Value Added Tax (VAT) is crucial for business transactions in the UAE, so it’s important to issue accurate and compliant invoices. Whether you’re new to VAT or looking to refine your invoicing process, understanding these key elements is essential to staying compliant and avoiding costly errors.
This blog covers the essential aspects of VAT invoices in the UAE, including formats, required fields, how to reclaim VAT on old invoices, and more.
What is a VAT Invoice?
A VAT invoice is a type of invoice issued by VAT-registered businesses. It details a sale and includes the invoice number, the supplier’s and customer’s information, a description of the goods or services sold, the price before adding VAT, the VAT rate applied, the amount of VAT charged, and the total amount owed. This invoice is important for buyers to claim VAT credits and for businesses to comply with VAT regulations.
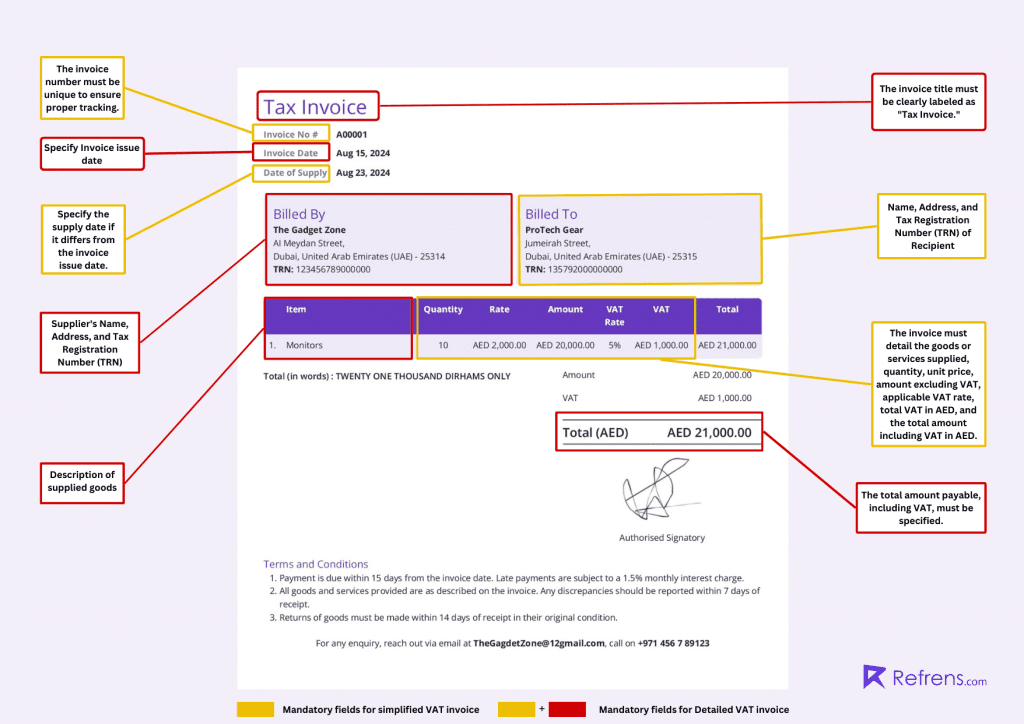
Mandatory Fields for a VAT Invoice
To comply with UAE VAT law, a VAT invoice must include the following mandatory fields:
- The words “Tax Invoice” are in a prominent position.
- Supplier’s name, TRN, and address.
- Recipient’s name, TRN, and address.
- A unique or sequential identifying invoice number.
- Date of the invoice.
- Date of supply (if different from the invoice date).
- Description of the goods or services supplied.
- Unit price, quantity supplied, VAT rate, and the amount payable.
- Any discounts offered (if applicable).
- Gross value payable.
- VAT amount payable.
- Reverse charge declaration (if applicable).
These fields ensure compliance with UAE VAT regulations and help avoid penalties for incorrect invoicing.
Standard Format for VAT Invoices in the UAE
In the UAE, businesses are required to issue VAT invoices in accordance with local regulations. There are two main types: Simplified VAT Invoices for smaller transactions under AED 10,000 and Detailed VAT Invoices for larger transactions over AED 10,000 or when interacting with VAT-registered entities.
To ensure compliance and maintain accurate records, both types of invoices must include specific mandatory fields, as outlined below.
1. Simplified Invoice
A Simplified Invoice in the UAE is a type of VAT invoice used for transactions totaling AED 10,000 or less, including VAT. It is a more concise version of a standard Tax Invoice, primarily issued for smaller sales, usually in retail, where the buyer is not VAT-registered.
Format Requirements:
- The words “Tax Invoice” at the top.
- Supplier’s name, address, and Tax Registration Number (TRN).
- Date of issue.
- Description of goods or services supplied.
- Total amount payable (inclusive of VAT).
2. Detailed VAT Invoice
A Tax Invoice in the UAE is a comprehensive VAT invoice issued for transactions exceeding AED 10,000 or when dealing with VAT-registered businesses. It includes detailed information on the buyer, seller, and VAT charged, and is necessary for VAT reclaim and compliance.
This type of invoice is required for businesses to reclaim VAT and for larger transactions to ensure full compliance with VAT regulations.
Format Requirements:
- The words “Tax Invoice” at the top.
- Supplier’s name, address, and TRN.
- Name, address, and TRN of the recipient (if registered).
- A unique invoice number
- Date of issue.
- Date of supply (if different from the invoice date).
- Description of goods or services supplied.
- Quantity or volume of the goods provided.
- Unit price and the amount payable excluding VAT.
- Applicable VAT rate.
- Total VAT amount payable in AED.
- Total amount payable inclusive of VAT in AED.
Should the customer’s VAT number be included in the invoice?
Including the customer’s VAT number on an invoice is essential for VAT compliance, particularly in business-to-business (B2B) transactions. This number allows the customer to claim input tax credits and ensures that the transaction is properly recorded for tax purposes.
- Purpose: Helps validate that the transaction is between two VAT-registered businesses and ensures proper tax treatment, especially for cross-border transactions.
- Placement: The VAT number should be included near the customer’s name and address in the “Bill To” section of the invoice.
- Verification: It’s important to verify that the VAT number provided is valid and correctly formatted according to local regulations.
- Non-VAT Registered Customers: If the customer is not VAT-registered or does not provide a VAT number, clearly state this on the invoice.
Including the customer’s VAT number is a basic yet crucial step in maintaining compliance and facilitating smooth tax processes.
Is VAT included in the gross invoice amount?
Yes, the gross invoice amount generally includes VAT. It represents the total amount payable by the customer, combining the net cost of goods or services with the applicable VAT. On the invoice, you’ll typically see the net amount, the VAT amount, and the gross amount, which is the sum of both.
For instance, if an item is priced at AED 1,000 with a 5% VAT, the VAT would be AED 50, making the gross amount AED 1,050.
Is VAT applicable on invoices that have yet to be paid?
Yes, in UAE, VAT must be paid based on the invoice date or when payment is received, whichever occurs first, regardless of whether the invoice has been paid. This means you must pay VAT on unpaid invoices when filing your VAT return.
Suppose the invoice remains unpaid for an extended period. In that case, you might be eligible to adjust your VAT liability by issuing a credit note or claiming bad debt relief, depending on the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) conditions.
Example:
A construction company in Dubai issued an invoice in January but hasn’t been paid yet. Based on the invoice date, they still had to pay the VAT in their January return. After several months of no payment, they were able to adjust their VAT by claiming bad debt relief according to FTA rules.
VAT on Advance Payments
When managing VAT on advance payments in the UAE, VAT must be accounted for as soon as the advance payment is received, regardless of when the goods or services are delivered. A VAT invoice should be issued immediately upon receiving the payment. The “time of supply” for VAT purposes is determined by the earliest payment date, invoice date, or supply date.
Advance payments should be recorded accurately, with VAT calculated based on the amount received. Adjustments are made when the final invoice is issued after the supply of goods or services.
Timely invoicing and correct VAT reporting are essential to avoid penalties. Customers can claim input tax credits as soon as they receive the VAT invoice for the advance payment.
Claiming VAT on Past Invoices
In the UAE, the general rule for claiming VAT on past invoices is that you can reclaim VAT within the same tax period when the invoice was issued or within the subsequent tax periods. However, if you missed claiming VAT in the correct tax period, you can claim it within the following two tax periods.
- Key Points:
- Immediate Claiming: VAT should ideally be claimed in the tax period in which the invoice was issued or within the next two tax periods.
- Exceptions: If you missed claiming VAT within this timeframe, you may need to request special approval from the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) to claim it later.
- Document Retention: The FTA requires that you maintain proper records for at least five years to support any VAT claims.
If VAT is not claimed within this window, it may be difficult or impossible to recover it, so timely claiming is crucial.
Example:
A retail business in Dubai purchased inventory in February but forgot to claim the VAT in that tax period. In April, they realized the mistake and successfully reclaimed the VAT because they were still within the allowed two tax periods (February being the first, March and April being the next two) If they had waited until May, they would have missed the deadline and lost the chance to reclaim the VAT.
Handling Late Invoices in VAT Returns
If you receive an invoice after submitting your VAT return for the relevant period, you can claim the VAT in your next VAT return. Here’s how to manage it:
- Next Return: Include the VAT from the late invoice in your next VAT return.
- Accurate Records: Ensure the invoice is recorded correctly in your accounts.
- Amendment: If the amount is substantial, you may need to consider amending the previous VAT return, depending on tax authority guidelines.
Claiming the VAT in a subsequent period is generally acceptable, but it’s important to process invoices promptly to avoid complications.
How does VAT apply to intercompany invoices?
Intercompany invoices between entities within the same corporate group are subject to VAT if the supply of goods or services is taxable. Here’s what to consider:
- VAT Application: Charge VAT if both entities are in the same VAT jurisdiction; rules may vary for cross-border transactions.
- Invoicing: Issue a standard VAT invoice with all required details, including VAT registration numbers and amounts.
- Input Tax Credit: The receiving entity can claim an input tax credit if the invoice is valid.
- Compliance: Maintain accurate records and ensure compliance with local VAT laws.
- Exemptions: Check for potential zero-rating or exemptions based on the transaction type and location.
For Instance, A UAE holding company provides IT services to its subsidiary within the same VAT jurisdiction. The holding company issues an intercompany invoice including VAT. The subsidiary pays the invoice and claims the VAT as an input tax credit in its next return. This transaction is compliant with UAE VAT regulations, as both companies are VAT-registered and within the same jurisdiction. If the subsidiary were in a different jurisdiction, different VAT rules might apply.
Invoice Format for VAT-Registered Suppliers
When a supplier becomes VAT registered, their invoices must include:
- Supplier Details: Business name, address, and VAT registration number.
- Invoice Details: Unique invoice number and issue date.
- Customer Details: Customer’s name, address, and VAT number (if applicable).
- Transaction Details: Description of goods/services, net amount, VAT rate, VAT amount, and gross amount.
- Payment Terms: Clearly state payment terms and due date.
Notify customers about your VAT registration and that VAT will now be applied to future invoices.
Issuing Invoices Before VAT Registration
When issuing invoices before VAT registration, here’s what to keep in mind:
- No VAT Applied: Do not include VAT on invoices issued before your VAT registration date, as you are not legally authorized to collect it.
- Invoice Clarity: Clearly state on the invoice that your business is not VAT-registered, using a note like, “Not VAT-registered; VAT not applicable.”
- Post-Registration: Once registered, start applying VAT on all invoices issued from your VAT registration date onwards.
- Customer Notification: Notify your customers when you become VAT-registered, so they are aware that VAT will be charged on future invoices.
These steps ensure your invoicing remains compliant during the transition to VAT registration.
VAT When Paying Invoices on Behalf of Other Companies
When paying invoices on behalf of another company, VAT handling requires careful attention. Here is how can it be done:
- VAT Entitlement: The company that receives the goods or services—not the one making the payment—can claim the VAT input tax credit, provided they have the correct VAT invoice.
- Reimbursement: If you pay an invoice for another company, ensure you get reimbursed for the total amount, including VAT. The reimbursement should reflect the full cost covered.
- Documentation: Maintain clear records of the payment, the original invoice, and any agreements regarding the reimbursement. This is essential for VAT compliance and audit purposes.
- Cross-Charge Consideration: If you charge the other company for making the payment, ensure this is properly documented and VAT is applied where applicable.
Properly managing VAT in such scenarios ensures compliance and clarity for both parties involved.
Claiming VAT on Proforma Invoices
No, you cannot claim VAT on proforma invoices. A proforma invoice is a preliminary document issued before a formal sale takes place, and it does not serve as a valid tax invoice for VAT purposes. To claim VAT, you must have a valid tax invoice that includes all the necessary details, such as the VAT registration number, VAT amount, and the total amount due.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing VAT invoices in the UAE is essential for compliance and efficient tax management. Whether it’s reclaiming VAT on old invoices, ensuring the correct format, or handling specific scenarios like advance payments and intercompany transactions, proper invoicing practices are key.
By following the guidelines and keeping accurate records, businesses can avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations in line with UAE tax laws.