1. Introduction
In today’s digital age, electronic invoicing, or e-invoicing, has emerged as a modern solution to streamline and digitize the invoicing process. Simply put, e-invoicing refers to the electronic generation, transmission, and processing of invoices between trading partners, eliminating the need for traditional paper-based invoices.
In Saudi Arabia, the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA) has been at the forefront of implementing e-invoicing initiatives. Thus, playing a significant effort to modernize and enhance the efficiency of the country’s taxation and customs processes. ZATCA serves as the regulatory body responsible for overseeing zakat (Islamic tax), tax, and customs matters in Saudi Arabia.
The introduction of e-invoicing by ZATCA is aimed at revolutionizing the way businesses conduct their invoicing operations, bringing about numerous benefits for both businesses and the government. By transitioning from paper-based to electronic invoicing, businesses can expect increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved accuracy, and enhanced compliance with tax regulations.
1.1. What is e-invoicing?
Electronic invoicing, commonly known as e-invoicing, is a digital method of creating, sending, receiving, and processing invoices between businesses and their trading partners. E-invoicing is mainly dependent on electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and digital formats to facilitate the invoicing process, as compared to the physical exchange of paper documents in the age-old methodologies.
E-invoicing streamlines the entire invoicing lifecycle, from invoice creation to payment reconciliation, by digitizing and automating key invoicing tasks. It typically involves the use of standardized electronic formats, such as XML or PDF, to represent invoice data in a structured and machine-readable manner.
Key features of e-invoicing include:
- Electronic Generation: Invoices are generated electronically using accounting or invoicing software, eliminating the need for manual paper-based processes.
- Digital Transmission: Invoices are shared electronically between trading partners using secure communication channels, such as email, electronic data interchange (EDI), or dedicated e-invoicing platforms.
- Data Integration: E-invoicing systems integrate seamlessly with accounting and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, enabling automatic data synchronization and reconciliation.
- Compliance: E-invoicing solutions often incorporate built-in compliance features to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, tax laws, and invoicing standards.
- Efficiency: By automating invoicing processes, e-invoicing reduces manual errors, accelerates invoice processing times, and improves overall efficiency in financial operations.
1.2. What is ZATCA? (Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority)
The Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA) is the regulatory body responsible for overseeing Zakat (Islamic wealth tax), taxation, and customs matters in Saudi Arabia. Established to enforce compliance with tax and customs regulations, ZATCA plays a pivotal role in ensuring fiscal transparency, revenue collection, and economic stability within the kingdom.
Key functions and responsibilities of ZATCA include:
- Taxation Regulation: ZATCA is tasked with formulating and enforcing tax policies, laws, and regulations governing various types of taxes, including value-added tax (VAT), income tax, and corporate tax. It ensures that taxpayers comply with their tax obligations and facilitates tax collection processes.
- Customs Oversight: ZATCA overseas customs operations and regulations to facilitate the movement of goods across Saudi Arabia’s borders. It implements customs duties, tariffs, and trade regulations to regulate imports, exports, and transit shipments by international trade standards.
- Zakat Administration: As part of its mandate, ZATCA administers the collection and distribution of zakat, a mandatory charitable contribution based on Islamic principles of wealth distribution. It ensures that eligible individuals and entities fulfill their zakat obligations and allocates zakat funds to support social welfare programs and charitable initiatives.
- Compliance Enforcement: ZATCA monitors compliance with tax, customs, and zakat regulations through audits, inspections, and enforcement actions. It imposes penalties, fines, and sanctions on non-compliant taxpayers and businesses to deter tax evasion, smuggling, and other illicit activities.
- International Cooperation: ZATCA collaborates with international organizations, government agencies, and tax authorities to exchange information, harmonize tax policies, and combat cross-border tax evasion and avoidance. It participates in global initiatives aimed at promoting tax transparency and cooperation among jurisdictions.
1.3. Why did ZATCA introduce e-invoicing? (Benefits for businesses and government)
The introduction of e-invoicing by ZATCA marks a significant step towards modernizing tax administration and enhancing compliance mechanisms in Saudi Arabia. Several factors have contributed to the adoption of e-invoicing, with notable benefits accruing to both businesses and the government:
1. Enhanced Tax Compliance:
- E-invoicing enables real-time reporting and tracking of transactions, reducing the likelihood of tax evasion, fraud, and underreporting of revenues.
- By automating the invoicing process, businesses can ensure greater accuracy in tax calculations and compliance with VAT regulations, thereby minimizing the risk of penalties and sanctions.
2. Streamlined Business Operations:
- Electronic invoicing systems streamline the issuance, distribution, and management of invoices, leading to increased operational efficiency and cost savings for businesses.
- Automation of invoicing processes reduces manual errors, eliminates paper-based documentation, and accelerates the invoice-to-cash cycle, improving cash flow management and liquidity.
3. Improved Transparency and Accountability:
- E-invoicing fosters transparency and accountability in business transactions by providing auditable records of invoices, payments, and tax declarations.
- Government authorities can access real-time data on transactions, facilitating tax audits, compliance assessments, and revenue forecasting to ensure fiscal sustainability.
4. Facilitated Trade and Economic Growth:
- The adoption of e-invoicing simplifies cross-border trade and enhances the competitiveness of Saudi businesses in the global market.
- Standardized electronic invoicing formats promote interoperability and compatibility with international trading partners, reducing barriers to trade and promoting economic growth.
5. Environmental Sustainability:
- E-invoicing contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing paper consumption, waste generation, and carbon emissions associated with traditional paper-based invoicing.
- The shift towards electronic documentation goes together with Saudi Arabia’s commitment to environmental conservation and sustainable development goals.
6. Technological Advancement and Innovation:
- Introducing e-invoicing demonstrates ZATCA’s commitment to embracing technological advancements and leveraging digital solutions to modernize tax administration.
- By harnessing innovative technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics, ZATCA aims to optimize tax compliance processes, enhance taxpayer services, and drive digital transformation in the public sector.
Use Case Scenario: Furniture Manufacturer in Riyadh
Scenario:
- Company: Al-Noor Furniture Manufacturing, is a medium-sized furniture company based in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- Challenges: Al-Noor previously used a paper-based invoicing system, leading to inefficiencies in managing a high volume of invoices, slow processing times, and difficulty tracking payments. Additionally, manual data entry resulted in errors and delays in filing VAT returns.
- Solution: Al-Noor implemented an e-invoicing solution to automate invoice generation and transmission. The E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) integrates with their existing accounting software, streamlining data entry and eliminating manual errors.
- Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: E-invoicing automates tasks, saving time and resources previously spent on manual processes.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated data entry minimizes errors and ensures accurate invoices and VAT calculations.
- Faster Payments: Electronic invoices are delivered and processed quicker, leading to faster payments from customers.
- Enhanced Compliance: E-invoicing simplifies VAT compliance by ensuring invoices adhere to ZATCA regulations and facilitating electronic filing of VAT returns.
- Better Visibility: Real-time invoice data provides Al-Noor with better visibility into their sales performance and cash flow.
Impact: By adopting e-invoicing, Al-Noor Furniture Manufacturing has significantly improved operational efficiency, reduced errors, and streamlined VAT compliance. This allows them to focus on core business activities like production and sales growth.
1.4. What is FATOORAH and how are FATOORAH and ZATCA related?
Fatoorah, developed by the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA), stands as a robust electronic invoicing platform in Saudi Arabia. It serves as a centralized portal where users, including buyers and tax authorities, can access and authenticate invoice details through QR code scanning. This platform plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency, accuracy, and compliance with e-invoicing regulations, thereby enhancing trust and efficiency in electronic transactions.
By leveraging Fatoorah, stakeholders can streamline invoice verification processes, mitigate the risk of fraud, and promote a seamless digital invoicing ecosystem in Saudi Arabia. Its robust features enable swift validation and verification of electronic invoices, contributing to smoother financial transactions and bolstering confidence in the integrity of electronic invoicing practices. Here is a deeper insight into how do they work together:
- Regulatory Compliance: Fatoorah operates under the regulatory framework set by ZATCA, ensuring that electronic invoices generated and verified through the platform adhere to the authority’s guidelines and standards.
- Data Exchange: Fatoorah serves as a central platform for exchanging invoice data between businesses and tax authorities. ZATCA relies on Fatoorah to collect, validate, and store electronic invoices, enabling efficient tax administration and compliance monitoring.
- Verification Process: ZATCA oversees the verification process conducted through Fatoorah, ensuring that invoices comply with tax regulations and contain accurate information. ZATCA’s involvement validates the authenticity and integrity of electronic invoices processed through Fatoorah.
- Enforcement of Penalties: ZATCA may use data from Fatoorah to identify non-compliant taxpayers and enforce penalties for violations of e-invoicing regulations. This interdependence reinforces the importance of both Fatoorah and ZATCA in ensuring compliance with electronic invoicing requirements.
As Saudi Arabia progresses in its digital transformation, e-invoicing emerges as a crucial initiative, showcasing the nation’s dedication to adopting technological advancements and spearheading progressive changes in tax management. By providing an environment for partnerships between the public and private sectors, stakeholders can take advantage of the potential of e-invoicing to foster growth, competitiveness, and prosperity throughout the Kingdom.
2. E-Invoicing Regulations in Saudi Arabia
The introduction of e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia by ZATCA signifies a significant leap forward in the country’s digital transformation journey, revolutionizing traditional tax systems. This move reflects Saudi Arabia’s dedication to enhancing transparency, efficiency, and compliance within the tax landscape, in alignment with Vision 2030.
By embracing digital innovation, the Kingdom aims to foster a favorable business environment, attract investment, and drive economic growth in accordance with global standards.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the timeline of implementation, phased rollout, and compliance requirements of e-invoicing regulations, while giving insights into their implications for resident taxpayers and exceptions for non-residents.
2.1. When were the e-invoicing regulations introduced?
The e-invoicing regulations were introduced in Saudi Arabia on December 4, 2021. This date marked the official implementation of electronic invoicing requirements by the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA). With the introduction of these regulations, businesses operating in Saudi Arabia were mandated to transition from traditional paper-based invoicing to electronic invoicing systems.
The decision to implement e-invoicing regulations reflects the Saudi government’s commitment to modernize and digitize financial processes, streamline tax administration, and enhance compliance with tax laws. By leveraging technology to digitize invoicing practices, the government aims to improve efficiency, transparency, and accuracy in financial transactions, while also combating tax evasion and fraud effectively.
2.2. What are the different phases of the rollout?
The implementation of e-invoicing regulations occurred in multiple phases, with each phase focusing on specific aspects of implementation. In this section, we will explore the timeline and key phases of the e-invoicing rollout, including Phase 1, which emphasizes invoice generation, and Phase 2, which focuses on integration with ZATCA’s electronic platform.
Phase 1: Introduction of QR Codes (December 4, 2021)
- Objective: Introduce a basic level of e-invoicing with standardized QR codes.
- Working: Businesses were mandated to issue simplified tax invoices with QR codes containing essential tax information.
- Compliance: All businesses subject to ZATCA e-invoicing regulations had to comply.
- QR Code Usage:
- Mandatory for Business-to-Consumer (B2C) transactions.
- Optional for Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions (became mandatory in Phase 2).
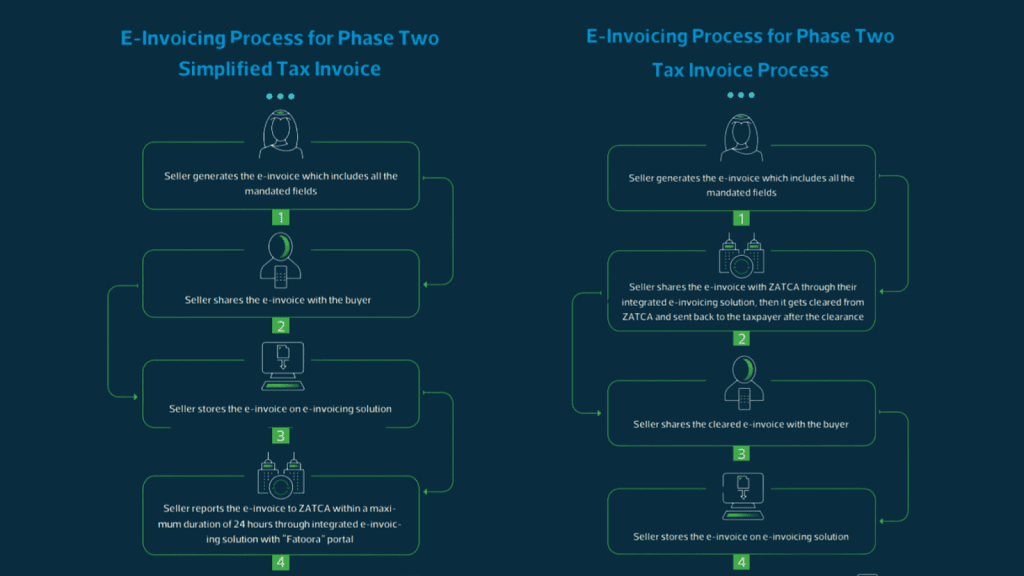
- Phase 2: Integration with Fatoora Portal (Phased rollout from January 1, 2023)
- Objective:
- Enhance e-invoicing with real-time data exchange between businesses and ZATCA.
- Working: Businesses integrate their Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Point-of-Sale (POS) systems with ZATCA’s Fatoora portal. This enables automatic and real-time invoice data transmission to ZATCA for validation, authentication, and generation of QR codes.
- Compliance: Phased rollout targeting specific taxpayer groups based on VAT turnover. Businesses are notified by ZATCA well in advance of their designated compliance wave.
Case Study Example:
Company: A clothing retailer (ABC Clothing) with a VAT turnover exceeding SAR 500 million in both 2021 and 2022.
Phase 1: ABC Clothing complied by generating QR codes for all invoices (B2C and B2B) as of December 4, 2021.
Phase 2: Since ABC Clothing falls under the high turnover category, ZATCA would have notified them about their specific compliance wave (e.g., Wave 3 with a deadline of October 1, 2023). ABC Clothing would need to integrate its POS system with the Fatoora portal by the deadline for automatic invoice transmission and processing.
| Feature | Phase 1 | Phase 2 |
| Objective | Introduce basic e-invoicing with QR codes | Enhance e-invoicing with real-time data exchange |
| Working | Manual generation of QR codes | Automatic invoice transmission through system integration |
| QR Code Usage | Mandatory (B2C), Optional (B2B) | Mandatory for all transactions |
| Compliance | All applicable businesses | Phased rollout based on VAT turnover |
ZATCA’s e-invoicing phases represent a strategic move towards a more efficient and transparent tax ecosystem in Saudi Arabia. Phase 1 laid the groundwork with standardized QR codes, familiarizing businesses with the concept of e-invoicing.
Phase 2 builds upon this foundation by leveraging technology for real-time data exchange. This not only simplifies tax compliance for businesses but also empowers ZATCA with better tax administration capabilities.
2.3. Who is mandated to comply with e-invoicing?
In Saudi Arabia, the implementation of e-invoicing regulations marks a significant step toward modernizing tax administration and streamlining business processes. Understanding the scope of compliance is crucial for businesses operating within the Kingdom’s jurisdiction. Let’s explore these elements in detail to grasp the implications for taxpayers and the broader business landscape.
- Resident Taxpayers:
- All resident taxpayers in Saudi Arabia are mandated to comply with e-invoicing regulations.
- This includes businesses registered for VAT and other tax purposes within the Kingdom.
- Exceptions for Non-Residents:
- Non-resident taxpayers who are not registered for VAT in Saudi Arabia are exempt from e-invoicing requirements.
- However, if a non-resident taxpayer is part of a VAT group with a presence in Saudi Arabia, they may be subject to e-invoicing regulations.
- Criteria for Compliance:
- Compliance with e-invoicing regulations is determined based on the residency status and tax registration of the taxpayer.
- Resident taxpayers must ensure that their invoicing processes align with ZATCA’s electronic invoicing requirements to avoid penalties and maintain regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, the introduction of e-invoicing regulations in Saudi Arabia represents a pivotal step towards modernizing tax administration and fostering digital transformation. With the phased rollout approach and mandated compliance for resident taxpayers, the Kingdom is aligning with global best practices, enhancing transparency, and driving efficiency in financial processes.
3. E-Invoice Requirements
The e-invoice requirements outlined by ZATCA are essential for businesses transitioning to digital invoicing in Saudi Arabia. Compliance with these standards is crucial for seamless integration and regulatory adherence.
This section explores key information elements, accepted formats, and security measures prescribed by ZATCA to ensure the integrity of electronic invoices. By adhering to these requirements, businesses can navigate the e-invoicing landscape effectively and contribute to the goals of digital transformation and regulatory compliance in the country.
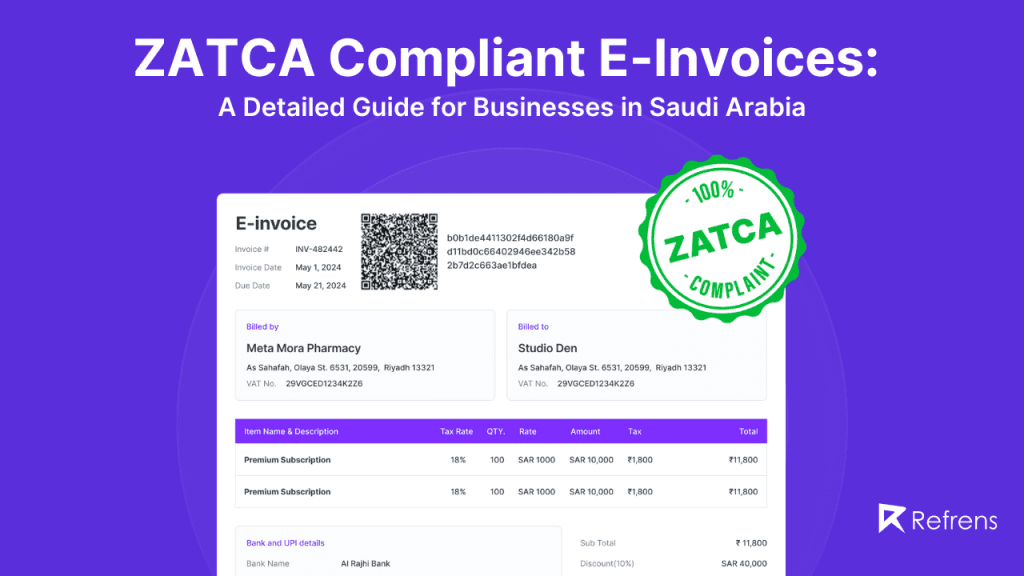
3.1. What information must be included in a ZATCA-compliant e-invoice?
To comply with ZATCA’s e-invoicing regulations, an electronic invoice must include specific information as outlined in Annex 2 of the E-Invoicing Resolution. These details typically encompass essential elements required for tax compliance and audit purposes. While the specific requirements may vary, depending on the nature of the transaction and applicable regulations, typical components include:
- Invoice Identification: A unique identifier for the invoice, such as an invoice number or code, to distinguish it from other invoices.
- Supplier Information: Details of the supplier, including their name, address, Tax Registration Number (TRN), and any other relevant identifiers.
- Buyer Information: Information about the buyer, including their name, address, TRN (if applicable), and any additional identification details required for tax purposes.
- Invoice Date: The date on which the invoice is issued, indicating the transaction’s timing and relevance for tax reporting periods.
- Description of Goods or Services: Clear and comprehensive description of the goods or services provided, including quantity, unit price, total amount, and any applicable taxes.
- Tax Details: Breakdown of taxes applicable to the transaction, including Value Added Tax (VAT) or any other relevant taxes, along with corresponding tax rates and amounts.
- Total Amount Due: The total amount payable by the buyer to the supplier, inclusive of all taxes and any additional charges.
- Payment Terms: Terms and conditions related to payment, such as payment due date, accepted payment methods, and any applicable discounts or penalties.
- Additional Requirements: Any additional information or disclosures mandated by ZATCA or other relevant regulatory authorities, depending on the nature of the transaction and industry-specific regulations.
3.2. What formats are accepted for e-invoices?
ZATCA accepts electronic invoices in two primary formats: XML and PDF/A-3 with embedded XML. These formats are designed to ensure compatibility, integrity, and accessibility of e-invoices within the electronic invoicing ecosystem. Here’s an overview of each format:
- XML (Extensible Markup Language):
- XML is a versatile, machine-readable markup language commonly used for structuring and exchanging data between systems.
- In the context of e-invoicing, XML allows for the standardized representation of invoice data in a hierarchical format, making it easily interpretable by both humans and computers.
- ZATCA mandates that e-invoices in XML format adhere to specific schemas or standards prescribed by the authority to ensure consistency and interoperability across different systems and stakeholders.
- XML-based e-invoices facilitate seamless integration with accounting software, tax reporting systems, and other business applications, enabling automated processing and compliance.
- PDF/A-3 with Embedded XML:
- PDF/A-3 is a variant of the Portable Document Format (PDF) optimized for the long-term preservation and archiving of electronic documents.
- Unlike traditional PDF documents, PDF/A-3 allows for embedding additional file attachments, such as XML data files, within the PDF container.
- In the context of e-invoicing, PDF/A-3 with embedded XML combines the benefits of a human-readable document (PDF) with structured machine-readable data (XML), providing a comprehensive and accessible format for invoices.
- This format ensures that e-invoices remain self-contained and compliant with archival standards, making them suitable for long-term storage, retrieval, and audit purposes.
- ZATCA requires that e-invoices in PDF/A-3 format include embedded XML files containing invoice data structured according to specified schemas or standards, ensuring data integrity and authenticity.
3..3. What are the security requirements for e-invoices?
Security is paramount in electronic invoicing to safeguard the authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality of invoice data. In compliance with ZATCA regulations, e-invoices must adhere to specific security requirements, including the following:
- Cryptographic Stamp Identifier (CSID):
- ZATCA mandates the inclusion of a Cryptographic Stamp Identifier (CSID) in e-invoices, which serves as a unique digital signature issued by the authority.
- The CSID validates the authenticity and integrity of the e-invoice, assuring that it originates from a legitimate source and has not been tampered with during transmission or storage.
- Businesses must obtain the CSID from ZATCA and incorporate it into their e-invoices as part of the authentication and validation process.
- QR Code with Specific Format:
- Each e-invoice must feature a Quick Response (QR) code containing essential invoice details in a predefined format specified by ZATCA.
- The QR code serves as a convenient and efficient means of accessing and verifying invoice information using mobile devices or scanning devices.
- The format of the QR code typically includes key invoice data such as invoice number, date, amount, taxpayer information, and other relevant details.
- By embedding this information in a QR code, e-invoices facilitate quick and accurate verification by tax authorities, auditors, and other stakeholders, enhancing transparency and compliance in the invoicing process.
These security measures ensure the authenticity, integrity, and traceability of e-invoices, reducing the risk of fraud, manipulation, and unauthorized access. By incorporating CSIDs and QR codes with specific formats into their e-invoices, businesses can demonstrate compliance with ZATCA regulations and bolster trust in electronic invoicing practices.
4. Types of e-invoices
In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA) have established comprehensive guidelines for different types of e-invoices, each tailored to specific transactional scenarios and regulatory phases. This guide explores the various types of e-invoices mandated by ZATCA, focusing on tax invoices and simplified tax invoices across two distinct phases: the Generation Phase and the Integration Phase.
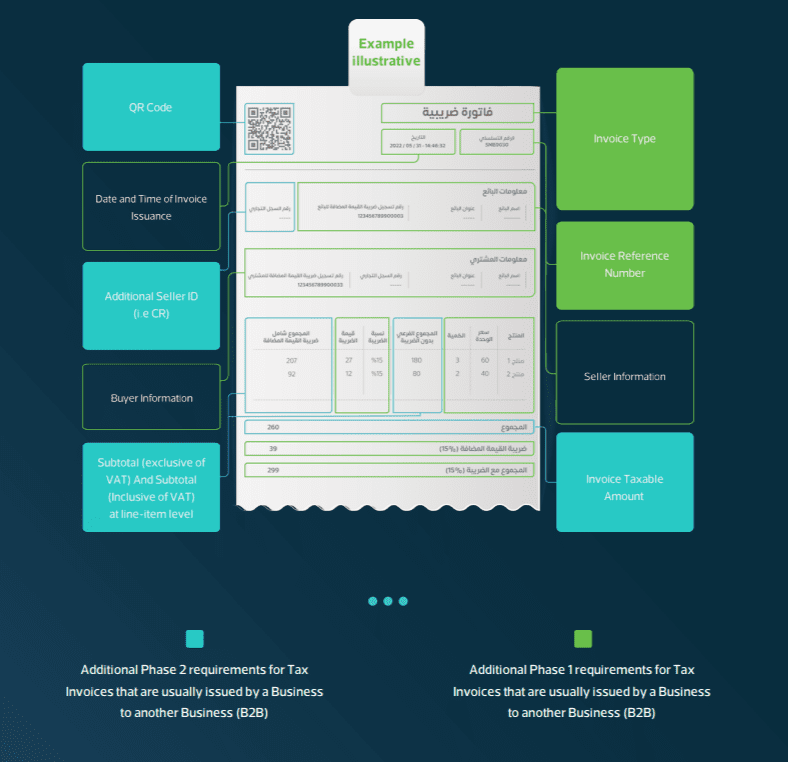
4.1. Tax Invoice
Phase 1 (Generation Phase):
- Description: An invoice issued for most B2B and B2G transactions with fields defined in Article 53(5) of the VAT Implementing Regulations and Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution.
- Format: Generated electronically using a compliant E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) without a specific format requirement.
- Sharing/Presentment: This can be presented in any electronic format.
Phase 2 (Integration Phase):
- Description: Tax invoices must include additional data fields prescribed in Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution.
- Format: Generated in XML format or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) using a compliant EGS.
- Submission: Submitted in XML format to FATOORA Platform for clearance using APIs.
- Sharing/Presentment: Presented to buyers in XML or PDF/A-3 format.
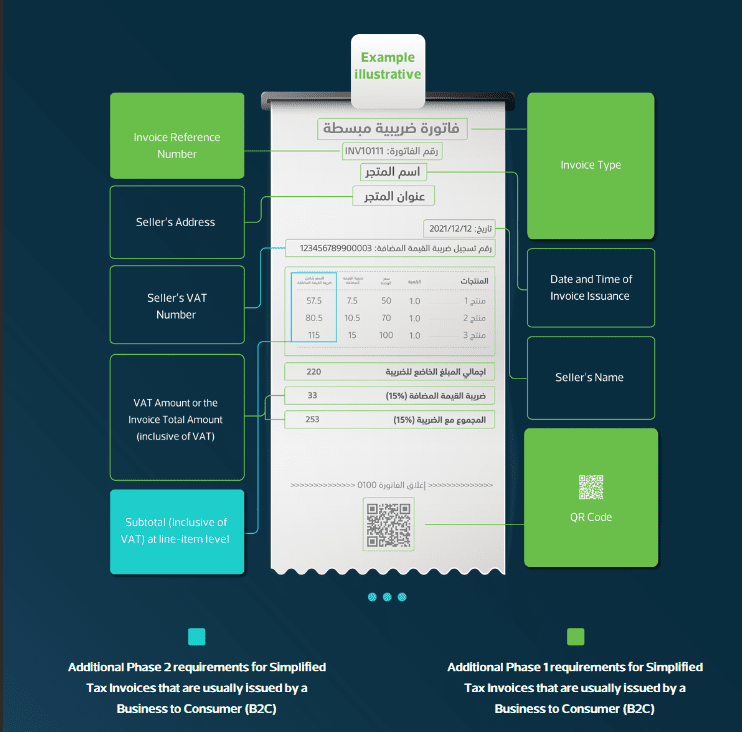
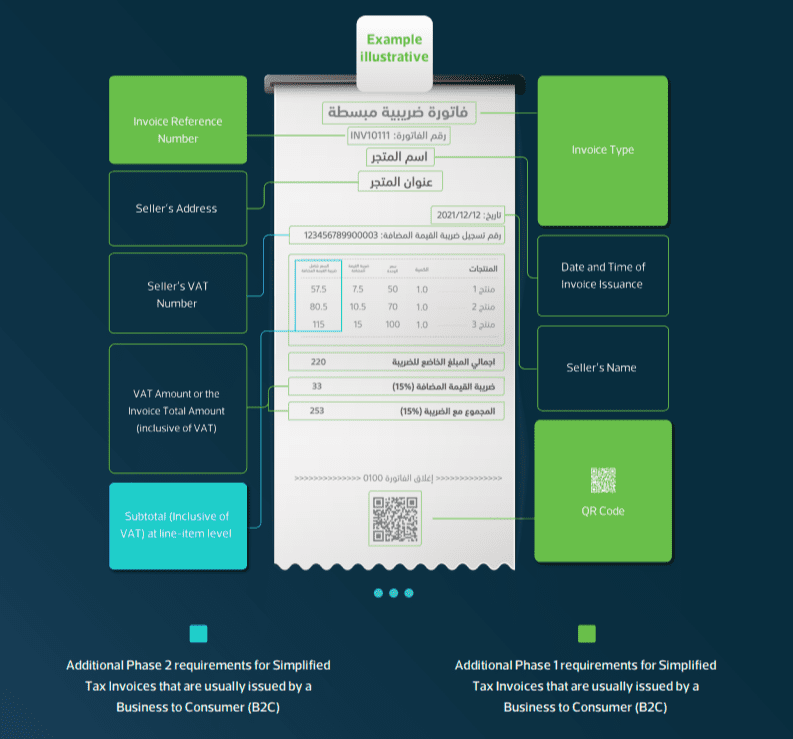
4.2. Simplified Tax Invoice
Phase 1 (Generation Phase):
- Description: An invoice issued mostly for B2C transactions with fields defined in Article 53(8) of the VAT Implementing Regulations and Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution.
- Format: Generated electronically using a compliant EGS without a specific format requirement.
- Sharing/Presentment: Shared with buyers in printed copy or electronic format.
Phase 2 (Integration Phase):
- Description: Simplified tax invoices must include additional data fields prescribed in Annex 2 of E-Invoicing Resolution.
- Format: Generated in XML format or PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML) using a compliant EGS.
- Submission: Submitted in XML format to FATOORA Platform for reporting within 24 hours of generation using APIs.
- Sharing/Presentment: Presented to buyers in printed copy or electronic format.
4.3. Credit and Debit Notes
- Description: Issued for adjustments to tax invoices or simplified tax invoices, referencing the original invoice(s) to which they are issued.
- Format: Electronically generated with reference fields to original invoices.
| Feature | Tax Invoice (Phase 1) | Tax Invoice (Phase 2) | Simplified Tax Invoice (Phase 1) | Simplified Tax Invoice (Phase 2) |
| Format | Any electronic | XML or PDF/A-3 | Any electronic | XML or PDF/A-3 |
| Submission to FATOORA | Not required | Required | Not required | Required |
| Sharing/Presentment | Any electronic | XML or PDF/A-3 | Printed copy or electronic | Printed copy or electronic |
5. Issuing E-Invoices
When it comes to sending e-invoices, it’s really important to follow the rules. By understanding these key aspects, businesses can navigate the landscape of electronic invoicing effectively, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and seamless integration with digital invoicing platforms.
5.1 Do I need special software to generate e-invoices?
To adhere to the stringent regulations established by the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA) in Saudi Arabia, businesses must leverage specialized software known as an E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS).
EGS is a tailored software that is meticulously crafted to streamline the creation, formatting, and transmission of electronic invoices, ensuring strict compliance with ZATCA’s stipulated requirements. The EGS serves as a cornerstone in guaranteeing that e-invoices encompass all essential information, conform to prescribed formats, and uphold the stringent security standards mandated by ZATCA.
Without access to an EGS, businesses risk encountering challenges in generating compliant e-invoices, potentially exposing themselves to non-compliance penalties. Thus, investing in a robust and compliant EGS emerges as an imperative for entities.
5.2. How to choose a compliant EGS provider?
Choosing a compliant EGS provider is a crucial decision for businesses aiming to navigate the e-invoicing landscape effectively in Saudi Arabia. While ZATCA provides an indicative list of approved EGS providers, it’s important to note that using a provider from this list is not mandatory. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a compliant EGS provider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the EGS provider complies with all regulations and guidelines set forth by ZATCA for electronic invoicing. This includes adhering to data formatting requirements, security standards, and integration protocols specified by ZATCA.
- Compatibility: Choose an EGS provider that offers compatibility with your existing accounting systems, ERP software, and other business applications. Seamless integration ensures smooth data exchange and workflow automation.
- User-Friendly Interface: Opt for an EGS solution with an intuitive and user-friendly interface that simplifies the invoice generation process. User adoption is crucial for successful implementation and compliance.
- Security Features: Prioritize EGS providers that offer robust security features to protect sensitive financial data and ensure confidentiality. This includes encryption mechanisms, access controls, and secure transmission protocols.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Select an EGS solution that can accommodate your business’s evolving needs and growth trajectory. Scalability allows for the handling of increasing invoice volumes, while flexibility enables customization to suit unique business requirements.
- Support and Training: Choose an EGS provider that offers comprehensive customer support, training resources, and technical assistance. Responsive support ensures timely resolution of issues and minimizes disruptions to invoicing operations.
By carefully evaluating their needs and conducting thorough due diligence, businesses can select a compliant EGS provider that aligns perfectly with their requirements. This approach facilitates a seamless adoption of electronic invoicing practices in Saudi Arabia.
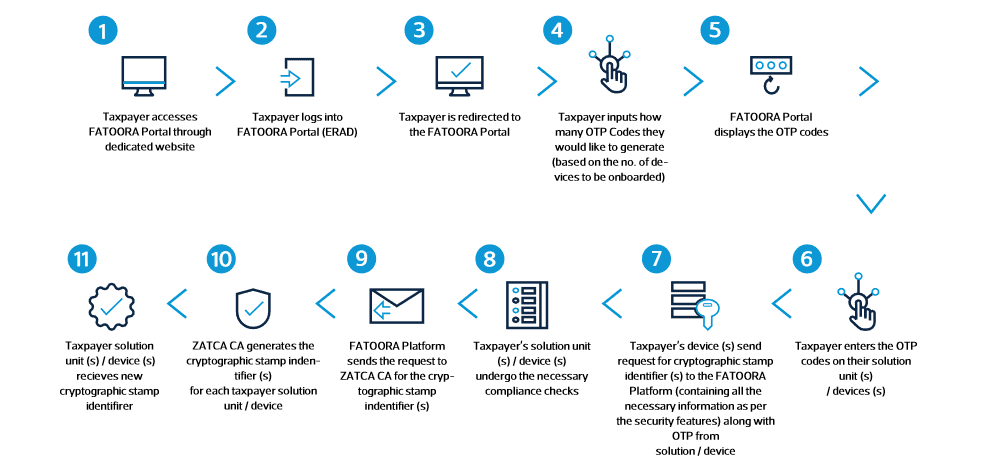
5.3. How does the e-invoice issuance process work?
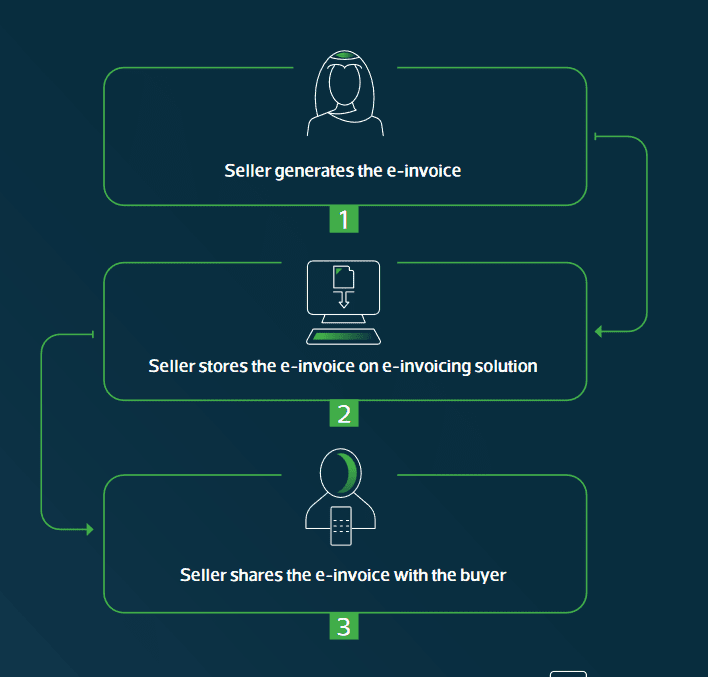
The e-invoice issuance process involves several steps to ensure compliance with regulations and the inclusion of essential information. Here’s a comprehensive overview of how the process works:
- Invoice Generation:
- The process begins with the generation of the invoice using an E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) or specialized invoicing software.
- Businesses input relevant transaction details, including buyer and seller information, invoice date, item descriptions, quantities, prices, and applicable taxes.
- The software formats the invoice data according to the specifications outlined by the Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority (ZATCA) in Saudi Arabia.
- Once the invoice is generated, it undergoes validation checks to ensure accuracy, completeness, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Stamping with CSID:
- After validation, the invoice is stamped with a Cryptographic Stamp Identifier (CSID) to provide a unique digital signature and ensure authenticity.
- The CSID is obtained from ZATCA and serves as a cryptographic certificate that authenticates the origin and integrity of the e-invoice.
- Integration with ZATCA’s electronic platform enables businesses to obtain CSIDs for their invoices securely and efficiently.
- Stamping the invoice with a CSID helps prevent tampering, forgery, and unauthorized alterations, enhancing the integrity and trustworthiness of the electronic document.
- QR Code Inclusion:
- As part of the e-invoice issuance process, a Quick Response (QR) code is generated and embedded in the invoice.
- The QR code contains encoded information such as the invoice number, invoice date, total amount, taxpayer details, and other relevant data.
- The inclusion of the QR code facilitates quick and easy verification of the invoice’s authenticity and validity by stakeholders, including tax authorities, buyers, and suppliers.
- The QR code follows a specific format prescribed by ZATCA, ensuring consistency and standardization across e-invoices generated by different businesses.
Overall, the process of issuing a typical e-invoice can be summarized in the following flowchart:
6. Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with e-invoicing regulations in Saudi Arabia can have serious consequences for businesses. ZATCA implements a tier-based penalty system to enforce compliance, with fines increasing for repeated offenses. Understanding these penalties is crucial for businesses to ensure adherence to regulations and avoid financial repercussions.
Non-compliance with e-invoicing regulations in Saudi Arabia can lead to penalties under ZATCA’s tiered penalty system. Here’s a breakdown of the penalties for repeated offenses:
- First Offense: Warning – ZATCA will issue a warning notice to the business, informing them of the violation and the need to comply.
- Second Offense: SAR 1,000 Fine – If the violation persists after the initial warning, a penalty of SAR 1,000 (Saudi Arabian Riyal) will be imposed.
- Third Offense: SAR 5,000 Fine – Continued non-compliance will result in a higher fine of SAR 5,000.
- Fourth Offense: SAR 10,000 Fine – The penalty amount increases significantly for the fourth offense to SAR 10,000.
- Subsequent Offenses: SAR 40,000 Fine – Any violations after the fourth offense will incur a maximum penalty of SAR 40,000.
It’s important to stay updated on the latest ZATCA regulations, as penalty amounts or the tiered system itself could be subject to change. You can find the most recent information on their website.
Complying with ZATCA’s e-invoicing regulations is not just about avoiding penalties; it aims to develop a transparent and efficient business environment. By understanding the tiered penalty system and staying updated on regulations, businesses in Saudi Arabia can ensure smooth financial transactions and achieve a compliant e-invoicing system.
7. Buyer Experience with E-Invoices
The buyer experience with e-invoices is a crucial aspect of the electronic invoicing ecosystem, shaping how transactions are conducted, verified, and managed. Understanding these dynamics is essential for both buyers and sellers to navigate the transition to electronic invoicing effectively and leverage its advantages for improved efficiency, transparency, and compliance.
7.1. How do buyers receive e-invoices?
Buyers typically receive e-invoices electronically through digital channels such as email, electronic data interchange (EDI), or electronic invoicing platforms.
Electronic invoices are transmitted directly to the buyer’s designated email address or integrated into their accounting or procurement systems for seamless processing. Alternatively, some sellers may also provide printed invoices with a QR code for buyers who prefer physical documentation.
The QR code embedded on printed invoices facilitates quick and convenient access to electronic invoice details when scanned using a compatible mobile device or QR code reader application.
7.2. What happens when a buyer scans the QR code?
In the digital world of e-invoicing, scanning QR codes has become crucial for checking if electronic invoices are real and follow the rules. By using ZATCA’s Fatoora portal, buyers can easily check invoice details, which helps ensure transparency and trust in online transactions.
- Scanning the QR code triggers verification through ZATCA’s Fatoora portal.
- The portal provides access to detailed invoice information, including seller details, invoice amount, and tax components.
- Verification against ZATCA’s database ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
- Confirms the authenticity of the e-invoice, enhancing transparency and trust in electronic transactions.
- Prevents the risk of fraud or manipulation by validating invoice data against official records.
7.3. Are there any benefits for buyers?
Moving to e-invoices brings several benefits for buyers, streamlining procurement and enhancing their experience. With electronic invoices, buyers gain better transparency, and efficiency, and contribute to sustainability in financial transactions.
- Enhanced Transparency: E-invoices provide buyers with detailed and accurate transaction records, promoting transparency in financial dealings.
- Faster Verification: Scanning the QR code embedded in e-invoices allows buyers to quickly verify the authenticity and validity of the invoice through ZATCA’s Fatoora portal, saving time and effort.
- Streamlined Processes: The digitization of invoicing eliminates the need for manual paperwork and reduces administrative burdens, leading to more efficient and streamlined procurement processes.
- Reduced Errors: Automated e-invoicing systems help minimize errors and discrepancies in invoicing, ensuring greater accuracy in financial transactions and reducing the risk of disputes between buyers and sellers.
- Environmental Sustainability: By transitioning to electronic invoicing, buyers contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing paper consumption and minimizing the ecological footprint associated with traditional paper-based invoicing methods.
In summary, the buyer experience with e-invoices is streamlined through electronic delivery or printed invoices with QR codes, enabling efficient verification via ZATCA’s Fatoora portal. This process enhances transparency, leads to quicker verification, and simplifies procurement for buyers, contributing to smoother financial transactions and regulatory compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What information must be included in a ZATCA-compliant e-invoice?
ZATCA mandates specific information to be included in a compliant e-invoice. Here are some key elements:
- Invoice details: Invoice number, date of issuance, and due date.
- Supplier and customer information: Names, tax identification numbers (TINs), addresses.
- Items or services details: Description, quantity, unit price, total amount.
- Tax details: VAT rate, VAT amount.
- QR code: A unique QR code linked to the invoice data for verification by ZATCA.
2. What formats are accepted for e-invoices in Saudi Arabia?
ZATCA adheres to international e-invoicing standards. Accepted formats include:
- Structured Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
- UBL (Universal Business Language)
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
The specific format might depend on your chosen e-invoicing solution provider.
3. What are the penalties for non-compliance with e-invoicing regulations?
ZATCA enforces a tiered penalty system for non-compliance:
- First Offense: Warning notice.
- Second Offense: SAR 1,000 fine.
- Third Offense: SAR 5,000 fine.
- Fourth Offense: SAR 10,000 fine.
- Subsequent Offenses: Maximum penalty of SAR 40,000.
4. Is there any assistance available for businesses transitioning to e-invoicing systems?
Yes, several resources can help businesses with the transition:
- ZATCA Website: Provides guidelines, user guides, and FAQs.
- Solution Providers: Many companies offer e-invoicing software and implementation assistance.
- Tax Consultants: Can advise on specific compliance requirements.
5. Are there any limitations on the size or type of businesses required to comply with e-invoicing regulations?
E-invoicing regulations apply to all VAT-registered businesses in Saudi Arabia, regardless of size or type. However, the implementation has been rolled out in phases based on turnover thresholds.
6. Is there a deadline for businesses to fully implement e-invoicing systems?
The deadline depends on your business’s turnover. ZATCA has notified businesses in waves, with the latest deadline being March 1, 2024, for businesses exceeding SAR 40 million in turnover during 2021 or 2022. Check the ZATCA website for the latest updates on deadlines for your business size.
7. Are there any exemptions or special considerations for specific industries or sectors?
Currently, no specific exemptions exist for industries or sectors. However, it’s advisable to stay updated on ZATCA’s website for any future announcements regarding exemptions.
8. Can businesses outsource their e-invoicing processes to third-party service providers?
Absolutely! Many businesses utilize e-invoicing solution providers who handle the technical aspects and ensure compliance with ZATCA regulations.
9. Are there any tax incentives or benefits associated with adopting e-invoicing systems?
While there aren’t direct tax incentives, e-invoicing offers benefits such as:
- Improved efficiency and reduced processing time.
- Enhanced accuracy and reduced errors.
- Streamlined tax filing and record-keeping.
- Increased transparency and reduced risk of fraud.
10. What support services are available to businesses transitioning to e-invoicing systems?
Many e-invoicing solution providers offer support services such as:
- Software implementation and training.
- Integration with existing accounting systems.
- Ongoing technical support and maintenance.
By leveraging these resources and understanding ZATCA’s e-invoicing requirements, businesses in Saudi Arabia can ensure a smooth transition to the new system and reap the associated benefits.