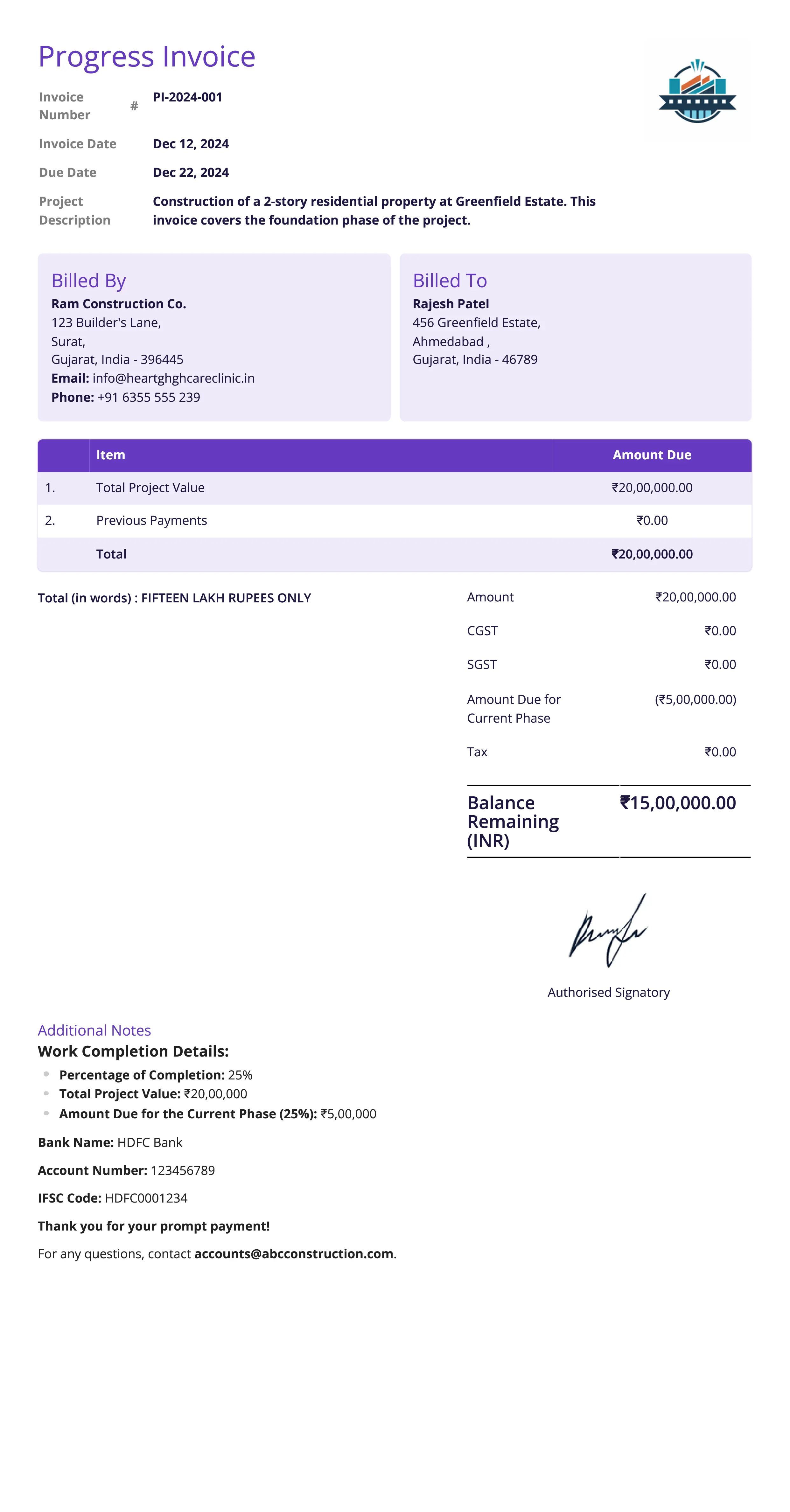
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the progress invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both the service provider and the client.
- Project Description: A brief overview of the project and the milestone or phase that has been completed.
- Percentage of Completion: The percentage of the total project completed at the time the progress invoice is issued.
- Amount Due for the Progress Payment: The portion of the total project value due for the current phase, typically based on the percentage of work completed.
- Previous Payments: A record of any payments made for earlier phases or milestones.
- Total Project Value: The total value of the project, showing how much remains to be paid.
- Payment Terms: Information about when and how the payment should be made, including any late fees or penalties.
Importance of Progress Invoice:
Progress invoices are essential for managing cash flow during long-term projects by ensuring that the seller receives payments throughout the project rather than waiting until the final completion. They also help manage client expectations, allowing both parties to track the project’s progress and payments. For businesses, progress invoices provide a systematic way to bill for work done and keep cash flow stable during the course of the project. For clients, these invoices ensure they are only paying for completed work, which reduces the risk of overpaying before the full project is finished.
The main differences between a Progress Invoice and a Milestone Invoice are:
1. Definition:
– A Progress Invoice is issued based on the percentage of work completed, often used in projects with continuous or phased progress.
– A Milestone Invoice is issued when specific, predefined milestones or deliverables within a project are achieved.
2. Payment Basis:
– Progress invoices rely on the work progress percentage and are calculated proportionally to the total project value.
– Milestone invoices are tied to specific agreed-upon events or stages, regardless of the percentage of total work completed.
3. Usage:
– Progress invoices are common in projects where progress is incremental and ongoing, such as construction or consulting.
– Milestone invoices are typically used in projects where key deliverables or events mark payment triggers, like software development or event planning.
4. Transparency:
– Progress invoices provide detailed insights into how much of the project is completed and the corresponding payment.
– Milestone invoices focus on achieving specific outcomes rather than the overall project’s progress.
5. Flexibility:
– Progress invoicing is more flexible and adjusts based on ongoing work and completion rates.
– Milestone invoicing is rigid, tied strictly to the completion of predefined milestones.
In short, progress invoices are proportional to ongoing work, while milestone invoices are tied to specific deliverables or events. Both ensure cash flow during projects but differ in structure
Consolidated Invoice
Definition:
A consolidated invoice combines multiple individual invoices from different transactions into one document, allowing the buyer to pay a single amount for several purchases or services rendered.
When is it used?
Consolidated invoices are used when a customer has made multiple purchases or received various services over a period and the seller wants to streamline the billing process by issuing one invoice for the entire amount due.
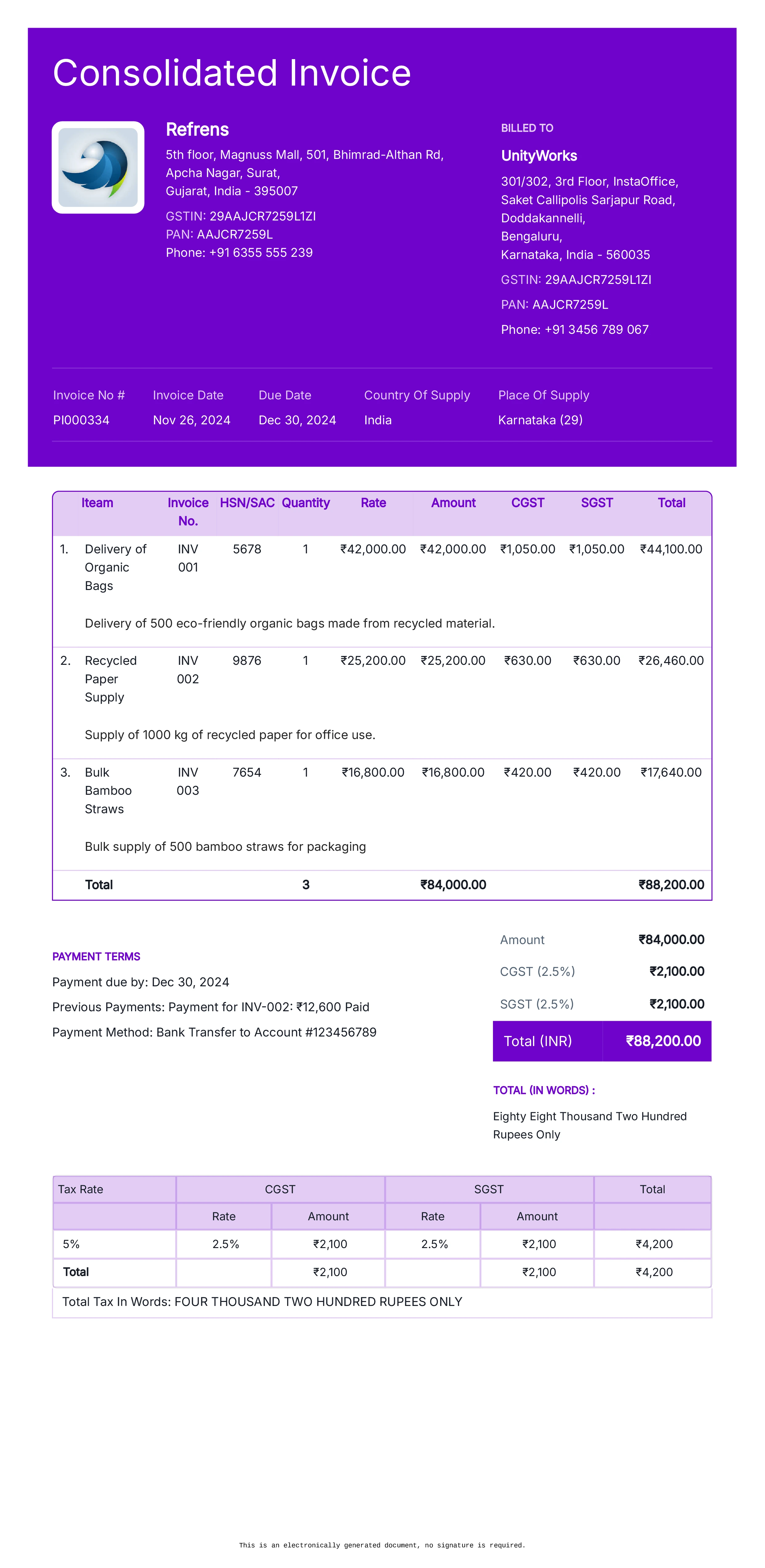
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the consolidated invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both parties.
- Summary of All Transactions: A list of individual invoices or purchases that are being consolidated, including the invoice numbers, dates, and amounts for each.
- Total Amount Due: The combined amount of all the individual invoices, including any applicable taxes, discounts, or additional charges.
- Previous Payments: A record of payments made for each of the individual invoices, if applicable.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how the total consolidated amount should be paid, including the due date and acceptable payment methods.
Importance of Consolidated Invoice:
Consolidated invoices simplify the billing process for both the buyer and the seller, as it consolidates multiple charges into a single document. This reduces administrative workload for both parties, especially in situations where the buyer has made multiple purchases or received several services. For businesses, consolidated invoices help in streamlining their accounts receivable and provide a clear overview of the outstanding amounts. For buyers, they reduce the need to process multiple payments for each invoice, offering a more convenient and efficient way to handle finances.
Difference Between Consolidated Invoice and Statement Invoice:
– A consolidated invoice combines multiple individual invoices into a single document for payment, typically issued when several transactions occur within a short period. It replaces multiple invoices with one, focused on payment for recent transactions.
– A statement invoice provides a summary of all transactions and outstanding balances over a specific billing period (e.g., monthly), including both paid and unpaid invoices. It is more of an account overview than a request for payment of specific recent transactions.
Key Difference:
Consolidated invoices are a replacement for multiple recent invoices to streamline payment, while statement invoices act as a summary of account activity over time, focusing on outstanding balances.
Provisional Invoice
Definition:
A provisional invoice is issued based on an estimate or provisional agreement, often before the actual delivery or completion of services. It is subject to adjustment once the final amount is determined.
When is it used?
Provisional invoices are commonly used in situations where the final amount cannot be precisely calculated at the time of billing, such as when the scope of work is still being defined or when certain variables, like material costs, are not yet finalized. They provide an initial request for payment while allowing for adjustments later.
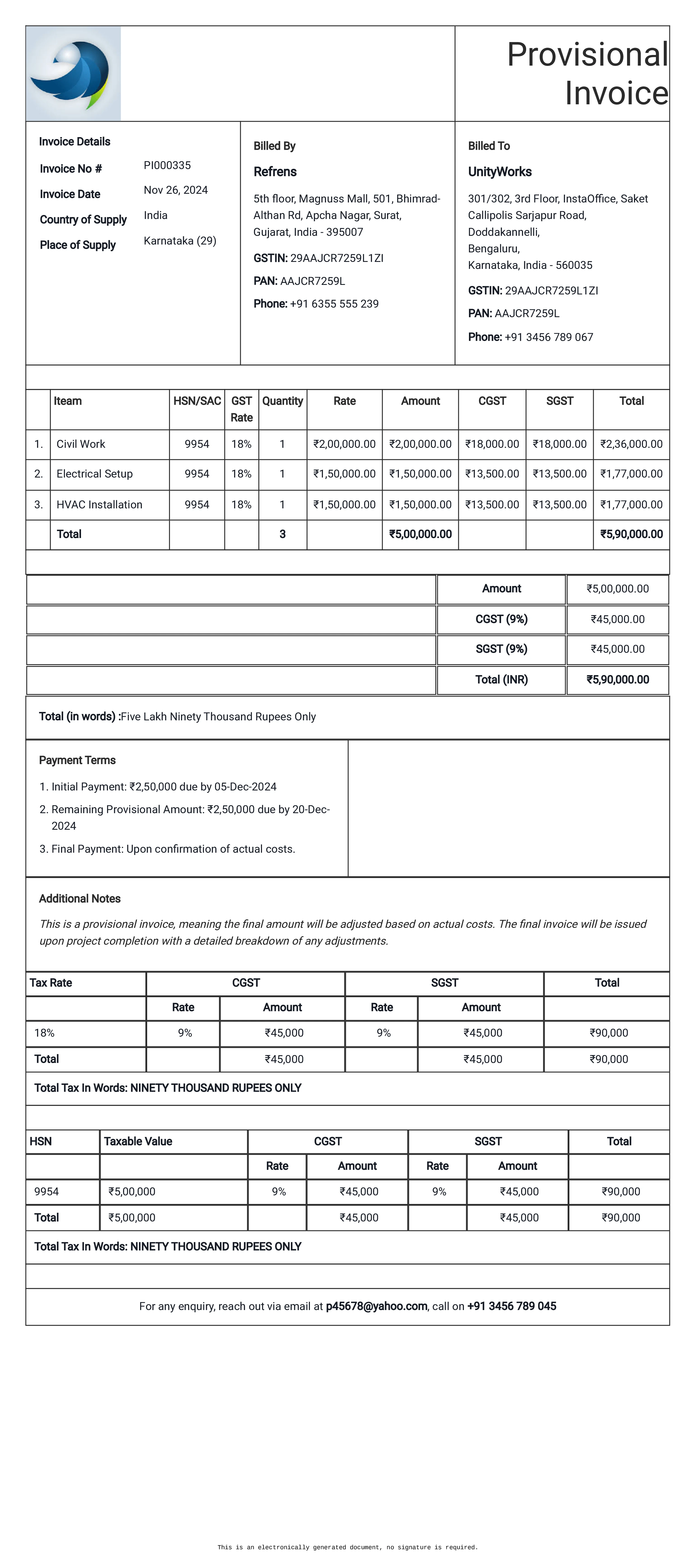
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the provisional invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both parties.
- Description of Goods/Services: A preliminary description of the goods or services expected to be delivered.
- Provisional Amount: An estimated amount based on initial calculations or an agreed-upon rate, with the understanding that it may change.
- Expected Total Cost: A rough estimate of the final cost, with a disclaimer that this is subject to adjustment.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how the provisional amount should be paid and when any final adjustments will be made.
- Adjustment Clause: A statement that the provisional invoice is subject to changes once the actual cost is confirmed.
Importance of Provisional Invoice:
Provisional invoices are important for ensuring that a business receives early-stage payments even when the final cost is not yet determined. This is particularly useful in situations where ongoing costs are incurred before the final scope or project details are fully known. For clients, it provides a clear understanding of the estimated costs upfront, so they can plan their budgets accordingly. Provisional invoices help to maintain cash flow for the business and establish transparency with the client about the nature of the billing arrangement.
Service Invoice
Definition:
A service invoice is issued for services rendered, rather than physical goods. It outlines the charges for specific tasks or professional services performed, typically by freelancers, consultants, or service-based businesses.
When is it used?
A service invoice is used whenever a service provider delivers a service to a client and requests payment for their time, expertise, or work done. This is common in industries such as consulting, legal services, marketing, repair, and maintenance.
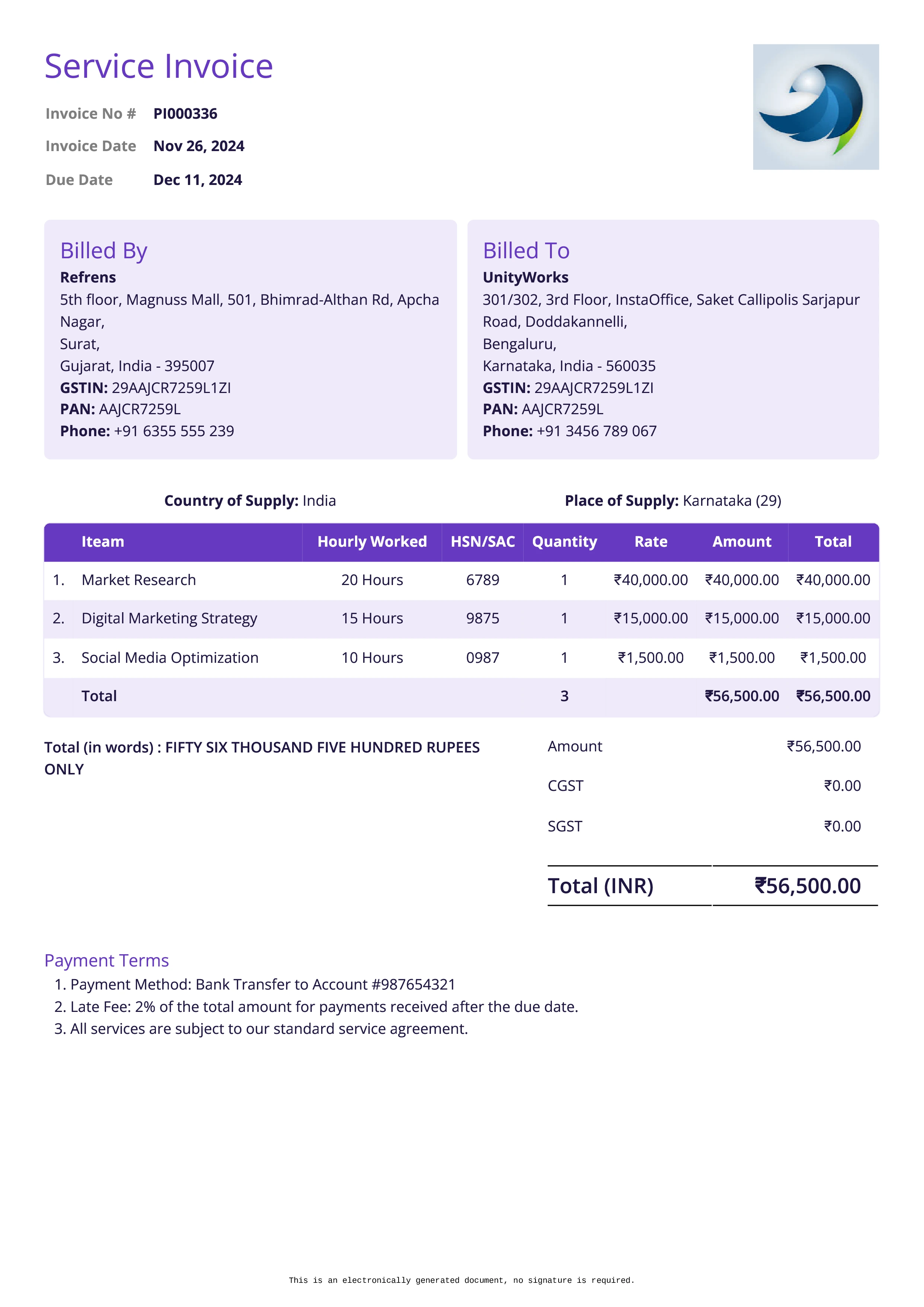
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the service invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both the service provider and the client.
- Description of Services Provided: A detailed breakdown of the services rendered, including the scope, number of hours worked (if applicable), hourly rates, and any special terms.
- Amount Due: The total amount charged for the services rendered, which may include taxes or additional fees.
- Payment Terms: Information on the payment deadline, acceptable payment methods, and any late fees or penalties.
- Invoice Date: The date the invoice is issued, typically right after services are completed.
- Due Date: The date by which payment is expected.
Importance of Service Invoice:
Service invoices are critical for documenting the work performed and ensuring that the service provider gets paid for their time, expertise, and effort. For businesses, service invoices are a key part of cash flow management and financial record-keeping. They help maintain a professional relationship with clients by providing clear and itemized billing details. Service invoices also serve as important documentation for tax reporting and audits, as they show the revenue earned from providing services. For clients, receiving a detailed service invoice ensures transparency in what they are paying for and when payment is due.
Tax Invoice
Definition:
A tax invoice is a document that includes details about the tax charged on a transaction. It is issued by the seller to the buyer, complying with tax regulations and providing the necessary information for the buyer to claim tax credits, such as VAT or GST.
When is it used?
A tax invoice is used when a taxable transaction occurs and tax needs to be collected. It is issued when the seller is required to collect tax (e.g., VAT, GST, sales tax) from the buyer, and it must meet legal requirements for tax reporting.
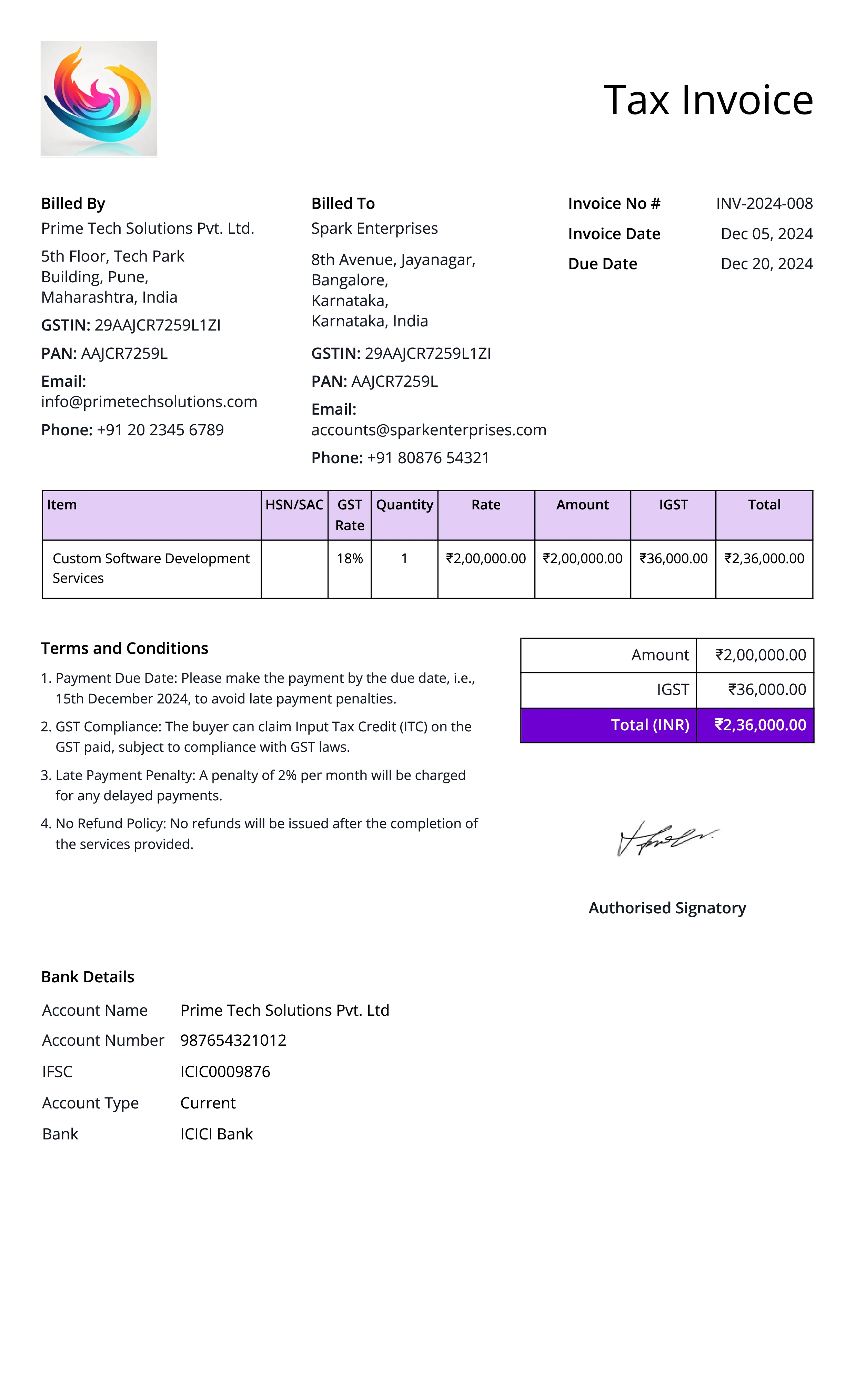
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the tax invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Full contact details, including the business name, address, and tax identification number (TIN or VAT number) for both the seller and buyer.
- Description of Goods/Services: A detailed list of goods or services sold, including quantities, unit prices, and total price.
- Tax Amount: The specific amount of tax charged on the transaction, along with the tax rate used.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount payable, including both the goods/services price and the tax charged.
- Tax Identification Numbers: The tax identification number (TIN or VAT number) of both the seller and buyer.
- Date of Transaction: The date the transaction occurred.
- Payment Terms: Details on payment methods and the due date for payment.
- Tax Rate: The rate of tax applied (e.g., 10%, 15%, etc.), depending on the jurisdiction.
Importance of Tax Invoice:
A tax invoice is essential for tax compliance, as it provides both the seller and the buyer with the necessary documentation to report the tax paid or collected. For businesses, it ensures that the tax authorities can verify the amount of tax owed and paid, facilitating accurate tax filings and audits.
Tax invoices also allow buyers to claim input tax credits (e.g., VAT refunds) on the taxes paid for business-related purchases. For both parties, it ensures transparency and legality in the transaction, helping to avoid disputes and ensuring that proper taxes are accounted for and remitted to tax authorities.
To learn more about creating a GST invoice and ensure your business complies with tax regulations, check out our detailed guide here >>> How To Create GST Invoices In 2 Minutes?
Utility Deposit Invoice
Definition:
A utility deposit invoice is issued by utility companies (such as electricity, water, gas, or internet providers) to request a deposit from a customer before providing the service. This deposit serves as security for the utility company in case the customer fails to pay future bills.
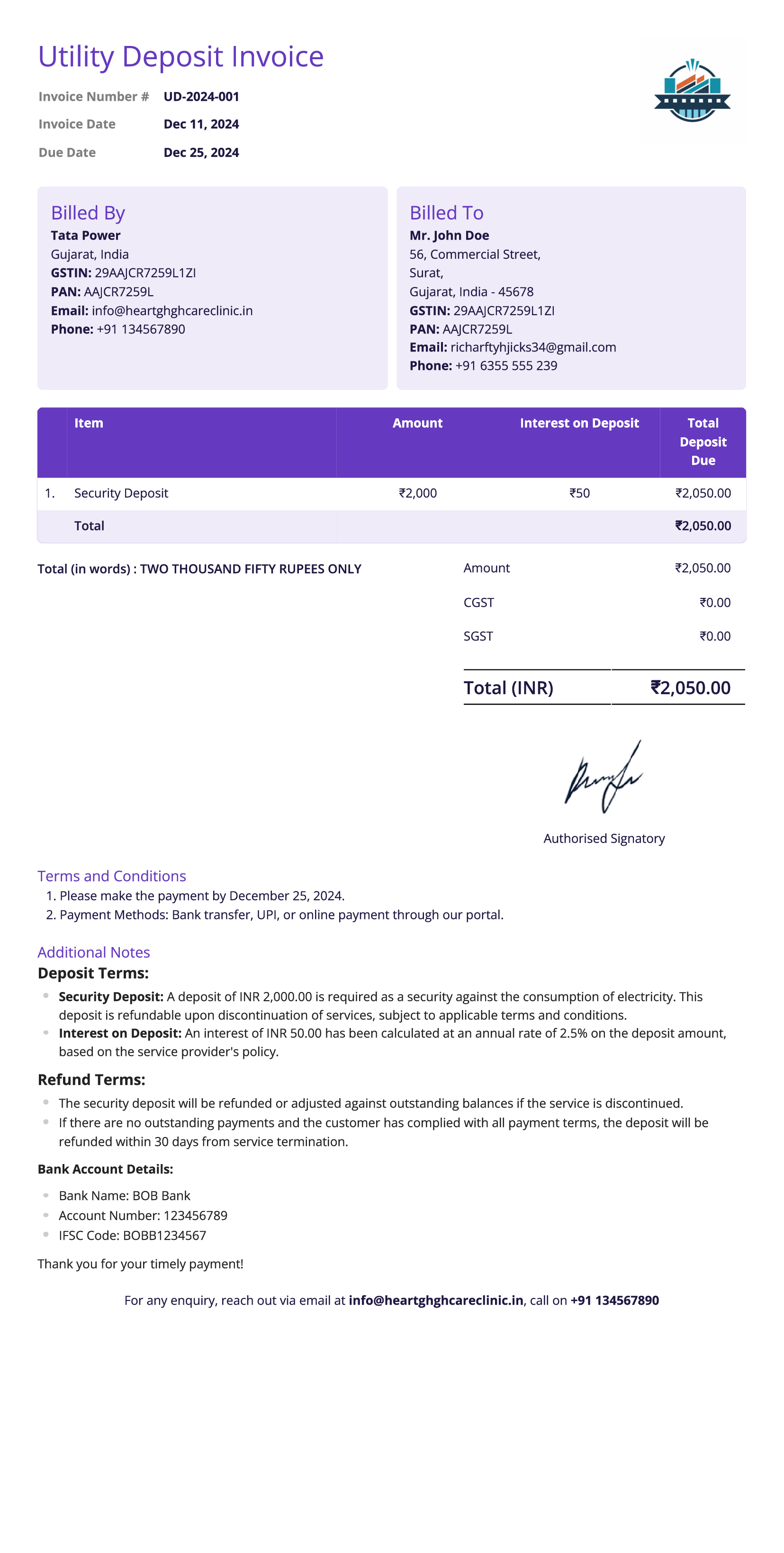
When is it used?
Utility deposit invoices are used when a customer is setting up a new account for utility services, or if they are required to provide additional security due to poor credit history or high usage. The deposit is typically refundable, depending on the terms of service and the customer’s payment history.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the utility deposit invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: The contact details of the utility company and the customer.
- Description of Deposit: A clear description of the deposit amount required and the purpose of the deposit (e.g., security for services rendered).
- Deposit Amount: The exact amount the customer is required to pay as a deposit.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how the deposit should be paid (e.g., payment methods, due date).
- Refund Terms: Information on when and how the deposit will be refunded (if applicable), and under what conditions (e.g., after a certain number of payments or account closure).
- Account Information: The customer’s utility account number and the type of services to which the deposit applies.
- Date of Issue: The date the deposit invoice is issued.
Importance of Utility Deposit Invoice:
A utility deposit invoice helps the utility company secure a financial safety net in case the customer defaults on future payments. It is essential for managing the risk of non-payment, particularly with new customers or those with a history of late payments.
For customers, it serves as clear documentation of the deposit required and the terms surrounding its refund. This invoice helps establish trust and ensures transparency in the terms of service and deposit refund processes. For businesses, utility deposit invoices play a role in maintaining cash flow and mitigating financial risks.
Interest Invoice
Definition:
An interest invoice is issued to charge a customer interest on overdue payments. It specifies the interest due on the outstanding amount, typically based on a percentage rate, and serves as a reminder that the payment was not made within the agreed timeframe.
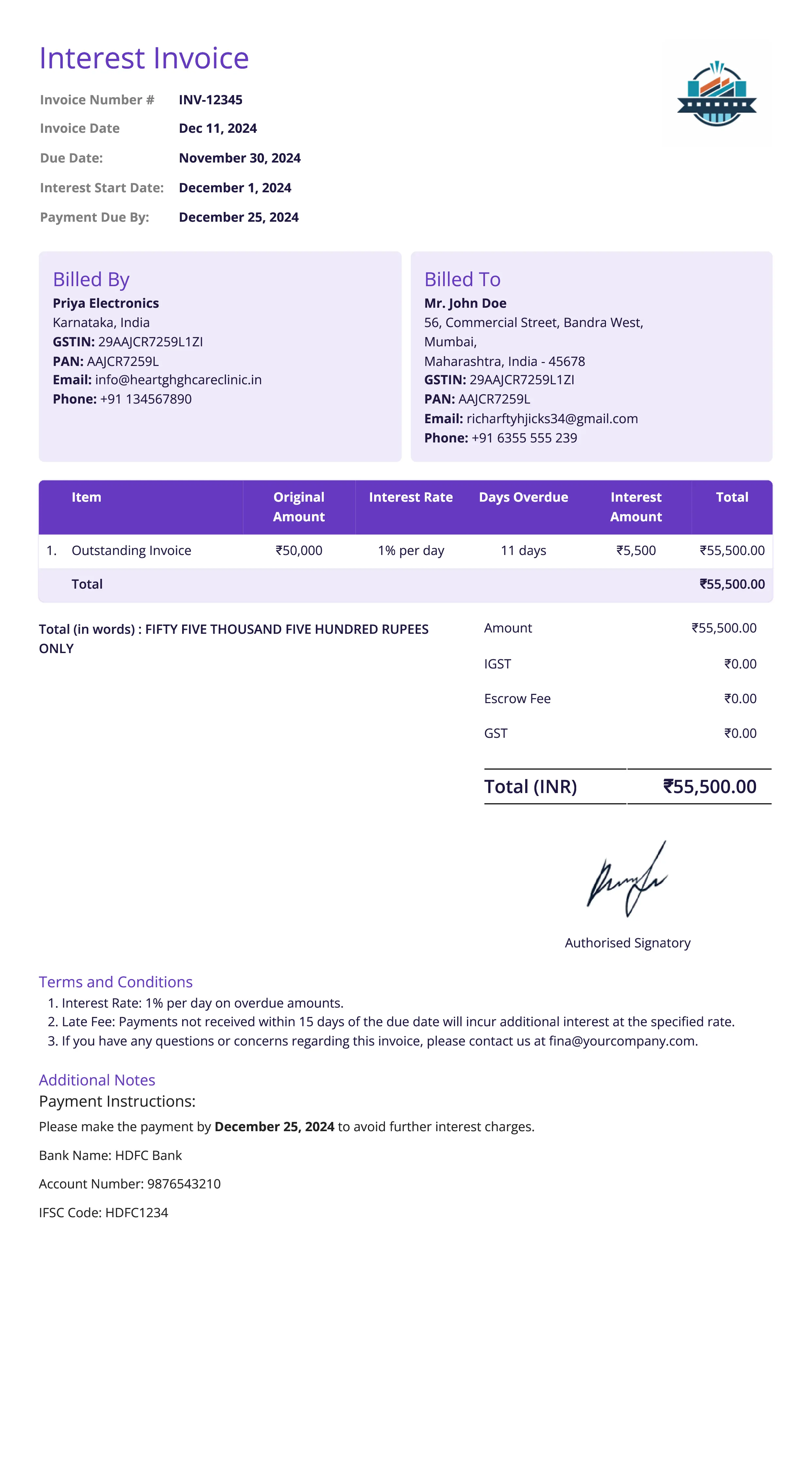
When is it used?
Interest invoices are used when a customer has not paid an invoice by the agreed due date, and the seller charges interest as a penalty for late payment. It helps businesses enforce payment terms and compensate for the delay in receiving funds.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the interest invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details for both the seller and buyer.
- Original Invoice Details: Reference to the original invoice number and the outstanding balance.
- Interest Amount: The amount of interest charged, calculated based on the outstanding balance and the interest rate, along with the period over which interest is being charged.
- Interest Rate: The rate applied to calculate the interest on overdue payments (e.g., 5% annually, or per day/month).
- Total Amount Due (Including Interest): The total amount payable, including the original balance and the interest charge.
- Payment Terms: The due date for paying the interest invoice and any other penalties for further delays.
- Late Payment Details: The date the payment became overdue and the number of days the payment has been late.
Importance of Interest Invoice:
Interest invoices are important for maintaining cash flow and enforcing payment terms. They serve as a deterrent to late payments by financially incentivizing customers to pay on time. For businesses, interest invoices ensure that they are compensated for the delay in payment, which can impact cash flow and profitability. Additionally, they help businesses avoid absorbing the costs of delayed payments and encourage customers to adhere to agreed-upon payment schedules. For customers, receiving an interest invoice serves as a clear reminder of their overdue payment and the consequences of delaying payment further.
Difference Between Interest Invoice and Overdue Invoice:
– An interest invoice specifically charges the customer for interest accrued on overdue payments. It focuses on compensating the seller for the delay in receiving funds and includes details about the interest amount and rate applied.
– An overdue invoice serves as a reminder for the unpaid original invoice. It includes the overdue amount, the original due date, and may mention late fees or penalties, but its primary purpose is to request immediate payment of the outstanding balance.
Key Difference:
Interest invoices charge for the financial penalty of delayed payment, while overdue invoices act as a formal reminder of the unpaid balance.
Reverse Charge Invoice
Definition:
A reverse charge invoice is used in certain tax systems where the buyer, instead of the seller, is responsible for paying the sales tax (e.g., VAT or GST) on the transaction. This typically applies in international transactions or specific industries like construction.
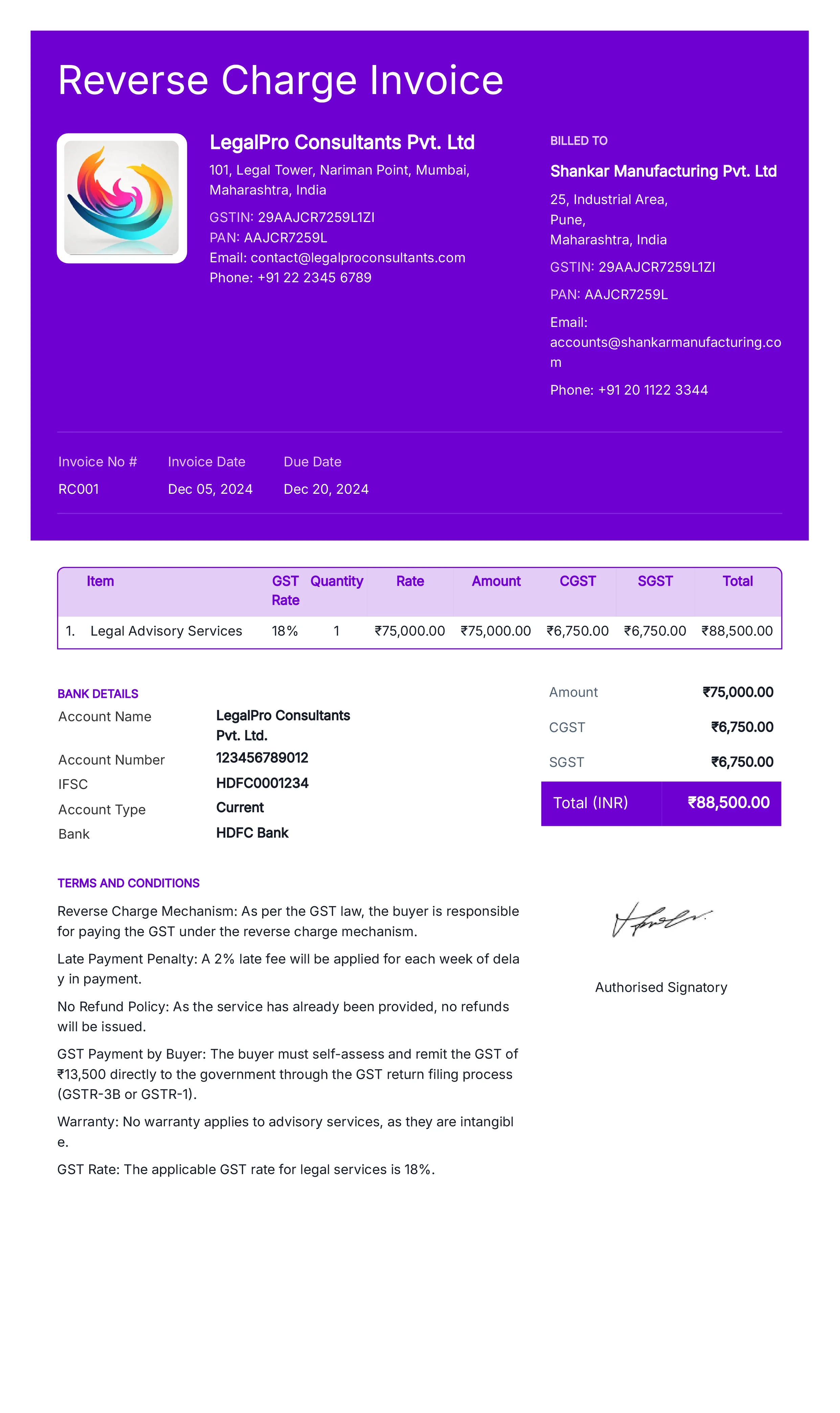
When is it used?
Reverse charge invoices are used when the buyer is required to self-assess and remit the tax to the tax authorities instead of the seller. This is common in cross-border transactions, certain domestic business-to-business (B2B) transactions, and when the goods or services fall under specific tax laws that require the buyer to handle the tax reporting.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the reverse charge invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Full contact details for both the seller and the buyer, including their respective tax identification numbers (TIN or VAT number).
- Description of Goods/Services: A clear description of the goods or services sold, including quantities, unit prices, and total prices.
- Tax Amount and Rate: The tax amount that would normally apply to the transaction, along with the applicable tax rate, but with a note that the buyer is responsible for paying the tax.
- Reverse Charge Statement: A statement indicating that the reverse charge mechanism applies, informing the buyer that they are responsible for paying the tax and reporting it to the tax authorities.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount due for the goods or services without including the sales tax, as the buyer will handle tax payment.
- Date of Transaction: The date the transaction took place or the service was rendered.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how and when the payment is expected for the goods/services, excluding the tax, since the buyer will pay the tax separately.
Importance of Reverse Charge Invoice:
Reverse charge invoices are important for complying with tax laws, particularly in international transactions or certain business sectors. They shift the responsibility of tax payment from the seller to the buyer, which can simplify tax reporting for sellers and ensure tax compliance in cross-border transactions. For businesses, reverse charge invoices reduce the administrative burden of calculating, collecting, and remitting tax on certain transactions. For buyers, this system can streamline the process of tax reporting and payment, particularly if they are able to reclaim the tax through their own tax filings. It also ensures that the right party is held accountable for the correct tax obligations under specific tax laws.
Maintenance Invoice
Definition:
A maintenance invoice is issued for the routine or preventive maintenance services provided by a service provider. It details the charges for repairs, upkeep, and maintenance work done on equipment, machinery, or property.
When is it used?
A maintenance invoice is used when a service provider completes routine maintenance, repairs, or service checks on equipment, machinery, buildings, or other assets. This could be for ongoing contractual maintenance services or one-time repairs.
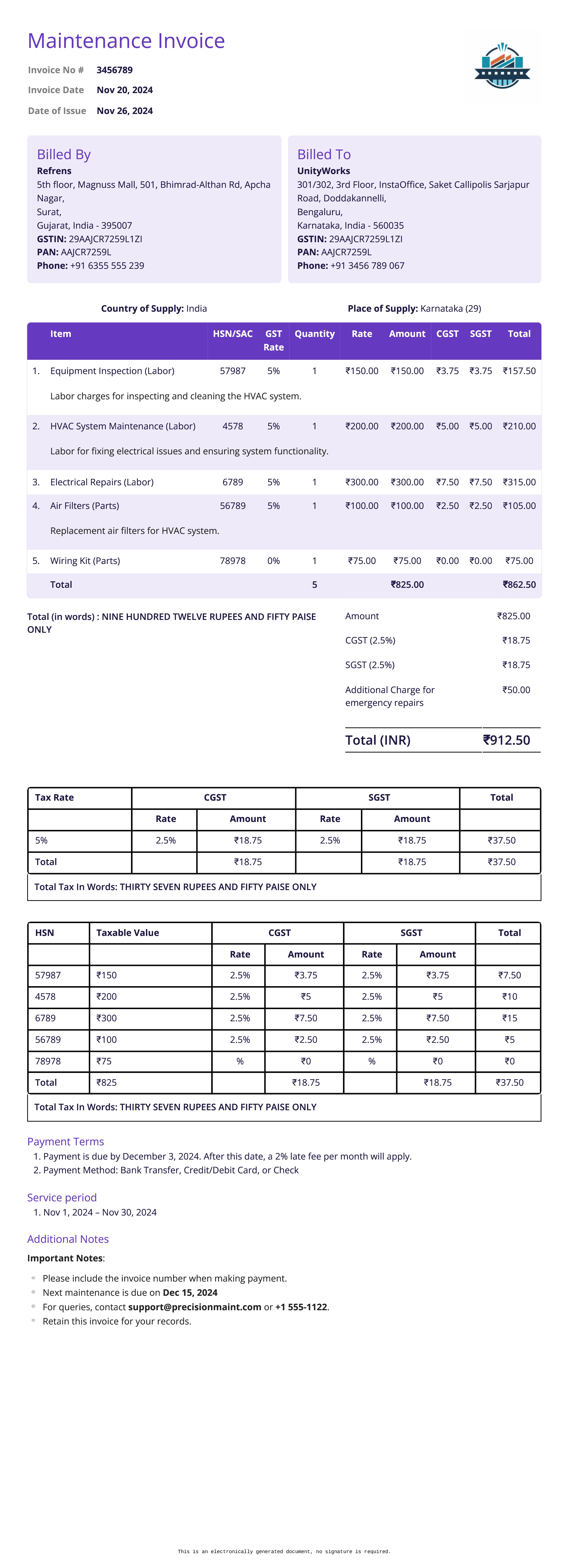
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the maintenance invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: The contact details of both the service provider and the customer.
- Description of Services Provided: A detailed list of maintenance services performed, including specific repairs, checks, or tasks completed.
- Materials and Parts Used: If any materials, spare parts, or equipment were used in the maintenance, these should be listed with quantities and prices.
- Service Charges: The labor or service charges associated with the maintenance work, usually detailed by hours worked or service fees.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount owed, including service charges, parts, and applicable taxes.
- Payment Terms: Instructions on how payment should be made, including the due date and accepted payment methods.
- Date of Service: The date(s) the maintenance service was performed.
Importance of Maintenance Invoice:
Maintenance invoices are important for documenting services related to the upkeep of assets and ensuring that the service provider is paid for their work. For businesses, these invoices help maintain accurate records of maintenance costs and schedule future work or maintenance sessions. They also provide clarity on what services were performed and what parts or materials were used.
For clients, maintenance invoices ensure transparency and provide a clear record of the work completed, which can be useful for budgeting, tax deductions, or warranty claims. This type of invoice also supports the continuity of maintenance contracts, ensuring ongoing services and proper record-keeping.
Installment Invoice
Definition:
An installment invoice is issued when a payment for goods or services is made in installments over a specified period, rather than in a lump sum. It outlines the amount due for each payment along with the payment schedule.
When is it used?
Installment invoices are used when a customer agrees to pay for goods or services over time, such as for high-value items, long-term contracts, or services rendered in stages. This is common for large projects, vehicle purchases, or subscription services with a payment plan.
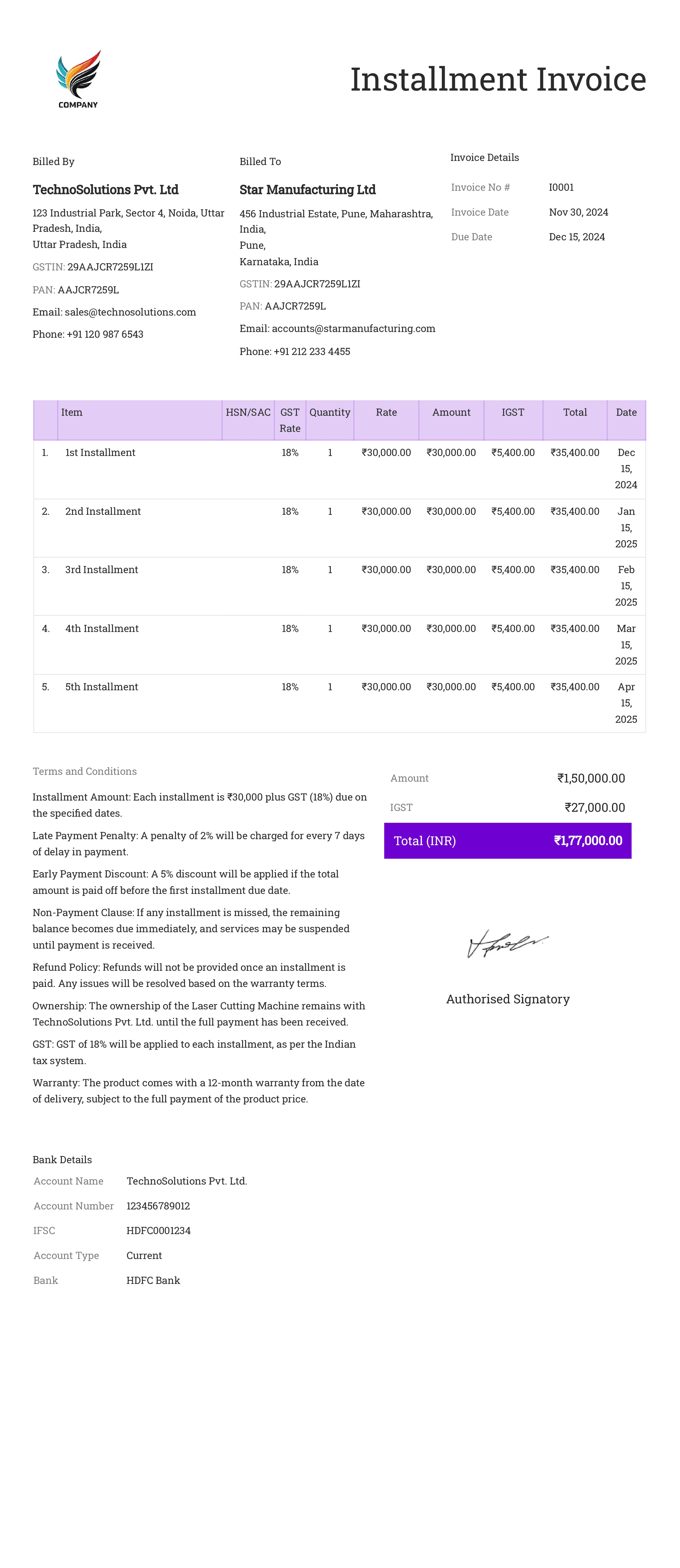
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the installment invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: The contact details of both the seller and the buyer.
- Description of Goods/Services: A clear description of the goods or services being purchased, including any terms of the installment plan (e.g., total amount, individual installment amounts, frequency of payments).
- Installment Amount: The amount due for each installment payment, including any applicable taxes.
- Total Amount Due: The total value of the goods or services, with the remaining balance noted.
- Due Date for Each Installment: The date when each installment is due, along with payment terms (e.g., penalties for late payments).
- Payment Terms: Details of acceptable payment methods and any consequences of missed or late payments.
- Remaining Balance: The outstanding balance after the current installment payment.
- Interest/Finance Charges (if applicable): Any additional charges for financing the purchase through installments, such as interest rates or processing fees.
Importance of Installment Invoice:
Installment invoices are important for businesses as they help in structuring payments for large transactions, making it easier for customers to afford high-cost goods or services. They ensure that businesses receive a steady cash flow throughout the duration of the payment plan, improving financial stability.
For customers, installment invoices provide clarity on payment expectations, allowing them to manage their budgets more effectively. This type of invoice also helps businesses track outstanding balances and payments, ensuring that all agreed-upon terms are met and that the full amount is eventually paid. Additionally, installment invoices may support ongoing relationships by making it easier for customers to commit to longer-term purchases.
Milestone Invoice
Definition:
A milestone invoice is issued when a specific stage or milestone of a project is completed, and payment is requested based on the achievement of that milestone. It is commonly used in project-based industries such as construction, consulting, and software development.
When is it used?
Milestone invoices are used in projects where work is divided into distinct stages or milestones. These invoices are issued when a milestone is reached, and they ensure that the service provider is paid for the progress made before the final project completion.
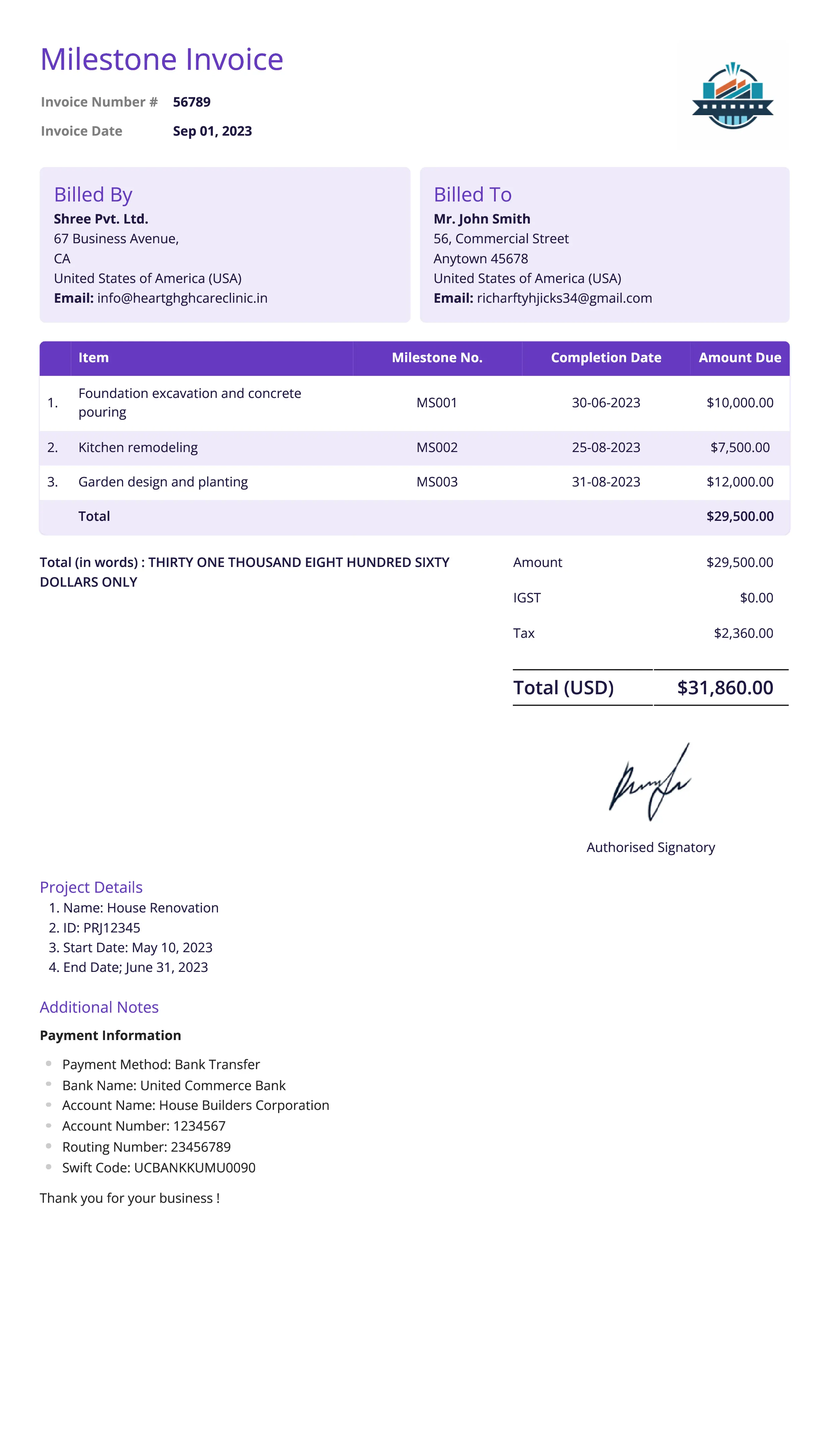
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the milestone invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Contact details of both the seller (service provider) and the buyer (client).
- Description of Milestone: A detailed description of the completed stage or milestone, outlining the specific deliverables or tasks that were accomplished.
- Amount Due: The amount due for the milestone achieved, which is usually a portion of the total project cost.
- Total Project Cost: The total agreed-upon cost for the entire project, with the amount already paid and the remaining balance.
- Payment Terms: Information on how and when the payment for the milestone is due, including payment methods, due dates, and penalties for late payments.
- Progress Summary: A summary of the project’s progress, indicating the percentage of completion or the number of milestones achieved.
- Date of Milestone Achievement: The date when the milestone was completed.
- Remaining Milestones: A list of future milestones and when they are expected to be reached.
Importance of Milestone Invoice:
Milestone invoices are important for managing cash flow during long-term or complex projects. They ensure that the service provider is compensated for the work completed at various stages, preventing financial strain. These invoices also provide transparency and accountability for both parties, as clients can see the progress made and ensure that the work aligns with expectations before making payments.
Milestone invoicing reduces the risk of non-payment for service providers and aligns payments with project achievements. For clients, milestone invoices allow them to pay incrementally, ensuring they are paying for work as it is completed, while also motivating the provider to meet specific project goals on time.
Difference Between Milestone Invoice and Interim Invoice
– A milestone invoice is tied to the completion of specific project stages or deliverables. Payment is requested only after a predefined milestone is achieved, with a focus on aligning payments to project accomplishments.
– An interim invoice is issued periodically, often based on time intervals (e.g., monthly), to request partial payment for ongoing work or progress, regardless of whether a specific milestone has been completed.
Key Difference:
Milestone invoices are deliverable-driven and linked to project achievements, while interim invoices are time-driven, ensuring consistent cash flow during the project.
Advance and Retainer Invoice
Definition:
An advance and retainer invoice is issued to request a payment upfront before goods or services are delivered. This invoice is typically used to secure partial payment or full payment in advance for products, services, or projects that require upfront capital investment.
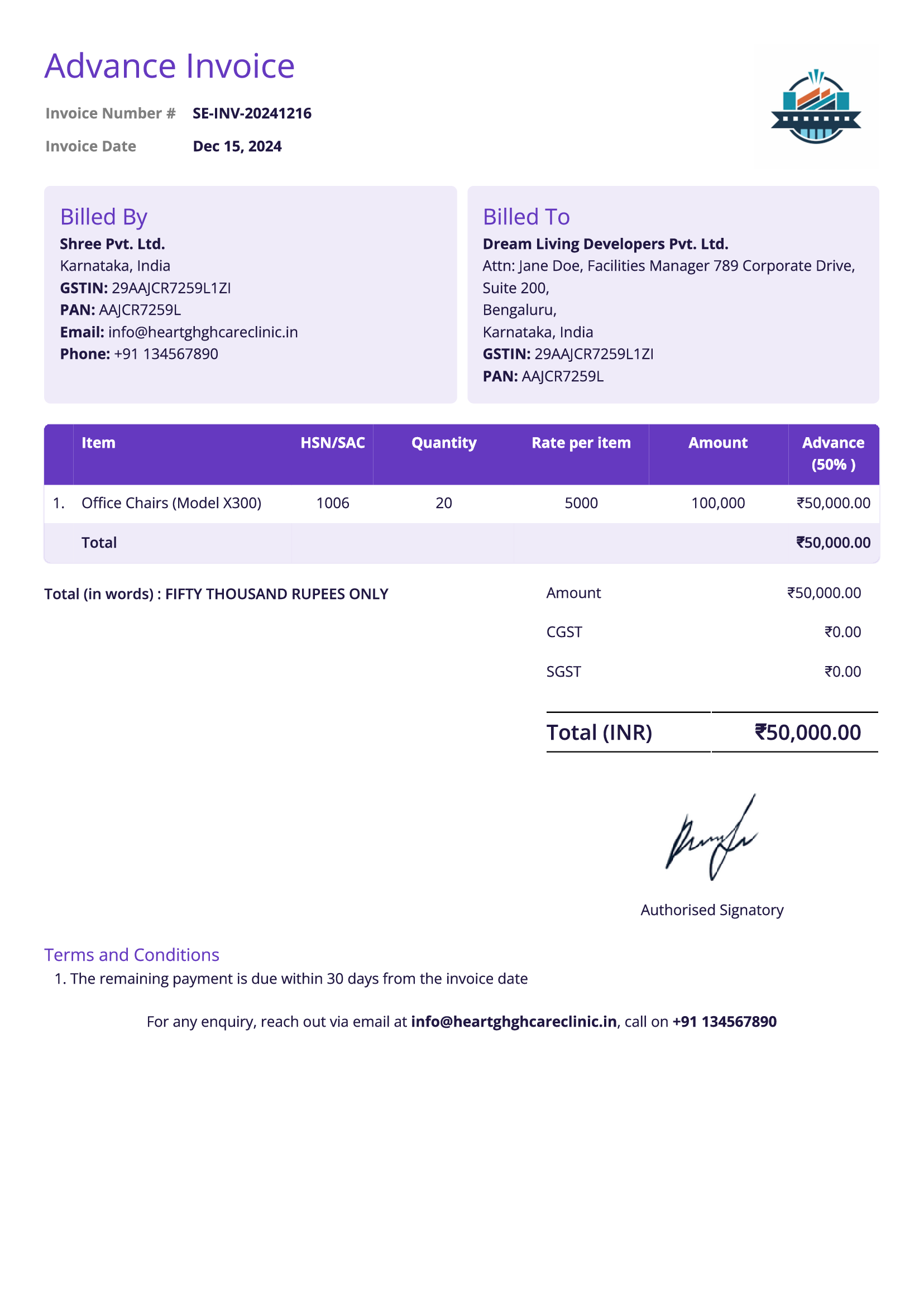
When is it used?
Advance invoices are used when a business requires upfront payment to initiate or secure a transaction. This is common in industries like construction, event planning, custom manufacturing, or any situation where significant resources need to be committed before the actual delivery of goods or services.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the advance invoice.
- Seller and Buyer Information: The contact details of both the seller and the buyer.
- Description of Goods/Services: A description of the goods or services that the advance payment will cover, even if the final delivery is scheduled for a later date.
- Advance Payment Amount: The amount requested as an advance, often a percentage of the total cost or the full amount.
- Total Amount Due: The total value of the goods or services being provided, with a clear distinction between the advance amount and any remaining balance.
- Payment Terms: Terms for how and when the advance payment should be made, including the payment methods and due dates.
- Due Date for Remaining Balance: The due date for the final payment once the goods/services have been delivered or the project is completed.
- Purpose of Advance Payment: A statement outlining the reason for the advance payment (e.g., securing materials, starting work, etc.).
Importance of Advance and retainer Invoice:
An advance and retainer invoice is crucial for securing payments before committing to the full provision of goods or services, which is especially important for businesses that require upfront capital or need to cover initial costs. It protects the seller by ensuring that some level of financial commitment is made before beginning work, reducing the risk of non-payment.
For customers, an advance invoice clarifies the payment expectations and provides transparency regarding the payment schedule. It also establishes a formal agreement between both parties, outlining the agreed-upon terms for advance payments and future payments. For businesses, it helps manage cash flow, especially when large projects or significant purchases are involved
Industry-Specific Invoices
Work Order Invoice
Definition:
A work order invoice is issued for services rendered based on a previously agreed-upon work order. It outlines the work completed according to the client’s specifications and serves as a billing document for those services.
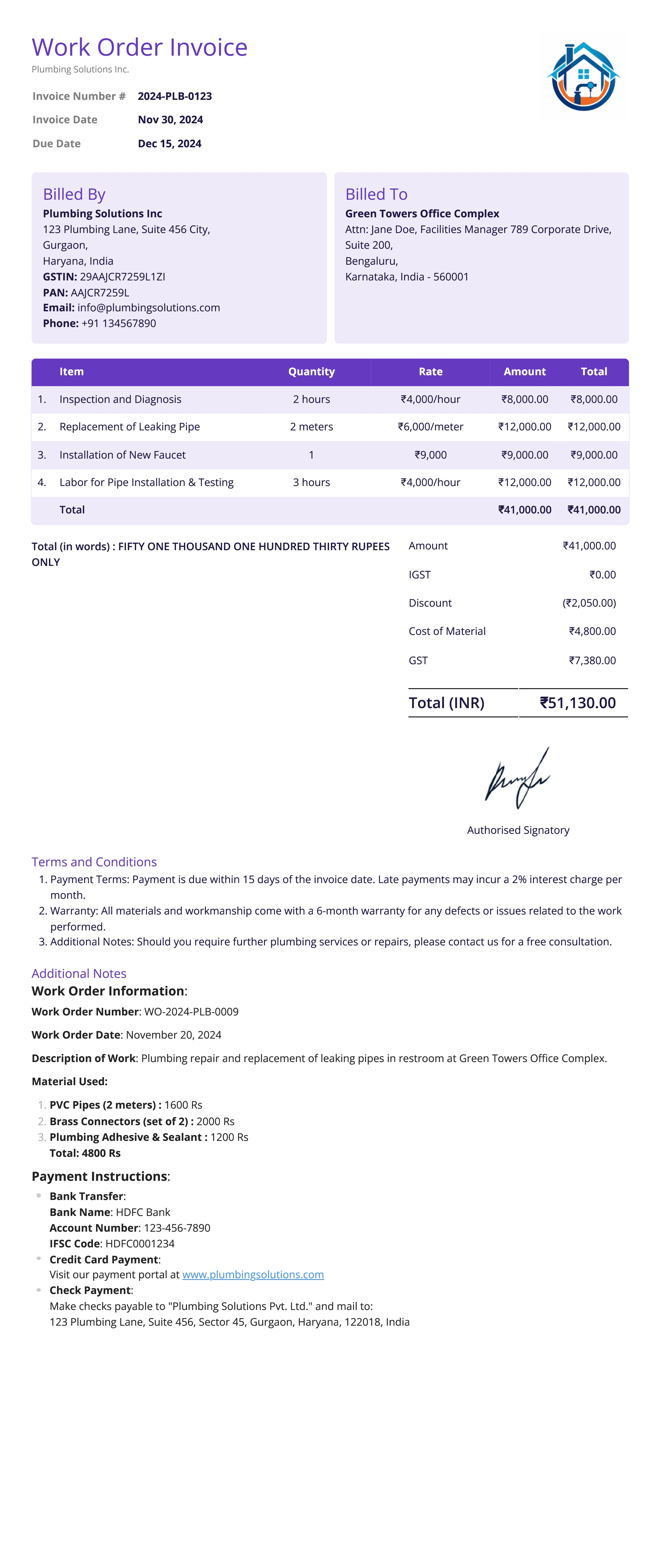
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the work order invoice.
- Client Information: Name, address, and contact details of the client.
- Service Provider Information: The name, address, and contact details of the service provider.
- Work Order Reference Number: A reference to the work order number, linking the invoice to the agreed-upon services.
- Service Description: Detailed description of the services provided as per the work order, including dates and specific tasks completed.
- Labor Charges: Charges for labor, broken down by hours worked and hourly rate, if applicable.
- Materials Used: List and cost of any materials used or supplied, as specified in the work order.
- Additional Fees: Any additional charges, such as travel fees or equipment rentals, not initially included in the work order but necessary for completion.
- Total Amount Due: The total payment required, summing labor, materials, and any additional fees.
- Due Date: The payment due date as per the agreed terms.
- Payment Terms: Payment instructions, including accepted methods and potential late fees
Freelancer Invoice
Definition:
A freelancer invoice is a billing document tailored for freelance work. It lists the services provided, such as hours worked or completed project milestones, and requests payment from the client.
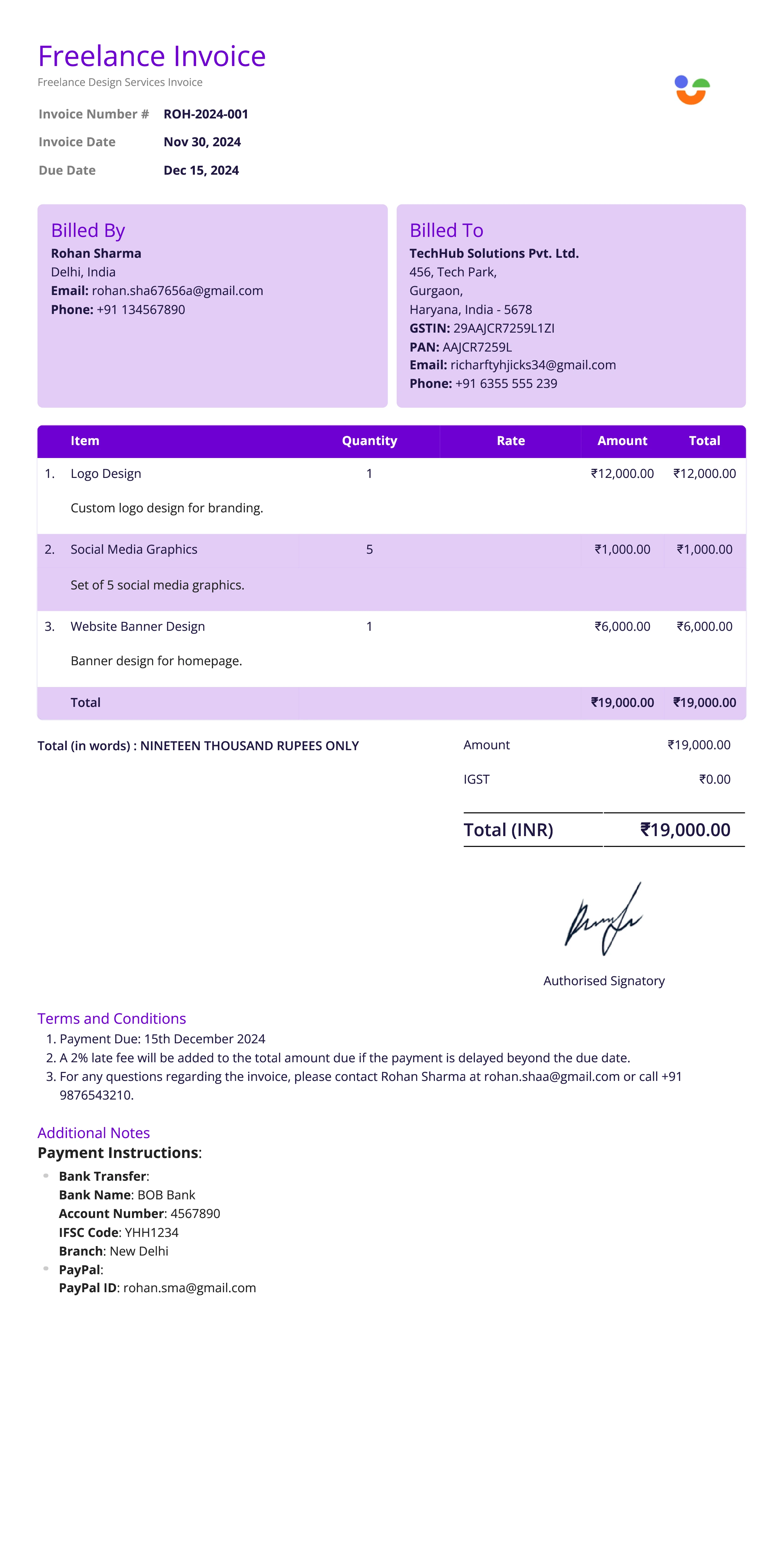
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for tracking the invoice.
- Freelancer Information: Name, address, contact details, and sometimes a business or tax ID for the freelancer.
- Client Information: Name, address, and contact details of the client.
- Project or Service Description: Brief description of the project or services rendered, such as “content writing” or “graphic design.”
- Hours Worked or Milestone Achieved: Breakdown of the hours worked with the hourly rate or a description of completed milestones (if billed per milestone).
- Project Rate or Hourly Rate: The agreed-upon rate, either hourly or per project, multiplied by hours or project portion completed.
- Additional Expenses (if applicable): Any reimbursable expenses, such as travel or software costs, approved by the client.
- Total Amount Due: Sum of all charges, including hourly/milestone rates and expenses.
- Due Date: Payment due date per the agreement terms.
- Payment Terms and Methods: Accepted payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, PayPal) and any late fees if payment is delayed.
Check out our list of the best invoicing software for freelancers, tailored to help you streamline your billing process and manage payments effortlessly. Plus, explore our guide on how to invoice for freelance work to ensure you get paid accurately and on time.
Professional Services Invoice
Definition:
A professional services invoice is issued by consultants, lawyers, architects, or other professional service providers to request payment for services rendered. This invoice often reflects billable hours, specialized tasks, or consultations provided.
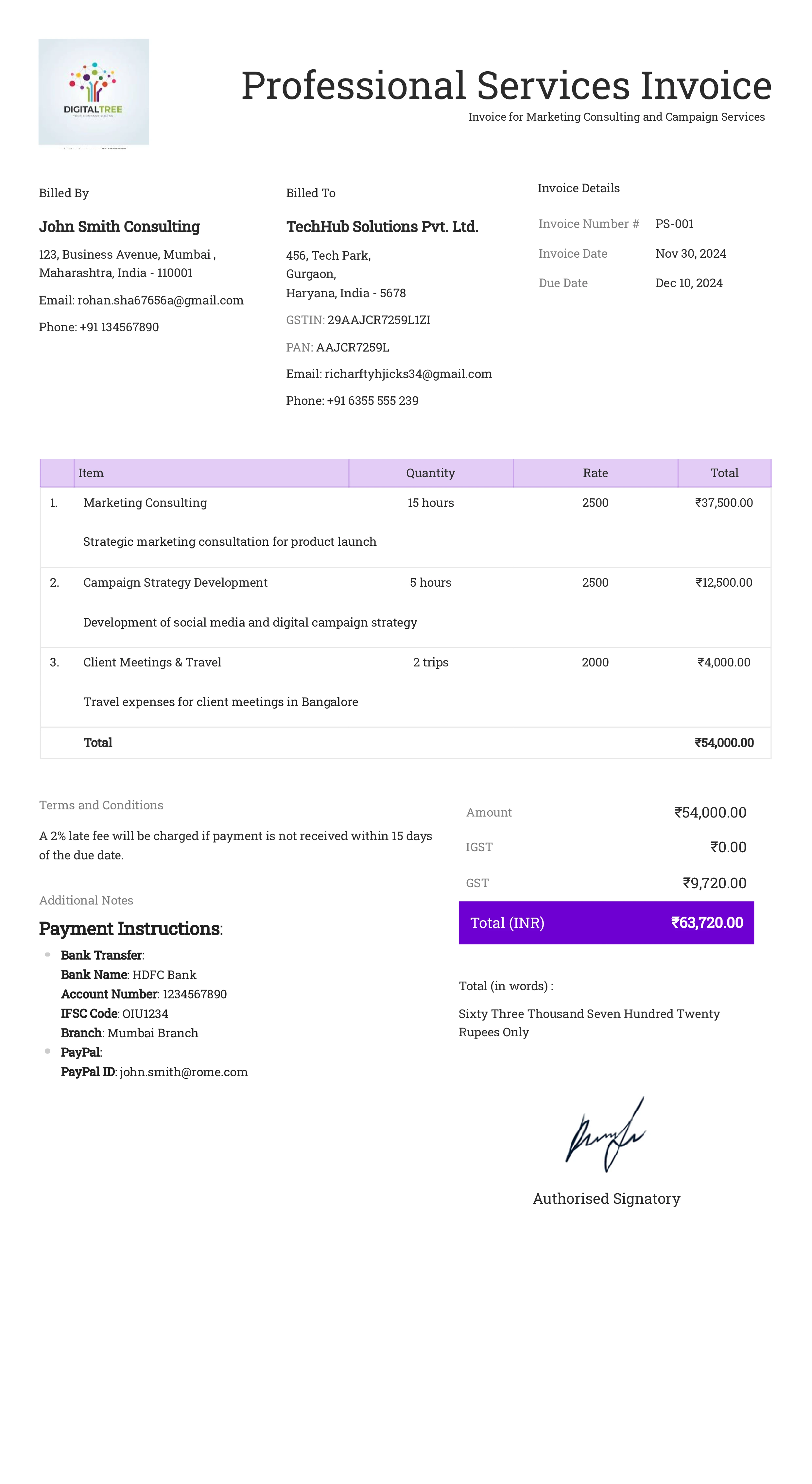
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the professional services invoice.
- Service Provider Information: Name, business address, contact details, and any relevant licensing or certification numbers.
- Client Information: Name, address, and contact details of the client receiving the services.
- Service Description: Detailed description of the professional services provided, such as consulting, legal advice, or architectural planning, including dates and any session details.
- Billable Hours or Task-Based Charges: Breakdown of time spent on each service task with corresponding hourly or flat rates.
- Additional Charges (if applicable): Any extra charges, such as travel expenses, filing fees, or materials used, that were agreed upon beforehand.
- Subtotal and Taxes: The subtotal of all charges with applicable taxes, based on local or professional requirements.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount owed, including services, taxes, and additional fees.
- Due Date: The payment due date, often reflecting net 30 or 45 days.
- Payment Terms: Accepted payment methods and any penalties for late payment.
Healthcare Invoice
Definition:
A healthcare invoice is issued by healthcare providers, such as doctors, clinics, or hospitals, to request payment for medical services, procedures, or treatments provided to patients. This invoice may include consultation fees, diagnostic tests, treatments, and medications.
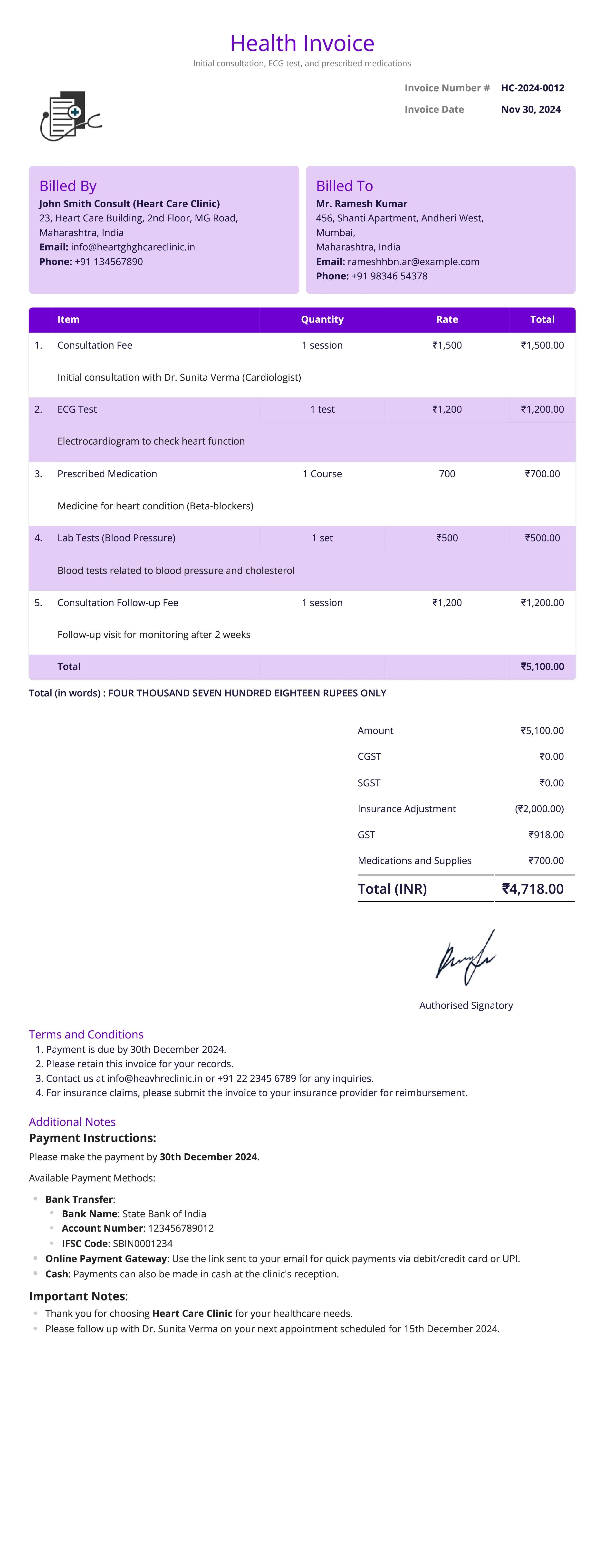
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the healthcare invoice.
- Patient Information: Name, address, contact details, and potentially insurance information of the patient.
- Healthcare Provider Information: Name, address, contact details of the provider, and any relevant professional credentials.
- Service Date(s): Date(s) when the healthcare services were rendered.
- Service Description: Detailed list of medical services provided, such as consultations, tests, surgeries, or therapies, along with codes if applicable.
- Itemized Charges: Cost breakdown for each service, treatment, or medication provided.
- Insurance Details (if applicable): Insurance provider information, co-pay amounts, or deductible details, if covered by insurance.
- Total Charges Before Insurance Adjustment: The total amount before insurance contributions, if any.
- Insurance Adjustments or Discounts: Any adjustments, discounts, or co-payments covered by insurance.
- Patient’s Total Due: The remaining amount owed by the patient after insurance deductions, if applicable.
- Payment Due Date: Date by which payment is expected.
- Payment Instructions: Accepted methods of payment, such as card, bank transfer, or cash.
Consignment Invoice
Definition:
A consignment invoice is used when goods are sent to a consignee, often a retailer, who sells the goods on behalf of the consignor (owner of the goods). Payment is typically made to the consignor only after the goods are sold. This invoice details the items consigned and sets the terms for the consignment sale.
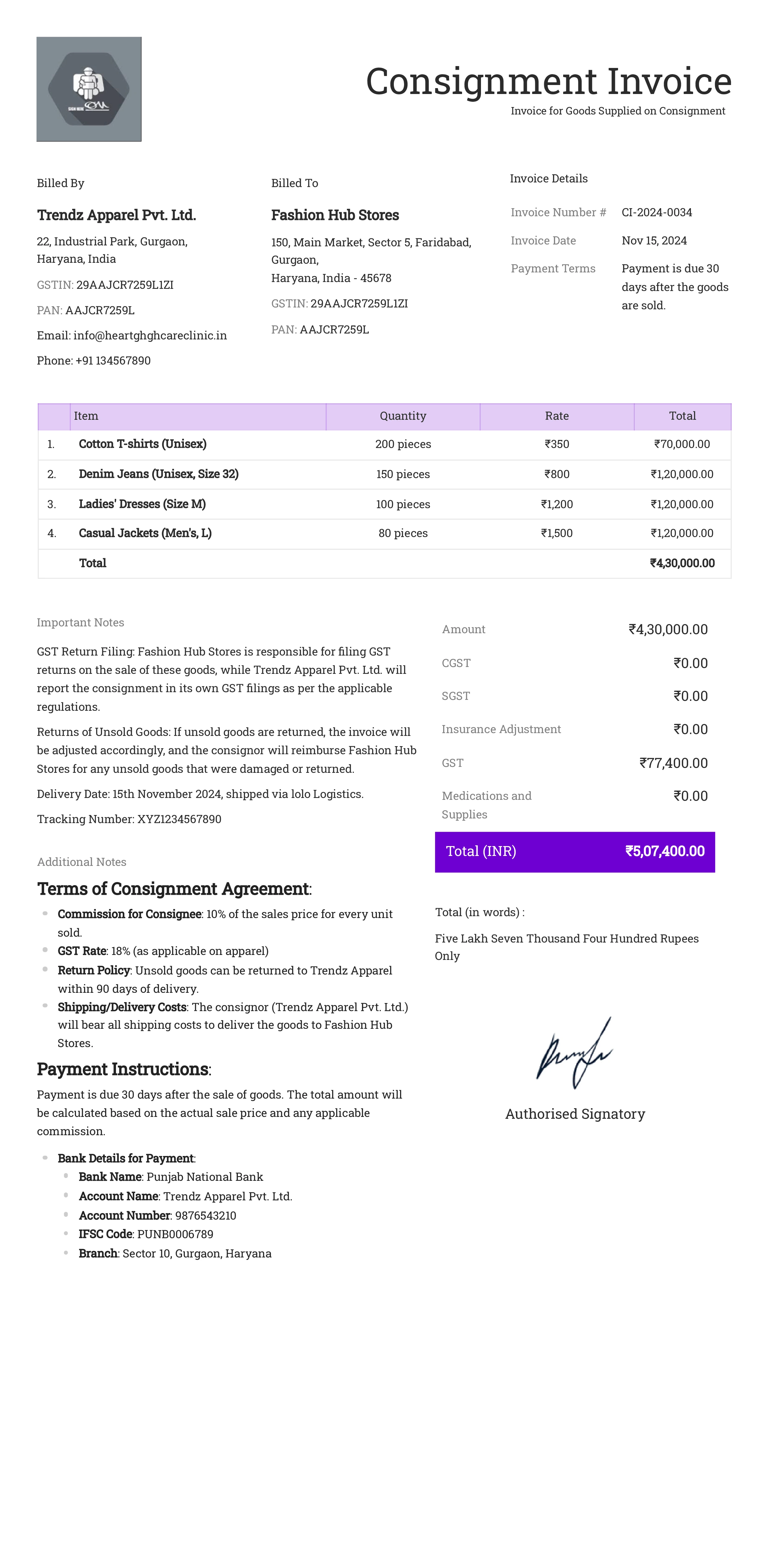
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the consignment invoice.
- Consignor Information: Name, address, and contact details of the consignor (owner of the goods).
- Consignee Information: Name, address, and contact details of the consignee (party receiving the goods).
- Consignment Agreement Reference: Reference number or details of the consignment agreement.
- Description of Goods: Detailed list of items sent on consignment, including item names, quantities, and specifications.
- Unit Price or Wholesale Price: The agreed-upon price per item, often the wholesale or cost price.
- Commission Rate (if applicable): The consignee’s commission rate on sold items, if applicable.
- Payment Terms: The terms of payment to the consignor after items are sold, such as payment within a certain number of days after each sale.
- Consignment Period: The duration for which the consignee holds the goods before returning unsold items or settling payment.
- Total Value of Goods Consigned: The total value of the goods sent on consignment, calculated based on the unit price and quantity.
- Return Policy: Any conditions for returning unsold items or handling damaged goods.
Drop Shipping Invoice
Definition:
A drop shipping invoice is issued for goods sold through a drop shipping arrangement, where the seller takes an order but a third-party supplier ships the goods directly to the buyer. The invoice details the sale and outlines payment terms between the seller and the buyer.
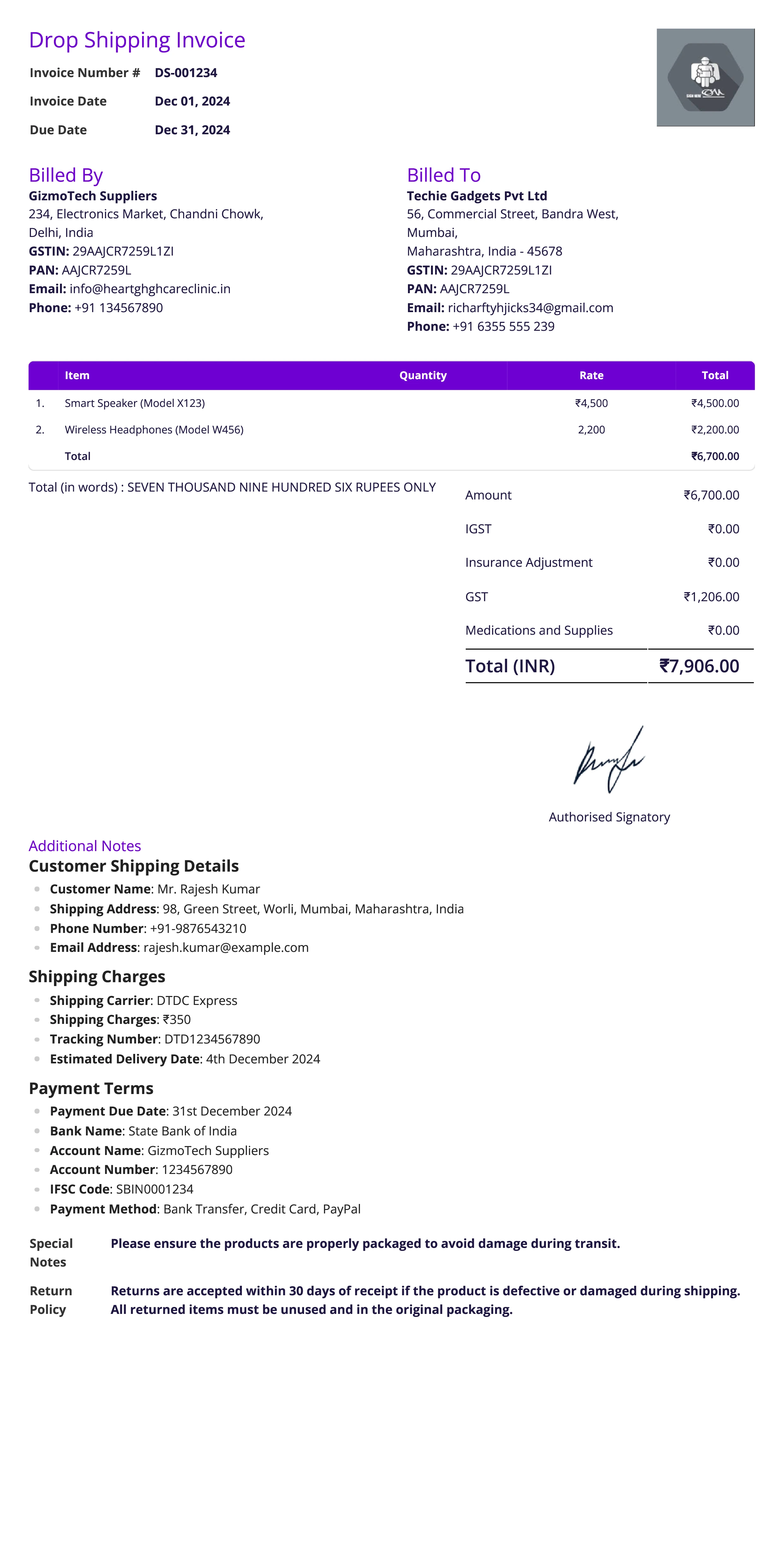
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the drop shipping invoice.
- Seller Information: Name, address, and contact details of the seller (who facilitated the sale but doesn’t handle shipping).
- Buyer Information: Name, address, and contact details of the buyer (end customer).
- Supplier/Manufacturer Information: Name and address of the third-party supplier fulfilling the order, if applicable for reference.
- Order Details: A list of items purchased, including descriptions, quantities, and item numbers.
- Unit Price and Total Cost: The price per unit and the total amount owed by the buyer for each item.
- Shipping Details: Shipping method, estimated delivery time, and any shipping charges applied to the buyer.
- Total Amount Due: The total cost for the goods and any additional fees, such as shipping and handling.
- Payment Terms: Payment methods and any terms agreed upon (e.g., immediate payment, net 30).
- Drop Shipping Arrangement Reference: Reference to the drop shipping arrangement, if applicable, such as an order or contract number.
Commission Invoice
Definition:
A commission invoice is issued by agents or salespeople to claim their commission on a sale or transaction they facilitated. It outlines the percentage or fixed fee earned on the total sales amount.
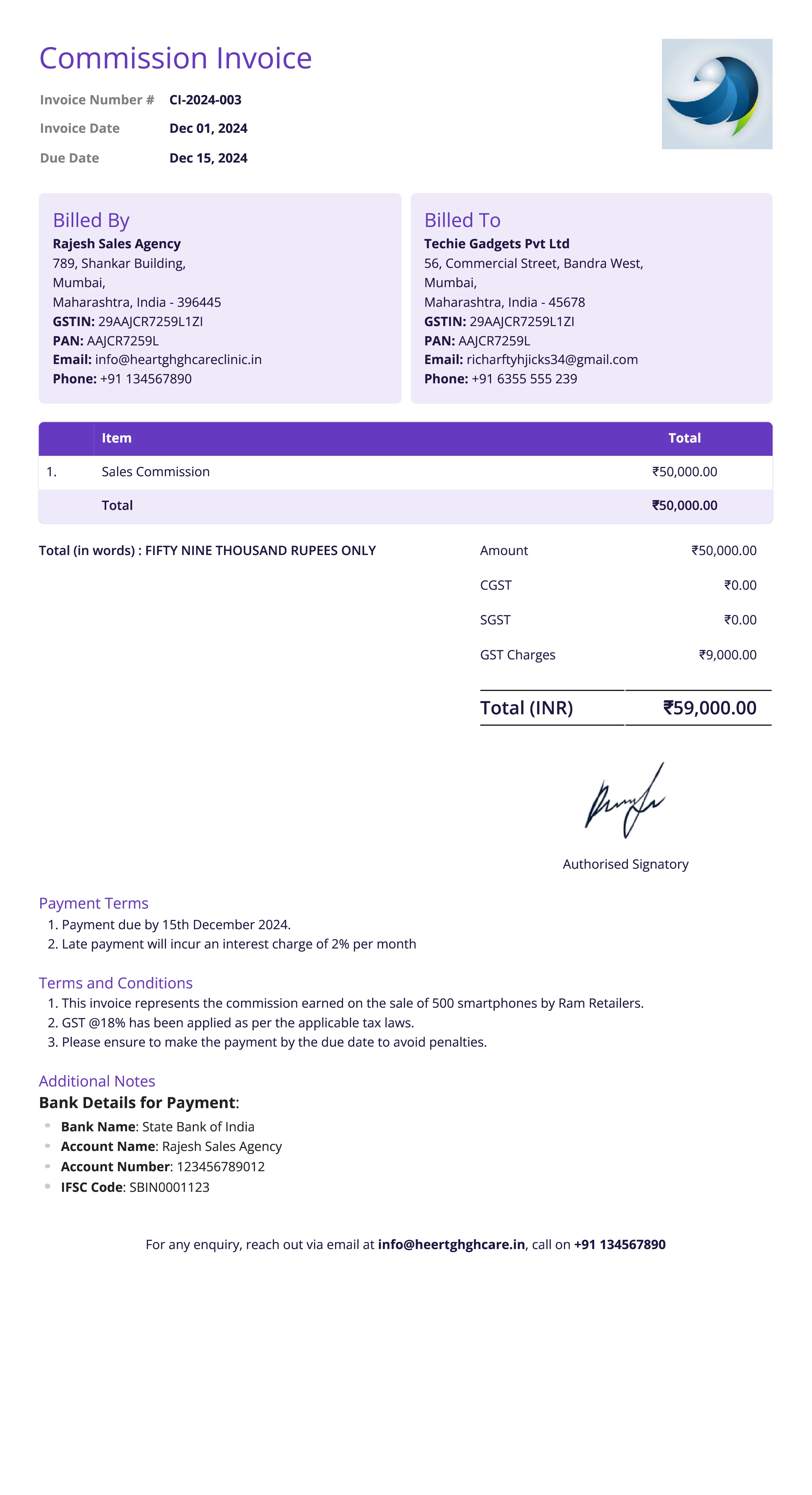
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the commission invoice.
- Salesperson/Agent Information: Name, address, and contact details of the person or agency receiving the commission.
- Client Information: Name, address, and contact details of the client who made the purchase or deal.
- Sale Details: Description of the sale or transaction, including the goods or services sold, sale date, and relevant contract numbers.
- Total Sale Amount: The full value of the sale or transaction, from which the commission will be calculated.
- Commission Percentage or Flat Fee: The agreed commission rate or flat fee based on the sale amount.
- Commission Amount: The exact amount the salesperson/agent is entitled to, calculated based on the sale amount and commission rate.
- Payment Terms: The terms of payment, such as the due date, and accepted payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, check).
- Due Date: The date by which the commission payment is due.
Customs Invoice
Definition:
A customs invoice is issued for international shipments and is required by customs authorities to assess duties and taxes on imported goods. It provides a detailed description of the items being shipped, their value, and other necessary information to clear goods through customs.
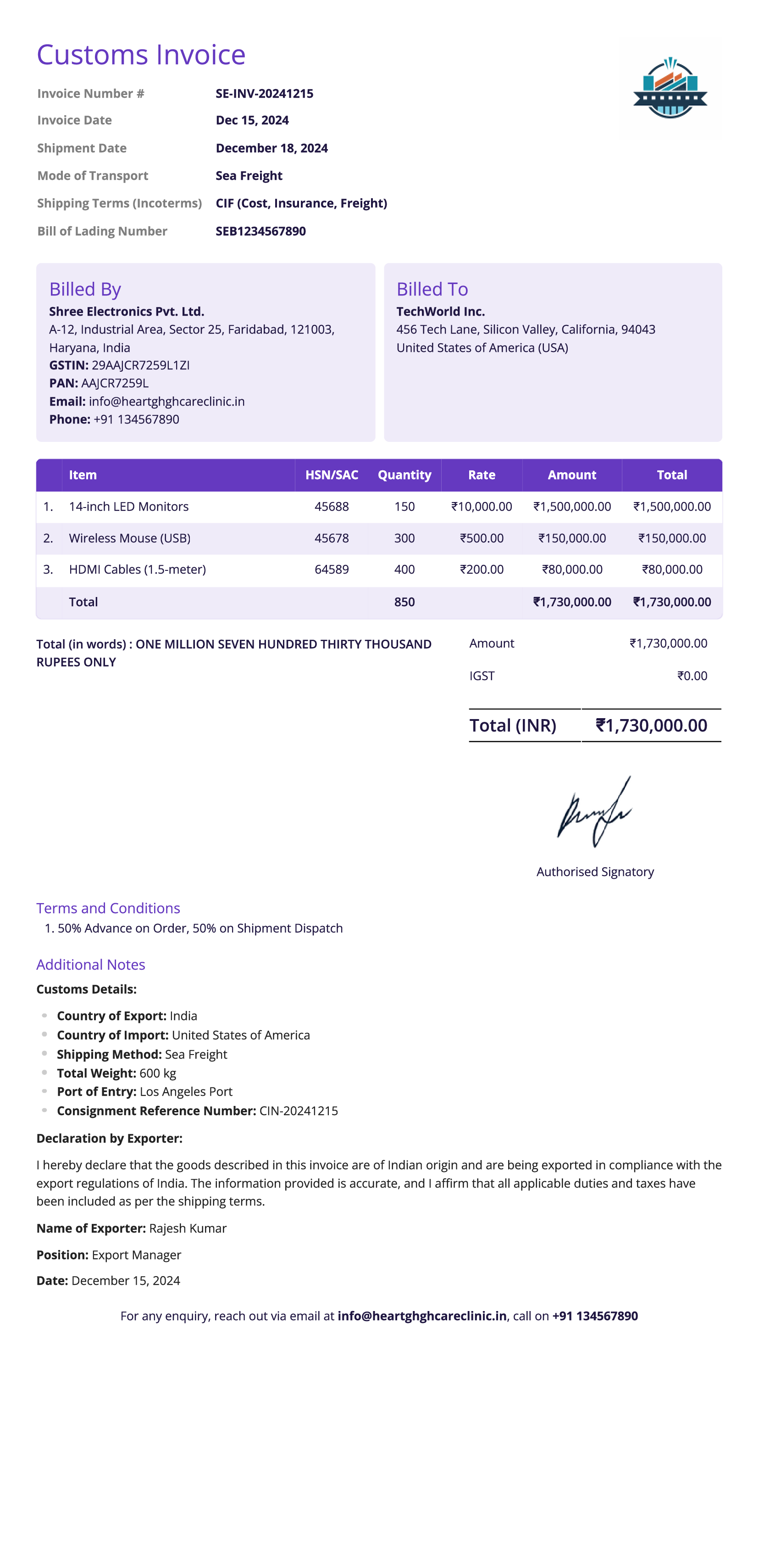
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the customs invoice.
- Seller Information: Name, address, and contact details of the seller/exporter.
- Buyer Information: Name, address, and contact details of the buyer/importer.
- Shipping Information: Shipping method, tracking number, and shipping company.
- Description of Goods: Detailed list of items being shipped, including descriptions, quantities, and Harmonized System (HS) codes for customs classification.
- Unit Value and Total Value: The declared value for each item, and the total value of the shipment.
- Country of Origin: The country where the goods were manufactured or produced.
- Incoterms: Terms indicating the shipping and responsibility details (e.g., FOB, CIF).
- Currency Used: The currency in which the invoice is issued (e.g., USD, EUR).
- Tax and Duty Details: Any applicable customs duties, taxes, or fees related to the shipment, if pre-paid or included.
- Declaration Statement: A statement certifying that the information provided is accurate, often signed by the seller or exporter.
The customs invoice format often requires a very detailed and specific layout to meet customs requirements, including customs codes and international trade terms.
Donation Invoice
Definition:
A donation invoice is issued by a charity or non-profit organization to acknowledge a donation made by an individual or entity. It serves as proof of donation for tax purposes and often includes specific details about the donation for the donor’s records.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the donation invoice.
- Donor Information: Name, address, and contact details of the donor (individual or organization).
- Charity Information: Name, address, and contact details of the charity or non-profit organization.
- Donation Date: The date when the donation was made.
- Donation Amount: The total amount donated, including any applicable breakdown (e.g., cash, goods, or services).
- Donation Description: A brief description of the donation, such as “cash donation” or “donation of goods.”
- Tax-Deductible Status: A statement confirming that the donation is tax-deductible, if applicable, based on the organization’s non-profit status.
- Acknowledgment Statement: A statement of thanks for the donation, often expressing appreciation for the donor’s support.
- Total Value of Donation: The total amount of the donation, which may include separate line items for cash, goods, and services if applicable.
- Donor’s Signature (optional): If required by the donor or for legal purposes, the signature of the donor or a representative from the charity organization.
This invoice format ensures clarity and provides necessary information for the donor to claim tax benefits, typically including a non-profit tax ID number and acknowledgment of the donation’s value.
Audit Invoice
Definition:
An audit invoice is issued by an accounting or audit firm after performing auditing services for a client. It details the services provided, such as reviewing financial statements, compliance checks, and other financial examinations, and requests payment for those services.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the audit invoice.
- Audit Firm Information: Name, address, contact details, and any professional credentials or registration numbers of the audit firm.
- Client Information: Name, address, and contact details of the client being audited.
- Audit Scope Description: A brief description of the audit services provided, such as “Annual Financial Statement Audit” or “Tax Compliance Review.”
- Time Charges: If billed by the hour, the number of hours worked, along with the hourly rate.
- Fixed Fees (if applicable): If the audit services are billed at a fixed price, the agreed-upon amount for the entire audit.
- Expenses (if applicable): Additional charges, such as travel or out-of-pocket costs incurred during the audit process.
- Subtotal and Taxes: The subtotal of the charges with applicable taxes (e.g., VAT) based on the services provided.
- Total Amount Due: The total payment required for the audit services.
- Payment Terms: Accepted payment methods and payment due date (e.g., net 30 or 45 days).
- Audit Report Reference: If applicable, a reference to the audit report or document produced during the audit.
Auction Invoice
Definition:
An auction invoice is issued for goods or services purchased at an auction. It serves as a formal request for payment from the buyer and includes details of the items sold, the winning bid, and any additional fees or charges related to the auction process.
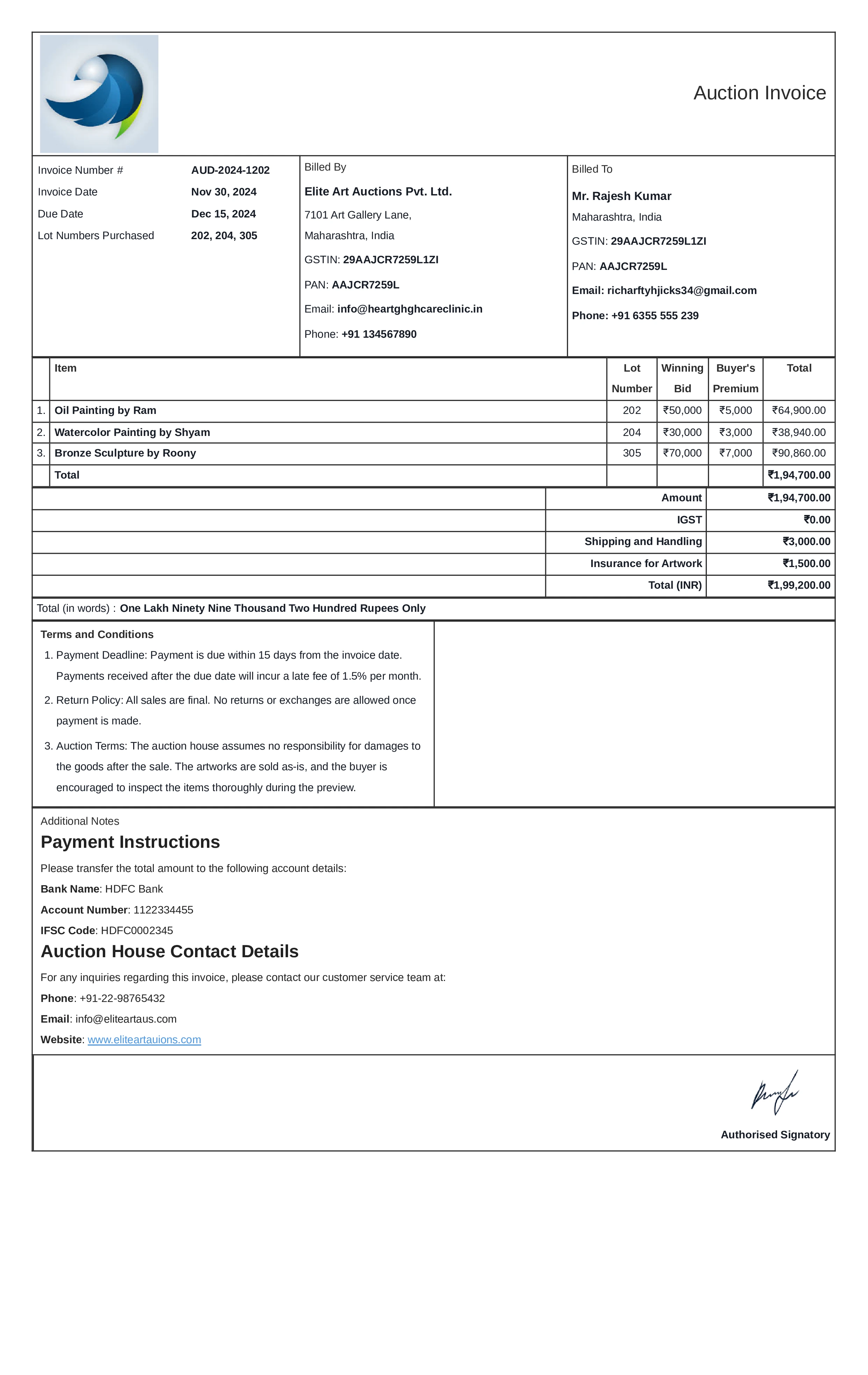
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the auction invoice.
- Auction House Information: Name, address, and contact details of the auction house or organization running the auction.
- Buyer Information: Name, address, and contact details of the buyer.
- Lot Number or Item Description: The auction lot number or detailed description of the items purchased, including quantities and any item-specific identifiers (e.g., serial numbers).
- Winning Bid Amount: The price at which the buyer successfully bid for the item.
- Buyer’s Premium: A percentage or fixed fee added to the winning bid (typically a commission charged by the auction house).
- Taxes and Duties: Any applicable taxes, such as sales tax or VAT, that apply to the auction purchase.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount owed by the buyer, including the winning bid, buyer’s premium, and taxes.
- Payment Terms: Accepted payment methods and due date for payment (e.g., immediate payment or within a certain number of days after the auction).
- Shipping and Handling Charges: If applicable, the cost of shipping or handling fees for the item(s) won at the auction.
The auction invoice format may require additional auction-specific details, such as auction lot details or buyer’s premium calculations. The clear itemization of charges ensures the buyer is fully informed of the costs associated with their purchase.
Warranty Invoice
Definition:
A warranty invoice is issued for services provided under a warranty agreement. This type of invoice is used when a product or service requires repair, replacement, or maintenance under its warranty terms, and payment may be required for additional services not covered by the warranty.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the warranty invoice.
- Service Provider Information: Name, address, and contact details of the company or technician providing the warranty service.
- Customer Information: Name, address, and contact details of the customer receiving the warranty service.
- Warranty Agreement Reference: Reference to the warranty agreement number or terms under which the service is provided.
- Description of Service or Parts: A detailed list of the services or parts provided under the warranty, including the nature of the repair, replacement, or maintenance performed.
- Cost of Additional Services: If any part of the service is not covered under warranty, it will be clearly stated with corresponding charges (e.g., labor or additional parts).
- Warranty Coverage Details: A breakdown of the items or services covered under the warranty and any exclusions, so the customer knows what is being billed.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount due, including any additional charges for services or parts not covered under the warranty.
- Payment Terms: Accepted methods of payment, payment due date, and any applicable late fees.
- Warranty Expiry Date (if applicable): The expiration date of the warranty, if relevant to the services provided.
This invoice format is often structured to separate warranty-covered services from additional charges, making it clear for the customer which aspects of the service are covered under the warranty and which are not.
Training Invoice
Definition:
A training invoice is issued for professional training services provided to employees, clients, or participants. It covers the cost of training sessions, workshops, or courses offered by individuals or organizations.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the training invoice.
- Trainer/Training Organization Information: Name, address, contact details, and credentials of the trainer or organization providing the training.
- Client/Participant Information: Name, address, and contact details of the client or participant receiving the training.
- Training Session Details: A description of the training provided, including topics covered, duration, location (if in-person), or delivery method (if online).
- Number of Participants (if applicable): The total number of participants attending the training, if the invoice is for a group session.
- Training Fees: The cost of the training, either as a per-participant fee, a flat fee for the entire session, or based on hours or days of training.
- Additional Costs: Any additional costs, such as materials, travel expenses, or accommodation for the trainer, if applicable.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount payable for the training services, including all fees and additional charges.
- Payment Terms: Accepted payment methods and due date for payment (e.g., immediate payment or net 30).
- Discounts (if applicable): Any discounts offered for early payment, group registrations, or multiple sessions.
This invoice format ensures that the client has a clear understanding of what training was provided, how much is due, and any extra charges for materials or services.
Loan Invoice
Definition:
A loan invoice is issued for loan repayments or interest charges. It serves as a reminder for the borrower to make a scheduled payment or settle interest due on the loan.
What All is Included in this Format:
- Invoice Number: A unique identifier for the loan invoice.
- Lender Information: Name, address, and contact details of the lending institution or individual providing the loan.
- Borrower Information: Name, address, and contact details of the borrower.
- Loan Agreement Reference: Reference to the loan agreement or contract under which the loan was granted.
- Loan Details: The principal loan amount, interest rate, and any relevant terms (e.g., repayment schedule or loan type).
- Payment Breakdown: A detailed breakdown of the amount due, including the principal repayment, interest charges, and any other fees (e.g., late fees or penalties).
- Due Date: The specific date by which the payment must be made.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount owed by the borrower, combining principal, interest, and any fees.
- Payment Methods: Accepted payment methods for loan repayment (e.g., bank transfer, check, online payment).
- Late Payment Penalties (if applicable): Details of any additional fees or charges for late payments.
Loan invoices are typically structured to reflect the terms of the loan agreement, ensuring the borrower is fully informed about the payment breakdown and any potential penalties.
Digital vs. Paper Invoices
With the rise of technology, businesses now have the option of choosing between digital invoices and paper invoices. While both serve the same basic purpose, there are several differences to consider. Let’s break down the pros and cons of each:
1. Digital Invoices
Pros:
- Faster and More Convenient: Digital invoices can be created, sent, and tracked instantly through email or invoicing software. This speeds up the payment process and reduces the risk of delays.
- Eco-Friendly: Since they don’t require paper, digital invoices are a more environmentally friendly option.
- Easier to Store and Organize: You can store digital invoices on your computer or in cloud storage, making them easy to organize and access at any time.
- Integration with Accounting Software: Many businesses use digital invoices alongside accounting software that automatically tracks payments and integrates with your books.
- Automatic Reminders: Some invoicing platforms can send automated reminders for overdue payments, which reduces the need for manual follow-ups.
Cons:
- Technical Barriers: Not all customers are tech-savvy or have access to email or digital payment methods.
- Security Risks: Storing invoices online can pose security risks if your system isn’t secure enough to protect sensitive customer data.
2. Paper Invoices
Pros:
- Traditional and Familiar: Paper invoices can feel more personal and may be preferred by some customers, especially those who are not as comfortable with digital technology.
- No Need for Internet: Paper invoices can be mailed to clients, making them ideal for businesses that deal with customers in areas with limited internet access.
Cons:
- Slower Processing: Paper invoices take longer to create, send, and process. The mailing time can delay payments and create unnecessary administrative work.
- Environmental Impact: Printing paper invoices contributes to deforestation and waste, which can be a concern for environmentally conscious businesses.
- Difficult to Organize: Paper invoices require physical storage space, and finding specific invoices can become a challenge without a well-organized filing system.
- Risk of Loss or Damage: Paper invoices are vulnerable to being lost, damaged, or misplaced, which could cause delays or disputes.
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between digital and paper invoices ultimately depends on your business needs and your customer base. For businesses that are looking to save time, reduce costs, and streamline their processes, digital invoices are generally the better choice. However, for businesses with a customer base that prefers traditional methods or doesn’t use technology, paper invoices may still have a place.
In many cases, businesses today are moving toward digital invoices due to the convenience and cost-efficiency they offer, but both methods have their time and place.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating Invoices
Creating invoices might seem straightforward, but there are several common mistakes that can cause confusion, delays in payment, or even legal issues. Here are the top mistakes to watch out for and how to avoid them:
1. Missing or Incorrect Invoice Number
Every invoice should have a unique number. Failing to include one, or using duplicate numbers, can lead to confusion and make it difficult to track payments or manage accounting.
Tip: Use a consistent numbering system to keep everything organized.
2. Not Including Complete Contact Information
Both your contact information and your customer’s contact information should be clearly listed. This includes your business name, address, phone number, and email address. If this information is missing or incorrect, it can lead to delays in communication and payment.
3. Forgetting to Mention Payment Terms
Clear payment terms are essential to ensure both you and your customer understand when and how payment should be made.
Tip: Always include payment due dates (e.g., “Due in 30 days”), and make sure to specify any late fees if applicable.
4. Failing to List All Products or Services
It’s easy to miss an item or service that was part of the agreement, but doing so can lead to disputes. Be thorough in listing everything provided, with a clear description and accurate pricing.
Tip: Double-check all items before sending the invoice.
5. Not Including Taxes or Discounts Properly
Tax information is crucial for both you and your customer. If your business is tax-registered, make sure you list the appropriate sales tax or VAT on the invoice. Similarly, if there are discounts, they should be clearly stated.
Tip: Use best invoicing software to automatically calculate taxes and discounts, ensuring accuracy.
6. Using Unclear or Complicated Language
Your invoice should be easy to understand. Avoid jargon, abbreviations, or complicated language that might confuse the recipient.
Tip: Use simple terms and be as clear as possible about the items or services provided and the amounts due.
7. Not Tracking Payments or Sending Reminders
Once you send an invoice, it’s important to track its status and follow up if necessary. Don’t assume your customer remembers the payment due date.
Tip: Use invoice reminder software to track the status of invoices and automatically send payment reminders.
8. Ignoring Legal Requirements
If you fail to meet local or international invoicing laws, you could face penalties. Ensure that you include all legally required details, such as tax identification numbers and accurate descriptions of goods or services.
Tip: Check local regulations to ensure compliance.
9. Forgetting to Send the Invoice
It’s easy to get caught up while running a business, but don’t forget to actually send your invoices! An invoice that isn’t sent isn’t going to get paid.
Tip: Set reminders to send invoices on time, and use digital tools to automate this process when possible.
10. Not Keeping Copies
Always keep a copy of every invoice you send, whether it’s paper or digital. This is vital for your records, accounting, and tax filings.
Tip: Save all invoices in an organized manner, either physically or digitally.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your invoicing process runs smoothly, your payments are received on time, and your business stays professional and compliant.
Tips for Creating Professional Invoices
A well-designed, professional invoice not only creates a lasting impression on your clients but also helps ensure that payments are processed quickly and accurately. Here are some tips to invoice like a pro and maintain a polished, professional image:
1. Use Clear and Simple Layouts
Your invoice should be easy to read and organized. Use a simple, clean layout with clearly defined sections, such as:
- Your business details
- Client’s details
- Itemized list of products or services
- Payment information (due date, payment method, etc.)
A cluttered or confusing invoice can delay payment or lead to misunderstandings.
Tip: Use pre-designed invoice templates (many invoicing tools offer them) to help maintain consistency and clarity.
2. Add Your Branding
Including your business logo, colors, and fonts gives your invoice a professional touch and reinforces your brand identity. This can make your business appear more established and trustworthy.
Tip: Ensure your branding is subtle and doesn’t overwhelm the document.
3. Include All Necessary Details
Make sure to include all the essential details like:
- Your business name, address, phone number, and email.
- Client’s name, address, and contact details.
- A unique invoice number, date of issue, and due date.
- A clear description of the goods or services provided, along with prices.
- Any applicable taxes, discounts, and total due.
By including all the required details, your invoice will look professional and be less likely to be questioned by your client.
Tip: Double-check the accuracy of these details before sending.
4. Use Itemized Lists
Break down your charges into individual items or services with clear descriptions and costs. This ensures transparency and makes it easier for your client to understand what they are paying for.
Tip: If you’re offering a service, provide a breakdown of the time spent or specific tasks completed.
5. Set Clear Payment Terms
State the payment terms clearly to avoid confusion or delays. This includes:
- The payment due date.
- Accepted payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, PayPal, credit card).
- Any late fees or penalties if payment isn’t made on time.
Tip: Be clear about late payment consequences to avoid any future misunderstandings.
6. Offer Multiple Payment Methods
Make it easy for clients to pay you by offering a variety of payment methods. This could include bank transfers, online payment systems (like PayPal or Stripe), credit cards, or checks.
Tip: The easier you make it for clients to pay, the faster you’ll get your money.
7. Proofread and Check for Errors
Mistakes, whether in the amount, date, or spelling of your client’s name, can create confusion and delay payment. Before sending your invoice, take a moment to proofread it for any errors.
Tip: If possible, have someone else review it for you.
8. Set Up Automatic Invoicing (If Possible)
If you have recurring clients or subscription-based services, setting up automatic invoicing saves you time and ensures invoices are sent on schedule.
Tip: Use recurring invoicing software that can automatically generate and send invoices at regular intervals.
By following these tips, your invoices will look professional, be easy to understand, and help ensure you get paid on time, all while enhancing your business’s reputation. Addressing common invoicing challenges can further streamline your billing process and reduce payment delays.
Tools for Managing Invoices
Managing invoices manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially as your business grows. Fortunately, there are many tools and software available to simplify the invoicing process, keep your records organized, and save you time. Here are some tools that can help you create, send, and track invoices more efficiently:
1. Invoicing Software
Invoicing software automates many parts of the invoicing process, such as generating invoice numbers, calculating taxes, and sending reminders for overdue payments. Some popular invoicing tools include:
- Refrens: A tool designed for businesses of all sizes, offering the convenience of generating professional-looking invoices in just minutes, providing users with a quick and efficient solution.
- Xero: A cloud-based accounting tool with invoicing features, inventory management, and reporting.
Tip: Choose a tool that integrates with your accounting software and payment systems to streamline your entire process.
2. Payment Platforms
Integrating payment platforms with your invoices makes it easier for clients to pay. Many invoicing tools allow you to link your invoices to payment gateways, such as:
PayPal: A widely used online payment system that lets you add “Pay Now” buttons directly to your invoices.
Stripe: Another popular payment gateway for online payments, allowing clients to pay via credit card or bank transfer.
Square: A payment processing system that also offers invoicing features, helping you send invoices and process payments directly.
Tip: Offering multiple payment options helps ensure your clients can pay quickly and conveniently, which improves your cash flow.
3. Accounting Software
Incorporating invoicing into your overall accounting software makes it easier to track your income and expenses, reconcile your books, and generate financial reports. Popular online accounting software options include:
Refrens: A top-tier accounting and invoicing software that goes beyond basic invoicing. It offers a full suite of tools, including CRM, inventory management, advanced accounting, expense management and sales pipeline features, making it a comprehensive solution for any business.
Wave: A free, cloud-based accounting tool that includes invoicing, expense tracking, and accounting features.
Sage Business Cloud: Offers invoicing along with payroll, accounting, and tax features, ideal for businesses that need more comprehensive solutions.
Kashoo: A simple accounting platform with invoicing, financial reporting, and expense tracking features.
Tip: Use accounting software that can automatically sync your invoices with your financial data to make tax season easier.
4. Templates and Customizable Invoice Generators
If you prefer to keep things simple, you can use invoice templates available in tools like:
- Microsoft Word or Google Docs: Basic invoice templates that you can customize to fit your business needs.
2. Canva: Offers easy-to-use templates for visually
3. Invoice Generator software: A free tool that allows you to quickly create simple invoices online, then download or send them directly.
Tip: Customizable templates are a good option if you don’t need complex features but still want professional-looking invoices.
5. Cloud Storage for Record Keeping
Cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive can be used to store and organize all your invoices in one place, ensuring that you can access them anytime and from anywhere.
Tip: Use folders and file naming conventions to keep your invoices organized by year, client, or project.
How To Choose The Best Invoicing Software? Essential Factors to Evaluate
Choosing the best invoice management software is a key decision for any business, as it directly affects cash flow, efficiency, and compliance. Here’s a guide on the essential factors to evaluate when selecting the right tool:
1. Ease of Use
The software should be user-friendly, even for those with little to no accounting experience. A clean interface and intuitive navigation are key for saving time and reducing errors.
2. Automation Features
Look for automation tools that simplify repetitive tasks, like recurring invoicing software, payment reminders, and invoice generation. Automation saves time and ensures consistency in your processes.
3. Customization Options
Your invoice management tool should allow for customization to match your brand. From logos to personalized terms and payment details, the ability to tailor invoices can enhance your professional appearance.
4. Payment Integration
Ensure the software integrates with your payment gateways (e.g., PayPal, Stripe, bank transfers) to enable seamless transactions. Quick and easy payment options can speed up your cash flow.
5. Cloud-Based vs. Desktop
Cloud-based software offers flexibility, as you can access your invoices from anywhere, anytime. It also ensures data backup and secure access. Desktop software might limit you to one device and doesn’t offer the same flexibility.
6. Multicurrency and Multi-Language Support
If you deal with international clients, the software should handle multiple currencies and languages. This will help you manage invoices efficiently across different regions and avoid mistakes related to conversions.
7. Security Features
Invoice data is sensitive, so look for encryption and secure data storage to protect your information. Many cloud-based tools offer two-factor authentication and regular backups for extra security.
8. Integration with Accounting Software
A good invoice management system should integrate seamlessly with your accounting or ERP software. This reduces manual entry and ensures accurate financial reporting.
9. Reporting and Analytics
Look for tools that offer detailed reports on your invoicing and payments. Real-time insights into overdue invoices, outstanding payments, and financial trends can help improve cash flow management.
10. Customer Support
Strong customer support is essential, especially if you run into technical issues or need guidance. Check if the software offers 24/7 support, live chat, or phone assistance.
11. Pricing
Pricing should match the features and benefits the software offers. Look for transparent pricing structures with no hidden fees. Some tools offer free trials, which can help you evaluate their features before committing.
12. Scalability
Choose software that grows with your business. As your invoice volume increases, the software should handle more transactions without performance issues.
By considering these factors, you’ll be better equipped to select the right invoice management software that aligns with your business needs, improves your financial processes, and supports long-term growth.
Legal Considerations for Invoices
When issuing invoices, it’s crucial to ensure that your business complies with legal requirements. Invoices are not just a way to request payment—they also serve as important legal documents. Here’s what you need to know to make sure your invoices meet legal standards:
1. Include Necessary Business Information
To make your invoice legally valid, you must include specific information about your business and the transaction. This includes:
- Your business name and address: This identifies the entity issuing the invoice.
- Your tax identification number (TIN): This is required in many jurisdictions, especially if you’re registered for VAT or sales tax.
- Your customer’s information: Include your client’s name, address, and contact information.
- Invoice number: Each invoice should have a unique number for tracking purposes.
- Date of the invoice: This serves as the starting point for payment terms.
Tip: Check local regulations to ensure you’re including all the necessary details specific to your jurisdiction.
2. VAT and Sales Tax Compliance
If your business is VAT or sales tax registered, you must include the relevant tax details on your invoice. This includes:
- VAT/Sales Tax Registration Number: This is especially important if you’re charging VAT or sales tax.
- Tax rate: Clearly show the tax rate applied to the sale.
- Total amount of tax: List the amount of tax charged on the invoice in a separate line item.
Failure to include proper tax details could lead to legal issues and may impact your ability to claim tax credits or deductions.
Tip: Be aware of different tax regulations that might apply depending on the client’s location (e.g., interstate or international sales).
3. Terms and Conditions
Incorporating clear terms and conditions on your invoice helps protect your business legally. These should include:
- Payment terms: Be clear about when the payment is due and what happens if the payment is delayed.
- Refund and return policies: If applicable, include your policy for refunds, returns, or exchanges.
- Late fees: Specify any penalties for late payments to ensure compliance and avoid disputes.
- Dispute resolution: Outline the process for resolving disputes, including jurisdiction and legal recourse if necessary.
Tip: Make sure the client agrees to these terms before issuing the invoice, either via contract or verbal agreement.
4. Invoice Retention
Invoices serve as official financial records, and in many cases, you are legally required to keep them for a certain period. This is important for accounting, tax reporting, and audits. The retention period varies by country, but typically, businesses are required to keep invoices for at least 5 years.
Tip: Store invoices securely (either digitally or physically) and organize them for easy access during audits or tax filing.
5. International Invoicing Laws
If you’re doing business internationally, be aware that different countries have different invoicing laws. For example:
- Currency: Invoices may need to be issued in the local currency of the client’s country.
- Language: Some jurisdictions may require invoices to be in the local language.
- Tax regulations: Different countries have varying VAT or sales tax rates, and you may need to register for tax purposes in other countries if you exceed a certain threshold.
Tip: Research the specific legal requirements in each country where you do business, especially if you’re invoicing clients in multiple jurisdictions.
6. Digital Invoices and E-Signatures
With the rise of digital transactions, it’s increasingly common to send invoices electronically. However, there are still legal considerations:
- E-Signatures: Many countries accept digital signatures on contracts and invoices as legally binding, but the rules vary. Ensure that your client has consented to receiving invoices electronically and that you have a method for obtaining a valid digital signature if required.
- Electronic Records: In some jurisdictions, businesses are required to store electronic invoices in a certain format (e.g., PDF) and make sure they are easily accessible for tax or legal purposes.
Explore the best electronic invoicing software that simplifies the management of digital invoices and e-signatures, ensuring compliance and efficiency in your invoicing process.
How To Create An Invoice on Refrens?
Refrens is trusted by over 150,000 businesses worldwide for managing everything from leads to accounts and taxes, all in one place. It also lets you create professional invoices in just a few minutes.
Here’s a simple guide to creating an invoice on Refrens:
- Create a New Invoice
- Go to your Invoicing Dashboard and click on “Create New Invoice.”
- Add basic details like the invoice number, date, and due date. You can also include client details, like a client number, if needed.
- Upload your logo and billing details.
- Choose your client from the list or add a new one.
- Customize Invoice Items
- Edit or add columns based on your needs (like service, quantity, rate).
- Use formulas for custom calculations, such as calculating the total amount for hours worked.
- Mark some columns as “Private” if they’re for internal use only.
- Add descriptions, images, or organize items into groups if necessary.
- Add Discounts and Charges
- Apply discounts to specific items or the whole invoice.
- Add any extra fixed or percentage-based charges.
- Final Touches
- Choose a template and customize the colors, fonts, headers, and footers to match your brand.
- You can also add terms, notes, attachments, and contact details.
- Sign the invoice for a professional finish.
- If needed, set up recurring invoices for ongoing projects.
- Send Your Invoice
- Add your bank or UPI details for easy payments.
- Offer early payment discounts to encourage faster payment.
- Once you’re done, send the invoice via email, WhatsApp, or a downloadable link/PDF. You can also print it for a physical copy.
Key Takeaways
– Refrens provides an intuitive platform that makes creating and customizing invoices a breeze.
– With a variety of customizable features, you can easily personalize your invoice to suit your business needs.
– Payment collection is seamless with built-in options for credit cards, bank transfers, and online payment gateways.
To ensure you’re sending professional and error-free invoices, check out our blog on the best practices for creating and sending invoices to clients
Conclusion: Mastering Invoicing for Business Success
Invoicing is an essential part of running any business. From freelancers to large corporations, having a solid invoicing system in place helps ensure you get paid on time, maintain healthy cash flow, and avoid legal complications. By understanding the different types of invoices, payment terms, and tools available to you, you can streamline your invoicing process and focus more on growing your business.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to improve your existing invoicing practices, always remember to:
- Be clear and detailed in your invoices to avoid confusion and disputes.
- Use professional invoicing software or tools to save time and reduce errors.
- Stay compliant with legal requirements to protect your business and financial interests.
With the right approach, invoicing can become a seamless, efficient task that not only supports your business operations but also enhances your professional reputation. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this blog, you’ll be well on your way to mastering invoicing and ensuring that your business runs smoothly.
FAQs
1. What is an invoice?
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer that specifies the amount and cost of products or services provided. It serves as a request for payment and includes details like payment terms, item descriptions, and total cost.
2. Why are invoices important for businesses?
Invoices are essential for maintaining accurate financial records, ensuring timely payments, and complying with tax regulations. They also serve as proof of transactions and can protect businesses in case of disputes.
3. What are the different types of invoices?
There are various types of invoices, including standard invoices, proforma invoices, credit invoices, debit invoices, recurring invoices, and more. Each type serves a specific purpose based on the transaction and payment structure.
4. What are payment terms in an invoice?
Payment terms specify when and how payment should be made, such as “Net 30” (payment due in 30 days), “Due on Receipt,” or “Installments.” Clear payment terms help prevent confusion and late payments.
5. Do I need to issue an invoice for every sale?
In most cases, yes. Issuing an invoice helps businesses keep accurate records for accounting and tax purposes. Some small businesses or cash-based transactions may not always require formal invoices but it’s good practice to issue them whenever possible.
6. Can I create invoices manually or do I need software?
You can create invoices manually using templates or accounting software. However, invoicing software can automate and streamline the process, reducing errors and saving time while keeping track of outstanding payments.
7. Are there legal requirements for invoices?
Yes, legal requirements vary by country and region. In most places, an invoice must include specific details such as the seller and buyer’s information, a unique invoice number, a description of goods/services, the total amount due, and applicable taxes.
8. How do I avoid common invoicing mistakes?
To avoid common mistakes, double-check for accuracy in your invoice details, clearly define payment terms, and ensure that all necessary information is included. Also, keep a consistent numbering system and track all sent invoices.
9. What happens if a client doesn’t pay their invoice on time?
If a client doesn’t pay on time, it’s important to follow up politely with a reminder. If payments continue to be delayed, consider offering payment plans or charging late fees, depending on your invoice terms.
10. How can I ensure my invoices look professional?
To create professional invoices, use a clean and organized layout, include your branding, and be consistent in your formatting. Providing all relevant details such as itemized costs and payment terms will also boost your professionalism.
11. How can I manage multiple invoices at once?
To manage multiple invoices, it’s best to use invoicing software or tools that allow batch invoicing. These platforms typically have features like automated reminders, recurring billing, and client management, making it easier to handle large volumes of invoices.
12. Can I send invoices by email?
Yes, you can send invoices via email. In fact, many businesses prefer emailing invoices for faster processing. Make sure the invoice is in a professional format (PDF is common) and contains all the necessary details.
13. What should I do if a client disputes an invoice?
If a client disputes an invoice, calmly review the details with them and provide any necessary documentation to clarify the issue. If the dispute is valid, issue a revised invoice or credit note as needed. Maintaining open communication is key to resolving these matters professionally.
14. Can I charge interest or late fees on overdue invoices?
Yes, businesses can charge interest or late fees on overdue invoices, as long as it’s outlined in the original payment terms. Ensure you specify the interest rate or late fee structure clearly to avoid any confusion.
15. What is the difference between an invoice and a receipt?
An invoice is a request for payment, typically issued before payment is made. It includes details about what is being sold, the terms of payment, and the amount owed. A receipt, on the other hand, is issued after payment is received, confirming that the buyer has paid the specified amount.
16. How do I create an invoice for international transactions?
When invoicing internationally, you need to account for currency differences, international taxes (like VAT), and shipping fees. You should also include the buyer’s country-specific details and payment methods that can handle international transactions (e.g., PayPal or wire transfer).
17. Is it possible to accept online payments through invoices?
Yes, many invoicing tools allow you to integrate payment options directly within your invoices. This can include links to payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or credit card processing, making it easy for clients to pay online.
18. Can invoices be used for tax purposes?
Yes, invoices are vital for tax purposes. They provide a detailed record of sales and expenses, which is necessary for reporting income and claiming deductions. Businesses should keep a copy of all invoices for tax filing and auditing purposes.


















