Value Added Tax (VAT) was introduced in the UAE in 2018 and has since played a significant role in shaping the country’s economy. Set at a standard rate of 5%, VAT applies to most goods and services, affecting both businesses and consumers. Hence, understanding how VAT works is essential whether you’re a buyer or a business owner.
This blog aims to give you a clear overview of the VAT basics, including key rates, exemptions, the latest rules, and more, to help you stay informed and compliant.
1. What is VAT in the UAE?
Implementation: Value Added Tax (VAT) was launched in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) on January 1, 2018.
Aim: VAT was implemented to diversify the economy away from oil dependency. Additionally VAT revenue aids in funding public services and infrastructure, strengthening the UAE’s economic stability and growth.
Eligibility:
- Businesses with taxable supplies and imports exceeding AED 375,000 are required to register for VAT.
- Those with taxable supplies between AED 187,500 and AED 375,000 can opt for voluntary registration to reclaim input VAT.
- Compliance mandates precise record-keeping, regular VAT filings, and timely tax payments to circumvent penalties.
Exemptions: To support specific industries, the UAE applies a zero-rated VAT to international transport, select educational and healthcare services, and exports outside the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). This allows businesses to recover VAT on inputs without charging VAT on sales.
Additionally, VAT exemptions apply to certain sectors like specific financial services and residential property sales post-initial transfer, where VAT cannot be reclaimed.
Penalty: Late VAT filings result in fines starting at AED 1,000, while delayed payments incur a 2% penalty that escalates over time. Ensuring proper VAT registration and compliance is essential for business success in the UAE.
Consequences: The implementation of VAT has necessitated sophisticated accounting systems for businesses and slightly increased the cost of living for consumers.
2. What is the VAT rate in UAE?
In the UAE, the standard VAT rate is 5%, which is applied to most goods and services. However, a 0% VAT rate also applies to specific categories, including exports, international passenger transport, the supply of crude oil and natural gas, and public education.
3. Benefits of VAT in UAE
Here are the key benefits of VAT in the UAE:
- Significant Cost Savings: Businesses can save costs by claiming input tax credits, which allow them to offset the VAT paid on purchases against the VAT charged on sales.
- Enhanced Financial Management: VAT registration promotes better financial management by requiring businesses to maintain accurate records and submit regular VAT returns.
- Eligibility for VAT Refunds: When the VAT paid on purchases exceeds the VAT collected on sales, businesses can apply for refunds, providing financial relief during growth phases or after major investments.
- Fair and Transparent Taxation: VAT ensures a fairer distribution of the tax burden across the supply chain, enhancing transparency and reducing opportunities for tax evasion.
- Improved Business Efficiency: The introduction of VAT encourages businesses to upgrade their accounting systems, leading to more efficient operations.
- New Market Opportunities: The need for VAT expertise creates opportunities for advisory firms and consultants specializing in VAT services.
- Non-Financial Advantages: VAT enhances government accountability, improves liability management, and helps reduce fraud, corruption, and waste in the economy.
- Support for Economic Growth and Infrastructure: Revenue from VAT contributes to the UAE’s economic stability and infrastructure improvements, facilitating easier and more cost-effective business operations.
- Encouragement of Savings and Investment: VAT promotes personal savings and investment by being a transparent, staged tax, minimizing the immediate financial impact on consumers.
4. How many types of VAT are there in the UAE?
Types of VAT in the UAE:
- Standard Rate (5%): This rate applies to most goods and services in the UAE, where businesses charge 5% VAT on their sales. They are also eligible to reclaim VAT on their purchases.
- Zero-Rated VAT: This category covers specific goods and services that are taxed at 0%. Although businesses must report these transactions, they do not pay VAT on them.
Examples include exports, international transport, certain healthcare and education services, and the first sale of residential properties within three years of their completion.
- Exempt VAT: Some goods and services are entirely exempt from VAT, meaning no VAT is charged. However, businesses involved in these transactions cannot recover VAT on related expenses. This includes financial services, the sale of residential properties after the initial transaction, and domestic passenger transport.
These classifications determine how VAT is applied across different sectors, ensuring alignment with the UAE’s VAT regulations.
5. What is the VAT formula in UAE?
In the UAE, VAT calculations can be done using two approaches. The first method involves applying VAT on top of the selling price, while the second method requires deducting VAT from the total price.
- Calculating the VAT-inclusive amount:
VAT Amount = Price × VAT Rate/100
Total Amount = Price × (1+ VAT Rate)/100
- Calculating the VAT-exclusive amount:
VAT Amount = Price × VAT Rate/(100+ VAT Rate)
Net Value = Price × 100/(100+ VAT Rate)
For example:
Suppose you bought office supplies for 1,000 AED. With a VAT rate of 5%, what would be the price exclusive of VAT, and what would the total amount be, including VAT?
When the sale price is inclusive of VAT:
VAT amount = AED 1,000 x (5/(100+5)) = AED 47.62
Net Value = AED 1,000 x (100/ (100+5)) = AED 952.38
When the sale price is exclusive of VAT:
VAT amount = AED 1,000 x (5/100) = AED 50
Total amount = AED 1,000 x (1+ (5/100)) = AED 1,050
This formula ensures that businesses and consumers can accurately calculate the VAT they need to charge or pay in the UAE.
6. What are the new VAT regulations in the UAE for 2024?
In 2024, the UAE continues to maintain its standard VAT rate of 5%, with no increase confirmed, which is beneficial for businesses as it provides stability for financial planning. However, several key updates and rules have been introduced
- Credit Note Regulations: Businesses must now declare VAT credit notes within 14 days, a significant reduction from the previous 90-day period. This change demands faster adjustments in VAT records when dealing with returns, discounts, or invoicing errors.
- Stricter Compliance: The criteria for issuing tax credit notes have been tightened, and refunds related to these notes are now processed more quickly, within 7 days.
- Zero-Rated Supplies: Companies that exclusively deal in zero-rated supplies, such as exports, can apply for VAT exemption, but they must still comply with other VAT obligations unless officially exempted.
- Tax Audits: Previously, the UAE’s Federal Tax Authority (FTA) could conduct tax audits up to five years after the relevant tax period. Now, the audit period remains five years but can extend up to four years under certain conditions.
- E-invoice: The UAE government has recognized e-invoices, with mandatory phases starting July 2025 for cross-border transactions and July 2026 for all invoices.
These updates aim to improve compliance, streamline VAT processes, and enhance the overall efficiency of VAT administration in the UAE.
7. Who pays VAT in UAE?
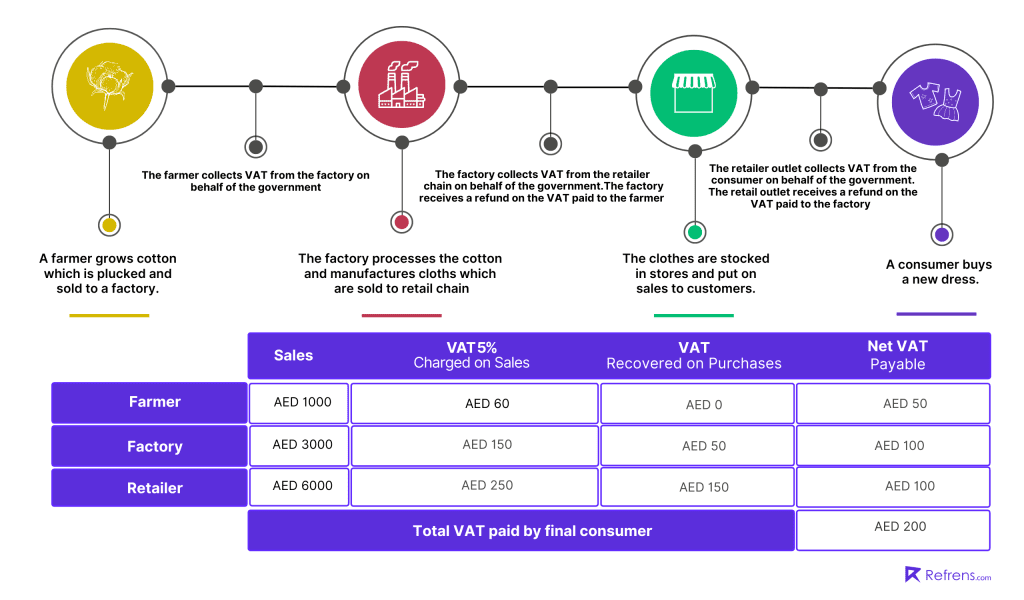
VAT (Value Added Tax) is systematically applied at each stage of the supply chain, with the end consumer bearing the tax cost. Businesses function as intermediaries in this process, collecting VAT from customers and remitting it to the government. Simultaneously, they are entitled to reclaim VAT paid on their own purchases, ensuring that the government receives tax solely on the value added at each production or distribution phase.
In the context of imports, VAT obligations are typically managed by the registered business or importer, often through the reverse charge mechanism. This approach is also employed for cross-border services where the supplier is located outside the UAE, transferring the VAT liability to the UAE-based recipient. This framework not only facilitates efficient VAT collection but also ensures strict adherence to UAE tax regulations.
8. Who is eligible for VAT in Dubai?
In Dubai, businesses must register for VAT based on their annual taxable turnover:
- Mandatory Registration: A business with an annual taxable turnover above AED 375,000 must register for VAT.
- Voluntary Registration: Businesses with a turnover or expenses over AED 187,500 can choose to register voluntarily. This is often done by smaller businesses looking to reclaim VAT on their expenses.
- Exemptions: Some entities, like government bodies or businesses dealing only in zero-rated supplies, do not need to register for VAT.
9. What is VAT exemption in UAE?
In the UAE, VAT exemption applies to certain goods and services, meaning they are not subject to VAT, and no tax is charged on their sale or purchase. However, businesses that provide these exempt goods and services cannot reclaim VAT on expenses related to these supplies through input tax credits.
In the UAE, two types of supplies are not subject to standard VAT rates: zero-rated and exempt transactions.
Zero-Rated Transactions: These supplies are taxable but at a 0% rate. Examples include:
- Exporting goods and services outside the GCC.
- International passenger transportation.
- Sales of new residential properties within three years of completion.
- Certain education and healthcare services.
- Investment-grade precious metals.
Exempt Transactions: No VAT is charged on these supplies, and businesses cannot reclaim input VAT on related expenses. Examples include:
- Specific financial services.
- Sales of residential properties after the first supply and sales of bare land.
- Local passenger transport.
10. Documents required for VAT registration in UAE?
To register for VAT in the UAE, businesses must provide the following documents online:
- A valid, non-expired trade license.
- Passport and Emirates ID copies of the owner/partners on the license, ensuring they are not expired.
- Memorandum of Association (MOA) if required (not needed for sole establishments).
- Complete contact details of the company, including address and P.O. Box.
- Contact details of the person responsible for VAT matters, including mobile number and email.
- Bank details, including account number, account name, bank name, branch name, and IBAN.
- A signed and stamped turnover declaration for the last 12 months, printed on company letterhead.
- Declaration of any export or import activities.
- VAT Registration Letter if the business deals with any customs department.
11. How to register for VAT in UAE for a new company?
Registering for VAT in the UAE is a crucial step for any new company engaging in taxable activities. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to successfully register for VAT:
Step-by-Step Guide to VAT Registration in UAE
1. Determine Eligibility
- Mandatory Registration: If your business’s annual taxable turnover exceeds AED 375,000, you must register for VAT.
- Voluntary Registration: If your turnover is between AED 187,500 and AED 375,000, you can opt to register voluntarily. This can be beneficial if you wish to reclaim VAT on business expenses.
2. Prepare Necessary Documents
Before initiating the registration process, gather all required documents, including:
- Business trade license
- Passport copies of the business owner and partners
- Emirates ID copies
- Description of business activities
- Bank account details
- Proof of business transactions and turnover
3. Apply Online
Registration is done electronically through the UAE Federal Tax Authority’s (FTA) online portal. Here’s how:
- Visit the FTA’s official website and create an account.
- Fill in the VAT registration form which includes details about your business and financial transactions.
- Upload the necessary documents as specified in the form.
4. Review and Submit
Double-check all information for accuracy to avoid any discrepancies that could delay the process. Once confirmed, submit your application.
5. Obtain Your VAT Number
After submission, the FTA will review your application, which typically takes between two and three weeks. Once approved, you will receive your VAT registration number.
6. Compliance and Record Keeping
Post-registration, ensure you comply with all VAT laws, including accurate record-keeping and timely filing of VAT returns. VAT returns are generally filed quarterly, and the deadline for filing and payment is the 28th day following the end of the VAT quarter.
Important Considerations
- Fiscal Representative: Non-resident businesses must appoint a fiscal representative in UAE to handle VAT matters, ensuring compliance with local tax laws.
- Single Tax Registration Number (TRN): Regardless of operations in different Emirates or through multiple branches, a business can only hold one TRN, unless specified otherwise in the UAE Executive Regulation.
- Tax Group Registration: Related parties with businesses in the UAE can apply for a VAT group registration which allows them to be treated as a single taxable entity, simplifying the VAT process.
Compliance and Penalties
Ensure timely compliance with VAT regulations to avoid penalties. Late filing of VAT returns can lead to a fine of AED 1,000, doubling if non-compliance continues for more than 24 months. Delayed VAT payments attract an initial penalty of 2% of the unpaid tax, increasing over time.
By following these detailed steps, a new company can ensure proper registration and compliance with the UAE’s VAT regulations, paving the way for successful business operations in the region.
12. What is VAT in UAE for imports?
In the UAE, both imported and domestic goods and services are subject to a 5% VAT rate. The importer is responsible for paying this VAT, not the foreign supplier, thanks to the reverse charge mechanism. This process ensures the VAT is properly reported and paid to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) by the UAE-based importer.
In addition, VAT paid on imports can be recovered by the importer as input tax, provided that the goods or services are used for taxable activities within the UAE. Importers are also required to maintain records of their imports for at least five years, ensuring compliance with VAT regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamentals of VAT in the UAE is essential for managing your finances effectively and avoiding potential issues. Staying informed and managing VAT efficiently can be achieved with the help of accounting software, which automates calculations, generates detailed reports, and ensures accurate record-keeping. This approach not only simplifies VAT management but also guarantees compliance with UAE tax regulations.